Abstract
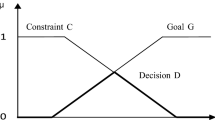
This paper presents the development and the first application of a superiority–inferiority-based inexact fuzzy-stochastic quadratic programming (SI-IFSQP) approach for sustainable water supply under multiple uncertainties. SI-IFSQP improves conventional nonlinear programming by tackling multiple uncertainties within an individual parameter; SI-IFSQP is also superior to existing inexact methods due to its reflection of economies of scale and reduction of computational requirements. An interactive solution algorithm with high computational efficiency was also proposed. The application of SI-IFSQP to long-term planning of a multi-source multi-sector water supply system demonstrated its applicability. The close reflection of system complexities, such as multiple uncertainties, scale economies and dynamic parameters, could enhance the robustness of the optimization process as well as the acceptability of obtained results. Corresponding to varied system conditions and decision priorities, the interval solutions from SI-IFSQP could help generate a series of long-term water supply strategies under a number of economic, environmental, ecological, and water-security targets.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aladenola OO, Adeboye OB (2010) Assessing the potential for rainwater harvesting. Water Resour Manag 24:2129–2137
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q (2009) An inexact optimization model for regional energy systems planning in the mixed stochastic and fuzzy environment. Int J Energ Res 33(5):443–468
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q, Chen B (2010) Identification of optimal strategies for improving eco-resilience to floods in ecologically vulnerable regions of a wetland. Ecol Model 222(2):360–369
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q, Yang ZF (2011) An integrated approach for climate-change impact analysis and adaptation planning under multi-level uncertainties. Part I: Methodology. Renew Sustain Energ Rev 15(6):2779–2790
Cao MF, Huang GH (2011) Scenario-based methods for interval linear programming problems. J Environ Informat 17(2):65–74
CDDC, Centre for Digital Discourse and Culture (2004) Choices and challenges project: sharing the earth’s water supply. Virginia Tech, Blacksburg
Chang NB (2005) Sustainable water resources management under uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:97–98
Chen MJ, Huang GH (2001) A derivative algorithm for inexact quadratic program—application to environmental decision-making under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 128:570–586
Escudero LF (2000) WARSYP: a robust modeling approach for water resources system planning under uncertainty. Ann Oper Res 95:313–339
Fry A (2005) Water Facts and Trends World Business Council for Sustainable Development, Switzerland
Hoekstra AY (2006) The global dimension of water governance: nine reasons for global arrangements in order to cope with local problems. Value of water research report. UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education, Delft
Huang GH (1996) IPWM: an interval parameter water quality management model. Eng Optim 26:79–103
Huang GH, Linton JD, Yeomans JS, Yoogalingam R (2005) Policy planning under uncertainty: efficient starting populations for simulation–optimization methods applied to municipal solid waste management. J Environ Manag 77:22–34
Huang GH, Cao MF (2011) Analysis of solution methods for interval linear programming. J Environ Informat 17(2):54–64
Jairaj PG, Vedula S (2000) Multireservoir system optimization using fuzzy mathematical programming. Water Resour Manag 14:457–472
Loucks DP, Stakhiv EZ, Martin LR (2000) Sustainable water resources management. J Water Resour Plann Manag 126(2):43–47
Luhandjula MK (1996) Fuzziness and randomness in an optimization framework. Fuzzy Set Syst 77(3):291–297
Lund JR, Israel M (1995) Optimization of transfers in urban water supply planning. J Water Resour Plan Manag 121(1):41–48
Rosenberg DE, Lund JR (2009) Modeling integrated decision for a municipal water system with recourse and uncertainties: Amman, Jordan. Water Resour Manag 23:85–115
Sauer J (2005) Economies of scale and firm size optimum in rural water supply. Water Resour Res 41(11):1–13
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2010a) A superiority-inferiority-based inexact fuzzy stochastic programming approach for solid waste management under uncertainty. Environ Model Assess 15(5):381–396
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2010b) Radial-interval linear programming for environmental management under varied protection levels. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 60(9):1078–1093
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2010c) Waste management with recourse: an inexact dynamic programming model containing fuzzy boundary intervals in objectives and constraints. J Environ Manage 91(9):1898–1913
Tan Q, Huang GH, Wu CZ, Cai YP (2011) IF-EM: an interval-parameter fuzzy linear programming model for environment-oriented evacuation planning under uncertainty. J Adv Transport 45(4):286–303
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2012) Robust planning of environmental management systems with adjustable conservativeness under compound uncertainty. J Environ Eng – ASCE 138(2):208–222
Van Hop N (2007) Solving fuzzy (stochastic) linear programming problems using superiority and inferiority measures. Inform Sci 177:1977–1991
Yang W, Yang Z (2010) An interactive fuzzy satisfying approach for sustainable water management in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water Resour Manag 24:1273–1284
Yang ZF, Li SS, Zhang Y, Huang GH (2011) Emergy synthesis for three main industries in Wuyishan City, China. J Environ Informat 17(1):25–35
Zheng C, Yang W, Yang ZF (2011) Strategies for managing environmental flows based on the spatial distribution of water quality: a case study of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J Environ Informat 18(2):84–90
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51209087 and 51009004), the MOE Key Project Program (311013), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1127). The authors would like to express special thanks to the editor and reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions in improving the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Q., Huang, G.H. & Cai, Y.P. Multi-Source Multi-Sector Sustainable Water Supply Under Multiple Uncertainties: An Inexact Fuzzy-Stochastic Quadratic Programming Approach. Water Resour Manage 27, 451–473 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0196-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0196-9