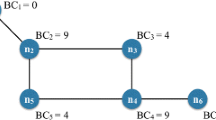
Abstract
The main objective of this paper is to introduce the proposed theory of vulnerability of water pipe network (TVWPN) and, in particular, its theoretical concepts. These concepts have a basis in the structural vulnerability theory (Agarwal et al., Civ Eng Environ Syst 18(2):141–165, 2001a, J Struct Saf 23(3):203–220, 2001b; Lu et al., Struct Eng 77(18):17–23, 1999; Lu 1998; Pinto 2002; Pinto et al., J Struct Saf 24:107–122, 2002; Yu 1997). The fundamental contribution of this theory is to help design water pipe networks (WPN) more robust against damage to the pipelines. This is achieved through an analysis of the form of the network. The application of the TVWPN is presented through an example of a water pipe network.
Similar content being viewed by others

Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Agarwal J, Blockley DI, Woodman NJ (1997) Improving system’s dependability. Advances in safety and reliability. In: Proceedings of ESREL’97. Lisbon, pp 2329–2337
Agarwal J, Blockley DI, Woodman NJ (2001a) Vulnerability of systems. Civ Eng Environ Syst 18(2):141–165. doi:10.1080/02630250108970297
Agarwal J, Blockley DI, Woodman NJ (2001b) Vulnerability of 3-dimensional trusses. J Struct Saf 23(3):203–220
Alvisi S, Franchini M, Marinelli A (2003) A stochastic model for representing drinking water demand at residential level. Water Resour Manag 17:197–222
Blockley DI, Godfrey P (2000) Doing it differently: systems for rethinking construction. Thomas Telford, London
Christodoulou S, Deligianni A (2010) A neurofuzzy decision framework for the management of water distribution networks. Water Resour Manag 24:139–156. doi:10.1007/s11269-009-9441-2
Fattahi P, Fayyaz S (2010) A compromise programming model to integrated urban water management. Water Resour Manag 24(6):1211–1227 doi:10.1007/s11269-009-9492-4
Jowitt PW, Xu C (1993) Predicting pipe failure effects in water distribution networks. ASCE J Water Resour Plan Manage 119(1):18–31. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1993)119:1(18)
Jun H, Loganathan GV, Kim JH, Park S (2008) Identifying pipes and valves of high importance for efficient operation and maintenance of water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 22(6):719–736
Kleiner Y, Rajani B (2000) Considering time-dependent factors in the statistical prediction of water main breaks. In: American Water Works Association: infrastructure conference, 12–15 March, Baltimore, Maryland, pp 1–12
Lu Z (1998) Structural vulnerability analysis. PhD thesis, University of Bristol, UK
Lu Z, Yu Y, Woodman NJ, Blockley DI (1999) A theory of structural vulnerability. Struct Eng 77(18):17–23
Michaud D, Apostolakis GE (2006) Methodology for ranking the elements of water supply networks. J Infrastruct Syst 12(4):230–242
Pinto JT (2002) The risk of a vulnerable scenario. PhD thesis, University of Bristol, UK
Pinto JT, Blockley DI, Woodman NJ (2002) The risk of vulnerable failure. J Struct Saf 24:107–122
Wu X, Blockley DI, Woodman NJ (1993) Vulnerability analysis of structural systems (Part I: rings and clusters, Part II: failure scenarios). J Civ Eng Syst 10:301–333
Yamout G, Jamali D (2007) A critical assessment of a proposed public private partnership (PPP) for the management of water services in Lebanon. Water Resour Manag 21:611–634. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9033-3
Yang S, Hsu NS, Louie PWF, Yeh WWG (1996) Water distribution network reliability: Connectivity analysis. J Infrastruct Syst 2(2):54–64
Yu Y (1997) Analysis of structural vulnerability. PhD thesis, University of Bristol, UK
Zidko V, Ramos H (2009) Fuzzy model in the vulnerability assessment of water supply systems. Recur Hídr 30(1):5–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinto, J., Varum, H., Bentes, I. et al. A Theory of Vulnerability of Water Pipe Network (TVWPN). Water Resour Manage 24, 4237–4254 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9655-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9655-3