Abstract
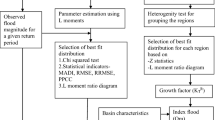
In this study, a regional flood frequency analysis has been carried out, using the index flood L-moments approach. Annual maximum stream flood data observed at 14 gauged sites on the Nile River tributaries (Blue Nile, White Nile, and Atbara River) are investigated. The aim of the study is to investigate and derive hydrologically homogeneous region or regions and to identify and establish the regional statistical distribution. To this end, five distribution functions are used, namely: generalized pareto, generalized extreme-value, generalized logistic, generalized normal, and Pearson type-3 distributions. Analyses have shown that 8 sites form a hydrologically homogeneous region, and this region follows a generalized logistic (GLO) distribution. Furthermore, the other remaining two regions (possibly heterogeneous and definitely heterogeneous) are also defined. Regional dimensionless growth curves for the identified three regions are derived. Results are assessed on the basis of relative RMSE% and relative BIAS% through the use of Monte Carlo simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atiem, I. A., 2004, ‘Regionalization of flood information: the case of the Nile River’, Ph.D. Thesis Submitted to the Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Dokuz Eylul University, Izmir, Turkey, July 2004.
Bayazit, M. and Onoz, B., 1994, ‘Robustness analysis of regional flood frequency models: A case study’, in G. Rossi, N. B. Harmancioglu, and V. Yevjevich, (eds), Coping with Floods, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Chap. 12, NATO ASI Series, Series E257, pp. 243–255.
Bobée, B. and Rasmussen, P. F., 1995, ‘Recent advances in flood frequency analysis, U.S National Report to International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics 1991–1994’, Reviews of Geophysics, supplement, pp. 1111–1116.
Burn, D. H., 1990, ‘Evaluation of regional flood frequency analysis with a region of influence approach’, Water Resour. Res. 26(10), 2257–2265.
Dalrymple, T., 1960, ‘Flood frequency methods, U.S. Geological Survey’, Water Supply paper, 1543A, 11–51.
FRIEND/Nile, 2002, ‘FRIEND-Nile Report’, Chap. 6, www.nilediscourse.org, Nile Basin, pp. 61–65.
Greenwood, J. A., Landwehr, J. M., Matalas, N. C., and Wallis, J. R., 1979, ‘Probability weighted moments: Definition and relation to parameters of several distributions expressible in inverse form’, Water Resour. Res. 15(5), 1049–1054.
Hosking, J. R., 1986, The theory of probability weighted moments, IBM Res. Rep. RC12210, IBM, Yorktown Heights, N.Y.
Hosking, J. R., 1990, ‘L-moments: Analysis and estimation of distributions using linear combinations of order statistics’, Journal of Royal Statistics. Soc., Ser. B 52, 105–124.
Hosking, J. R. and Wallis, J. R., 1993, ‘Some statistics useful in regional frequency analysis’, Water Resour. Res. 29(2), 271–281.
Hosking, J. R. and Wallis, J. R., 1997, Regional Frequency Analysis: An Approach based on L-Moments, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Hosking, J. R., Wallis, J. R., and Wood, E. F., 1985, ‘Estimation of the generalized extreme – value distribution by the method of probability weighted moments’, Technometrics 27(3), 251–261.
Jin, M. and Stedinger, J. R., 1989, ‘Flood frequency analysis with regional and historical information’, Water Resour. Res. 25(5), 925–936.
Lettenmaier, D. P. and Potter, K. W., 1985, ‘Testing flood frequency estimation methods using a regional flood generation model’, Water Resour. Res. 21(12), 1903–1914.
Lettenmaier, D. P., Wallis, J. R., and Wood, E. F., 1987, ‘Effect of regional heterogeneity on flood frequency estimation’, Water Resour. Res. 23(2), 313–323.
Murphy, P. J., 2001, ‘Evaluation of mixed-population flood-frequency analysis’, ASCE J. of Hydrologic Eng. 6(1), 62–70.
Natural Environmental Research Council (NERC), 1975, Flood Studies Report, vol.1, Hydrological Studies, London.
Potter, K. W., 1987, ‘Research on flood frequency analysis: 1983–1986’, Reviews of Geophysics 25(2), 113–118.
Potter, K. W. and Lettenmaier, D. P., 1990, ‘A Comparison of regional flood frequency estimation methods using a resampling method’, Water Resour. Res. 26(3), 415–424.
Robson, A. and Reed, D., 1999, ‘Statistical procedures for flood frequency estimation’, in Flood Estimation Handbook (Institute of Hydrology, Wallingford), Chap. 3, 337p.
Rossi, F. and Villani, P., 1994, ‘Regional flood estimation methods’, in G. Rossi, N. B. Harmancioglu, and V. Yevjevich (eds), Coping with Floods, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Chap. 8, NATO ASI Series, Series E257, pp.135–169.
Singh, V, 1998, ‘Methods of parameter estimation’, in Entropy-Based Parameter Estimation in Hydrology, Chap. 2, Water Science and Technology Library, vol. 30, Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 12–44.
Stedinger, J. R., Vogel, R. M., and Georgiou, E. F., 1993, ‘Frequency analysis of extreme events’, in D. R. Maidment (ed), Handbook of Hydrology, Chap. 18, McGraw-Hill.
Vogel, R. M., Thomas, W. O., Jr, and McMahon, T. A., 1993, ‘Flood-flow frequency model selection in Southwestern United States’, J. Water Resour. Planning and Management 119(3), 353–366.
Wallis, J. R. and Wood, E. F., 1985, ‘Relative accuracy of log Pearson III procedures’, J. Hydraul. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 111(7), 1043–1056.
Waylen, P. R. and Won, M. K., 1982, ‘Prediction of annual floods generated by mixed processes’, Water Resour. Res. 18(4), 1283–1286.
Zrinji, Z. and Burn, D. H., 1996, ‘Regional flood frequency with hierarchical region of influence’, J. Water Resour. Planning and Management 122(4), 245–252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atiem, I.A., Harmancio˘lu, N.B. Assessment of Regional Floods Using L-Moments Approach: The Case of The River Nile. Water Resour Manage 20, 723–747 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-005-9004-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-005-9004-0