Abstract
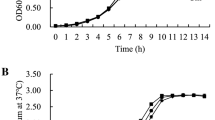
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) are recognized as being responsible for many cases of foodborne diseases worldwide. Cattle are the main reservoir of STEC, shedding the microorganisms in their feces. The serogroup STEC O91 has been associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Locus of Adhesion and Autoaggregation (LAA) and its hes gene are related to the pathogenicity of STEC and the ability to form biofilms. Considering the frequent isolation of STEC O91, the biofilm-forming ability, and the possible role of hes in the pathogenicity of STEC, we propose to evaluate the ability of STEC to form biofilms and to evaluate the expression of hes before and after of biofilm formation. All strains were classified as strong biofilm-forming. The hes expression showed variability between strains before and after biofilm formation, and this may be due to other genes carried by each strain. This study is the first to report the relationship between biofilm formation, and hes expression and proposes that the analysis and diagnosis of LAA, especially hes as STEC O91 virulence factors, could elucidate these unknown mechanisms. Considering that there is no specific treatment for HUS, only supportive care, it is necessary to know the survival and virulence mechanisms of STEC O91.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available.
References
Alonso MZ, Krüger A, Sanz ME, Padola NL, Lucchesi PMA (2016) Serotipos, perfiles de virulencia y subtipos de stx en Escherichia coli productor de toxina shiga aislados de productos de pollo. Rev Argent Microbiol 48(4):325–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2016.04.009
Angel Villegas N, Baronetti J, Albesa I, Polifroni R, Parma AE, Etcheverría A, Becerra M, Padola N, Paraje M (2013) Relevance of biofilms in the pathogenesis of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection. The Scientific World Journal, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/607258
Barton K (2022) Package ‘MuMIn’ Version 1.46.0. R Package, Version 1.46.0
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67(1). https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bielaszewska M, Stoewe F, Fruth A, Zhang W, Prager R, Brockmeyer J, Mellmann A, Karch H, Friedrich AW (2009) Shiga toxin, cytolethal distending toxin, and hemolysin repertoires in clinical Escherichia coli O91 isolates. J Clin Microbiol 47(7):2061–2066. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00201-09
Cáceres ME, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL (2019) Effects of the culture medium and the methodology applied on the biofilm formation of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains. Rev Argent Microbiol 51(3):208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2018.04.007
Cadona JS, Burgán J, González J, Bustamante AV, Sanso AM (2020) Differential expression of the virulence gene nleB among Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04277
Carter MQ, Laniohan N, Lo CC, Chain PSG (2022) Comparative Genomics Applied to Systematically Assess Pathogenicity Potential in Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O145:H28. Microorganisms 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050866
Colello R, Cáceres ME, Ruiz MJ, Sanz M, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL (2016) From farm to table: follow-up of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli throughout the pork production chain in Argentina. Front Microbiol 7(FEB):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00093
Colello R, Vélez MV, González J, Montero DA, Bustamante AV, Del Canto F, Etcheverría AI, Vidal R, Padola NL (2018) First report of the distribution of locus of adhesion and autoaggregation (LAA) pathogenicity island in LEE-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from Argentina. Microb Pathog 123(July):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.07.011
Colello R, Vélez MV, Nieto Farias MV, Rodríguez M, Montero D, Vidal R, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL (2023) Expression of hes, iha, and tpsA codified in Locus of Adhesion and Autoaggregation and their involvement in the capability of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains to adhere to epithelial cells. BMC Res Not 16(1):163. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-023-06433-9
de Sablet T, Bertin Y, Vareille M, Girardeau JP, Garrivier A, Gobert AP, Martin C (2008) Differential expression of stx2 variants in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli belonging to seropathotypes A and C. Microbiology 154(1):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2007/009704-0
Donlan RM, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microb Rev 15(2):167–193. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.15.2.167-193.2002
EFSA. (2012) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2010. Euro Surveillance: Bulletin Européen Sur Les maladies Transmissibles. Eur Commun Disease Bull, 17(10), 1–442. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2597
EFSA (2020) Pathogenicity assessment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and the public health risk posed by contamination of food with STEC. EFSA J 18(1):1–105. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.5967
Etcheverría AI, Padola NL, Sanz ME, Polifroni R, Krüger A, Passucci J, Rodríguez EM, Taraborelli AL, Ballerio M, Parma AE (2010) Occurrence of Shiga toxin-producing E. Coli (STEC) on carcasses and retail beef cuts in the marketing chain of beef in Argentina. Meat Sci 86(2):418–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.05.027
FAO & WHO, (2018). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and food: attribution, characterization, and monitoring in Microbiological risks. Assesment series. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/272871/9789241514279-eng.pdf
Fernández D & Padola NL (2012). Escherichia coli verocitotoxigénico: Varias cuestiones...y los tambos también. Rev Argent Microbiol, 44(4), 312–323. ISSN 0325–7541.
Fernández D, Sanz ME, Parma AE, Padola NL (2012) Short communication: characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from newborn, milkfed, and growing calves in Argentina. J Dairy Sci 95(9):5340–5343. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2011-5140
García AB, Percival SL (2011) Zoonotic infections: the role of Biofilms. Biofilm and Veterinary Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21289-5_3
Gómez J, Gómez-Lus ML, Bas P, Ramos C, Cafini F, Maestre JR, Prieto J (2013) ¿Es la cuantificación del biofilm un elemento diferenciador en la patogénia de bacilos gramnegativos? Rev Esp De Quimiot 26(2):97–102
Haymaker J, Sharma M, Parveen S, Hashem F, May EB, Handy ET, White C, East C, Bradshaw R, Micallef SA, Callahan MT, Allard S, Anderson B, Craighead S, Gartley S, Vanore A, Kniel KE, Solaiman S, Bui A, Sapkota AR (2019) Prevalence of Shiga-toxigenic and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in untreated surface water and reclaimed water in the Mid Atlantic U.S. Environ Res 172:630–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.019
Herold S, Paton JC, Paton AW (2009) Sab, a novel autotransporter of Locus of Enterocyte Effacement-negative shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli O113:H21, contributes to adherence and biofilm formation. Infect Inmun 77(8):3234–3243. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00031-09
Lindsay D, Holy A, Von (2006) What food safety professionals should know about bacterial biofilms. Br Food J 108(1):27–37. https://doi.org/10.1108/00070700610637616
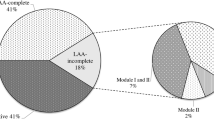
Montero D, Velasco J, Del Canto F, Puente JL, Padola NL, Rasko DA, Farfán M, Salazar JC, Vidal R (2017) Locus of adhesion and autoaggregation (LAA), a pathogenicity island present in emerging Shiga Toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Sci Rep 7(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06999-y
Naves P, del Prado G, Huelves L, Gracia M, Ruiz V, Blanco J, Dahbi G, Blanco M, del Carmen Ponte M, Soriano F (2008) Correlation between virulence factors and in vitro biofilm formation by Escherichia coli strains. Microb Pathog. 2008;45:86–91
Nüesch-Inderbinen M, Cernela N, Wüthrich D, Egli A, Stephan R (2018) Genetic characterization of Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli belonging to the emerging hybrid pathotype O80:H2 isolated from humans 2010–2017 in Switzerland. Int J Med Microb 308(5):534–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.05.007
Nüesch-Inderbinen M, Stevens MJ, Cernela N, Müller A, Biggel M, Stephan R (2021). Distribution of virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance genes and phylogenetic relatedness among shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serogroup O91 from human infections. Int J Med Microbiol 311(8):151541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2021.151541
Padola NL, Sanz ME, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Blanco J, Etcheverria AI, Arroyo GH, Usera MA, Parma AE (2004) Serotypes and virulence genes of bovine shigatoxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from a feedlot in Argentina. Vet Microb 100(1–2):3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1135(03)00127-5
Parma AE, Sanz ME, Blanco JE, Blanco J, Viñas MR, Blanco M, Padola NL, Etcheverría AI (2000) Virulence genotypes and serotypes of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from cattle and foods in Argentina: Importance in public health. Eu J Epidemiol 16(8):757–762. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026746016896
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acid Reserarch 29:2007. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21196.x
Pfaffl MW, Graham WH, Dempfle L (2002) Erratum: Corrigendum to Modeling of the planetary ball-milling process: The case study of ceramic powders J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36 (9) (2016) 2205–2212] (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.09.032) (S0955221915301515) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.09.026
Roberfroid S, Vanderleyden J, Steenackers H (2016) Gene expression variability in clonal populations: causes and consequences. Crit Rev Microb 42(6):969–984. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2015.1122571
Sauer K, Stoodley P, Goeres DM, Hall-Stoodley L, Burmølle M, Stewart PS, Bjarnsholt T (2022) The biofilm life cycle: expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nat Rev Microbiol 20(10):608–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00767-0
Smith-Palmer A, Hawkins G, Couper S, Maxwell H, Reynolds B, Harkins V, Allison L, Hanson M (2018) Global spread of stec and managing the consequences. Arch Dis Childhood 103(1). https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2018-rcpch.469. A196 LP-A197
Spears KJ, Roe AJ, Gally DL (2006) A comparison of enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli pathogenesis. FEMS Microb Let 255(2):187–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00119.x
Tarr PI, Gordon CA, Chandler WL (2005) Seminar shiga-toxin-producing. Epidemiology, 1073–1086
Toma C, Espinosa EM, Song T, Miliwebsky E, Chinen I, Iyoda S, Iwanaga M, Rivas M (2004) Distribution of putative adhesins in different seropathotypes of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 42(11):4937–4946. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.42.11.4937-4946.2004
Vélez MV, Colello R, Etcheverría AI, Vidal RM, Montero DA, Acuña P, Guillén Fretes RM, Toro M, Padola NL (2020) Distribution of Locus of Adhesion and Autoaggregation and hes gene in STEC Strains from countries of Latin America. Curr Microbiol 77(9):2111–2117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02062-8
Vélez MV, Colello R, Etcheverría S, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL (2021) Biofilm formation by LEE-negative Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli strains. Microb Patho 157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105006
Vélez MV, Colello R, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL (2022) Escherichia coli productora de toxina shiga: El desafío De adherirse para sobrevivir. Rev Argent Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2022.04.001
Vogeleer P, Tremblay YDN, Jubelin G, Jacques M, Harel J (2016) Biofilm-forming abilities of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates associated with human infections. App Environ Microb 82(5):1448–1458. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02983-15
Wang R, Bono JL, Kalchayanand N, Shackelford S, Harhay DM (2012) Biofilm formation by shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 and non-O157 strains and their tolerance to sanitizers commonly used in the food processing environment. J Food Prot 75(8):1418–1428. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-427
Acknowledgements
The authors thank María Rosa Ortíz for her technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by PICT 2015–2666, CIC, and SECAT from Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, R. Colello., M.V. Vélez, and N.L. Padola.; Funding acquisition, N.L. Padola.; Investigation, R. Colello. and M.V. Vélez.; Methodology, M.V. Vélez and L. E. Paz.; Supervision, N.L. Padola. and A.I. Etcheverría.; Validation, M.V.Vélez and M.V. Nieto Farias.; Visualization, R. Colello., and N.L. Padola.; Writing-original draft, M.V. Vélez.; Writing-review and editing, R. Colello., M.V. Vélez., M.V. Nieto Farias., R. Vidal., A.I. Etcheverria. and N.L. Padola.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vélez, M.V., Colello, R., Nieto, M.V. et al. Transcription levels of hes and their involvement in the biofilm formation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91. Vet Res Commun 48, 1821–1830 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10308-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10308-0