Abstract
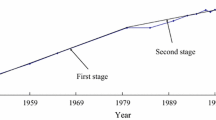
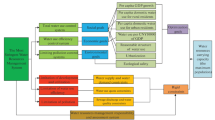
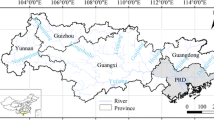
Water resources allocation in a river basin is customarily determined based on long-term mean water availability. However, inter-annual variability of water resources caused by climate fluctuation should also be considered in order to keep an effective and flexible allocation policy. This paper analyzes the historical evolution of the water resources allocation system in the Yellow River basin of China. Based on the concept of water use flexible limit to water shortage and actual water use data from 1988–2006, a set of flexible limits to water shortage adapted to the Yellow River basin has been proposed. This includes total water use flexible limit to water shortage for all provinces, which is approximately 70%; and the different water use flexible limits to water shortage for each social sector, which are approximately 90% for agriculture, 85% for domestic use, and 50% for other industries. It offers a simple, yet effective, method for future water resources allocation in the Yellow River basin to achieve the optimal use of water resources. It likewise provides a beneficial reference for water resources management in the water deficient regions of China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
City of Santa Cruz Water Department (2005) Urban water management plan. Santa Cruz City Council, pp 86–99
Devi S, Scrivastava DK, Mohan C (2005) Optimal water allocation for the transboundary Subernarekha River, India. J Water Resour Plan Manage 131(4):253–269
Feng S, Li L, Duan Z, Zhang J (2007) Assessing the impacts of South-to-North water transfer project with decision support systems. Decis Support Syst 42:1989–2003
Garrote L, Martin-Carrasco F, Flores-Montoya F, Iglesias A (2007) Linking drought indicators to policy actions in the Tagus basin drought management plan. Water Resour Manag 21:873–882
Giacomelli P, Rossetti A, Brambilla M (2008) Adapting water allocation management to drought scenarios. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 8:293–302
Jouravlev A (2005) Integrating equity, efficiency and environment in water allocation reform. Water rights system development in China international seminar, 6–7 December 2005, Beijing
Maqsood I, Huang G, Yeomans JS (2005) An interval-parameter fuzzy two-stage stochastic program for water resources management under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 167:208–225
Peng X, Hu H (2006a) A game equilibrium model for water resources deployment in the Yellow River basin. J Hydraul Eng 37(10):1199–1205 (In Chinese)
Peng X, Hu H (2006b) System evaluation of the allocation plan of available water of the Yellow River. Yellow River 28(4):41–43 (In Chinese)
Shangguan Z, Shao M, Horton R, Lei T, Qin L, Ma J (2002) A model for regional optimal allocation of irrigation water resources under deficit irrigation and its applications. Agric Water Manag 52:139–154
Solanes M, Jouravlev A (2006) Water rights and water markets: lessons from technical advisory assistance in Latin America. Irrig Drain 55:337–342
The Ministry of Water Resources of China (1988–2006) China water resources bulletin. China Water Power Press, Beijing, pp 1–20 (In Chinese)
Wang L, Fang L, Hipel KW (2007a) Mathematical programming approaches for modeling water rights allocation. J Water Resour Plan Manage 133(1):50–59
Wang X, Zhao J, Wang Z, Weng W, Li H (2007b) Allocation model for water right. Adv Water Sci 18(2):241–245 (In Chinese)
Wheida E, Verhoeven R (2007) An alternative solution of the water shortage problem in Libya. Water Resour Manag 21:961–982
Wood AW, Lettenmaier DP, Palmer RN (1997) Assessing climate change implications for water resources planning. Clim Change 37:203–228
Xu Z, Kawamura A, Jinno K, Ito K (1996) Decision support system for water-supply risk management. Proc. Int. Conf. on Ind. & Eng. Appl. of Artif. Intel. & Exp. Syst. Fukuoka, Japan, pp 234–240
Xu Z, Ito K, Jinno K, Kojiri T (1998) Development of a decision support system for integrated water management in river basins. Lecture notes in computer science: tasks and methods in applied artificial intelligence. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 678–686
Xu Z, Takeuchi K, Ishidaira H, Yang Z (2003) Risk analysis for water resources system by using system dynamics technique: case study in Yellow River basin. IAHS General Assembly, Sapporo, Japan
Yang D, Li C, Hu H, Lei Z, Yang S, Kusuda T, Koike T, Musiake K (2004) Analysis of water resources variability in the Yellow River of China during the last half century using historical data. Water Resour Res 40:W06502. doi:10.1029/2003WR002763
Yellow River Conservancy Commission (1998–2006) Bulletin of Yellow River water resources. Yellow River Water Resources Press, Zhengzhou, pp 1–30 (In Chinese)
Zhao J, Wang Z, Wang D, Ma J (2005) Analysis on the macroeconomic effect of integrated water regulation conducted in the Yellow River. Academic Annual Meeting of Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society 2005, pp 85–93 (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, W., Yang, D., Hu, H. et al. Water Resources Allocation Considering the Water Use Flexible Limit to Water Shortage—A Case Study in the Yellow River Basin of China. Water Resour Manage 23, 869–880 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9304-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9304-2