Abstract
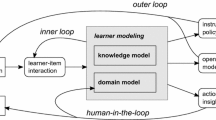
We investigate applications of learner modeling in a computerized adaptive system for practicing factual knowledge. We focus on areas where learners have widely varying degrees of prior knowledge. We propose a modular approach to the development of such adaptive practice systems: dissecting the system design into an estimation of prior knowledge, an estimation of current knowledge, and the construction of questions. We provide a detailed discussion of learner models for both estimation steps, including a novel use of the Elo rating system for learner modeling. We implemented the proposed approach in a system for practising geography facts; the system is widely used and allows us to perform evaluation of all three modules. We compare the predictive accuracy of different learner models, discuss insights gained from learner modeling, as well as the impact different variants of the system have on learners’ engagement and learning.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuhamdeh, S., Csikszentmihalyi, M.: The importance of challenge for the enjoyment of intrinsically motivated, goal-directed activities. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 38(3), 317–330 (2012)
Barla, M., Bieliková, M., Ezzeddinne, A.B., Kramár, T., Šimko, M., Vozár, O.: On the impact of adaptive test question selection for learning efficiency. Comput. Educ. 55(2), 846–857 (2010)
Barnes, T.: The q-matrix method: mining student response data for knowledge. In: American Association for Artificial Intelligence 2005 Educational Data Mining Workshop, pp. 1–8 (2005)
Basu, S., Biswas, G., Kinnebrew, J.S.: Learner modeling for adaptive scaffolding in a computational thinking-based science learning environment. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. J. Pers. Res. 17, this issue (2017)
Carbonell, J.R.: AI in CAI: an artificial-intelligence approach to computer-assisted instruction. IEEE Trans. Man–Mach. Syst. 11(4), 190–202 (1970)
Conati, C., Gertner, A., Vanlehn, K.: Using bayesian networks to manage uncertainty in student modeling. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 12(4), 371–417 (2002)
Corbett, A., Anderson, J.: Knowledge tracing: modeling the acquisition of procedural knowledge. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 4(4), 253–278 (1994)
Csikszentmihalyi, M.: Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. Harper Perennial, New York (1991)
De Ayala, R.: The Theory and Practice of Item Response Theory. The Guilford Press, New York (2008)
Delaney, P.F., Verkoeijen, P.P., Spirgel, A.: Spacing and testing effects: a deeply critical, lengthy, and at times discursive review of the literature. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 53, 63–147 (2010)
Desmarais, M.C., Baker, R.S.: A review of recent advances in learner and skill modeling in intelligent learning environments. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 22(1–2), 9–38 (2012)
Desmarais, M.C., Beheshti, B., Naceur, R.: Item to skills mapping: deriving a conjunctive q-matrix from data. In: Trausan-Matu, S., Boyer, K.E., Crosby, M.E., Panourgia, K. (eds.) Proceedings of Intelligent Tutoring Systems. LNCS, vol. 8474, pp. 454–463. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Doebler, P., Alavash, M., Giessing, C.: Adaptive experiments with a multivariate Elo-type algorithm. Behav. Res. Methods vol. 47, pp. 384–394. Springer (2015)
Doignon, J.P., Falmagne, J.C.: Knowledge Spaces. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Elo, A.E.: The Rating of Chessplayers, Past and Present, vol. 3. Batsford, London (1978)
Gierl, M.J., Haladyna, T.M.: Automatic Item Generation: Theory and Practice. Routledge, New York (2012)
Gierl, M.J., Lai, H., Turner, S.R.: Using automatic item generation to create multiple-choice test items. Med. Educ. 46(8), 757–765 (2012)
Glickman, M.E.: Parameter estimation in large dynamic paired comparison experiments. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 48(3), 377–394 (1999)
González-Brenes, J., Huang, Y., Brusilovsky, P.: General features in knowledge tracing: applications to multiple subskills, temporal item response theory, and expert knowledge. In: Stamper, J., Pardos, Z., Mavrikis, M., McLaren, B. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 84–91 (2014)
Grawemeyer, B., Mavrikis, M., Holmes, W., Gutierrez-Santos, S., Wiedmann, M., Rummel, N.: Affective learning: improving engagement and enhancing learning with affect-aware feedback. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. J. Pers. Res. 17, this issue (2017)
Herbrich, R., Minka, T., Graepel, T.: Trueskill: a Bayesian skill rating system. In: Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Hofmann, T. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 569–576. MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Jansen, B.R., Louwerse, J., Straatemeier, M., Van der Ven, S.H., Klinkenberg, S., Van der Maas, H.L.: The influence of experiencing success in math on math anxiety, perceived math competence, and math performance. Learn. Individ. Differ. 24, 190–197 (2013)
Karpicke, J.D., Roediger, H.L.: Repeated retrieval during learning is the key to long-term retention. J. Memory Lang. 57(2), 151–162 (2007)
Käser, T., Klingler, S., Schwing, A.G., Gross, M.: Beyond knowledge tracing: modeling skill topologies with bayesian networks. In: Micarelli, A., Stamper, J.C., Panourgia, K. (eds.) Proceedings of the Intelligent Tutoring Systems. LNCS, vol. 9684, pp. 188–198. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Khajah, M., Wing, R., Lindsey, R., Mozer, M.: Integrating latent-factor and knowledge-tracing models to predict individual differences in learning. In: Stamper, J., Pardos, Z., Mavrikis, M., McLaren, B. (eds.) Proceedings of the Educational Data Mining, pp. 99–106 (2014a)
Khajah, M.M., Huang, Y., González-Brenes, J.P., Mozer, M.C., Brusilovsky, P.: Integrating knowledge tracing and item response theory: a tale of two frameworks. In: Proceedings of Personalization Approaches in Learning Environments Workshop (2014b)
Khajah, M.M., Roads, B.D., Lindsey, R.V., Liu, Y.E., Mozer, M.C.: Designing engaging games using bayesian optimization. In: Kaye, J., Druin, A., Lampe, C., Morris, D., Hourcade, J.P. (eds.) Proceedings of CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 5571–5582. ACM (2016)
Klinkenberg, S., Straatemeier, M., Van der Maas, H.: Computer adaptive practice of maths ability using a new item response model for on the fly ability and difficulty estimation. Comput. Educ. 57(2), 1813–1824 (2011)
Koedinger, K.R., Corbett, A.: Cognitive tutors: technology bringing learning sciences to the classroom. In: Sawyer, K. (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Koedinger, K.R., Corbett, A.T., Perfetti, C.: The knowledge-learning-instruction framework: bridging the science-practice chasm to enhance robust student learning. Cogn. Sci. 36(5), 757–798 (2012)
Koren, Y., Bell, R.: Advances in collaborative filtering. In: Ricci, F., Rokach, L., Shapira, B., Kantor, P.B. (eds.) Recommender Systems Handbook, pp. 145–186. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Liu, C., White, R.W., Dumais, S.: Understanding web browsing behaviors through Weibull analysis of dwell time. In: Crestani, F., Marchand-Maillet, S., Chen, H., Efthimiadis, E.N., Savoy, J. (eds.) Proceedings of Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 379–386. ACM (2010)
Lomas, D., Patel, K., Forlizzi, J.L., Koedinger, K.R.: Optimizing challenge in an educational game using large-scale design experiments. In: Wendy, E., Mackay, S.B., Stephen, A., Brewster, (eds.) Proceedings of Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 89–98. ACM, New York (2013)
Lomas, D., Forlizzi, J., Poonwala, N., Patel, N., Shodhan, S., Patel, K., Koedinger, K., Brunskill, E.: Interface design optimization as a multi-armed bandit problem. In: Kaye, J., Druin, A., Lampe, C., Morris, D., Hourcade, J.P. (eds.) Proceedings of CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 4142–4153. ACM, (2016)
Long, Y., Aleven, V.: Enhancing learning outcomes through self-regulated learning support with an open learner model. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. J. Pers. Res. 17, this issue (2017)
Mettler, E., Massey, C.M., Kellman, P.J.: Improving adaptive learning technology through the use of response times. In: Carlson, L., Holscher, C., Shipley, T. (eds.) Proceedings of Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, pp. 2532–2537. Cognitive Science Society, Boston (2011)
Millán, E., Loboda, T., Pérez-de-la Cruz, J.L.: Bayesian networks for student model engineering. Comput. Educ. 55(4), 1663–1683 (2010)
Minka, T.P.: A family of algorithms for approximate bayesian inference. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2001)
Mitkov, R., Ha, L.A., Karamanis, N.: A computer-aided environment for generating multiple-choice test items. Nat. Lang. Eng. 12(2), 177–194 (2006)
Mostow, J., Tobin, B., Cuneo, A.: Automated comprehension assessment in a reading tutor. In: Proceedings of ITS 2002 Workshop on Creating Valid Diagnostic Assessments, pp. 52–63 (2002)
Nižnan, J., Pelánek, R., Řihák, J.L.: Using problem solving times and expert opinion to detect skills. In: Stamper, J., Pardos, Z., Mavrikis, M., McLaren, B. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 434–434 (2014a)
Nižnan, J., Pelánek, R., Řihák, J.: Student models for prior knowledge estimation. In: Santos, O.C., Boticario, J.G., Romero, C., Pechenizkiy, M., Merceron, A., Mitros, P., Luna, J.M., Mihaescu, C., Moreno, P., Ventura, A.H.S., Desmarais, M. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 109–116 (2015)
Nižnan, J., Pelánek, R., Řihák, J.: Mapping problems to skills combining expert opinion and student data. In: Hlinený, P., Dvorak, Z., Jaros, J., Kofron, J., Korenek, J., Matula, P., Pala, K. (eds.) Proceedings of Mathematical and Engineering Methods in Computer Science. LNCS, vol. 8934, pp. 113–124. Springer, Berlin (2014b)
Papoušek, J., Pelánek, R.: Impact of adaptive educational system behaviour on student motivation. In: Conati, C., Heffernan, N.T., Mitrovic, A., Verdejo, M.F. (eds.) Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence in Education. LNCS, vol. 9112, pp. 348–357. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Papoušek, J., Pelánek, R., Stanislav, V.: Adaptive practice of facts in domains with varied prior knowledge. In: Stamper, J., Pardos, Z., Mavrikis, M., McLaren, B. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 6–13 (2014)
Papoušek, J., Pelánek, R., Řihák, J., Stanislav, V.: An analysis of response times in adaptive practice of geography facts. In: Santos, O.C., Boticario, J.G., Romero, C., Pechenizkiy, M., Merceron, A., Mitros, P., Luna, J.M., Mihaescu, C., Moreno, P., Ventura, A.H.S., Desmarais, M. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 562–563 (2015)
Papoušek, J., Pelánek, R., Stanislav, V. (2016a) Adaptive geography practice data set. J. Learn. Anal. Submitted http://www.fi.muni.cz/adaptivelearning/
Papoušek, J., Stanislav, V., Pelánek, R.: Evaluation of an adaptive practice system for learning geography facts. In: Gasevic, D., Lynch, G., Dawson, S., Drachsler, H., Rosé, C.P. (eds.) Proceedings of Learning Analytics & Knowledge, pp. 40–47. ACM (2016b)
Papoušek, J., Stanislav, V., Pelánek, R.: Impact of question difficulty on engagement and learning. In: Micarelli, A., Stamper, J.C., Panourgia, K. (eds.) Proceedings of Intelligent Tutoring Systems. LNCS, vol. 9684. Springer, Berlin (2016c)
Pardos, Z.A., Heffernan, N.T.: Modeling individualization in a bayesian networks implementation of knowledge tracing. In: User Modeling, Adaptation, and Personalization, pp 255–266. Springer, Berlin, (2010)
Pavlik, P.I., Anderson, J.R.: Practice and forgetting effects on vocabulary memory: an activation-based model of the spacing effect. Cogn. Sci. 29(4), 559–586 (2005)
Pavlik, P.I., Cen, H., Koedinger, K.R.: Performance factors analysis-a new alternative to knowledge tracing. In: Dimitrova, V., Mizoguchi, R., du Boulay, B., Graesser, A.C. (eds.) Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence in Education, Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, vol. 200, pp. 531–538. IOS Press, Amsterdam (2009)
Pavlik Jr., P., Bolster, T., Wu, S.M., Koedinger, K., Macwhinney, B.: Using optimally selected drill practice to train basic facts. In: Woolf, B.P., Aïmeur, E., Nkambou, R., Lajoie, S.P. (eds.) Proceedings of Intelligent Tutoring Systems. LNCS, vol. 5091, pp. 593–602. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Pelánek, R.: Metrics for evaluation of student models. J. Educ. Data Min. 7(2), 1–19 (2015)
Pelánek, R.: Modeling students’ memory for application in adaptive educational systems. In: Santos, O.C., Boticario, J.G., Romero, C., Pechenizkiy, M., Merceron, A., Mitros, P., Luna, J.M., Mihaescu, C., Moreno, P., Ventura, A.H.S., Desmarais, M. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp. 480–483 (2015)
Pelánek, R.: Applications of the elo rating system in adaptive educational systems. Comput. Educ. 98, 169–179 (2016)
Qiu, Y., Qi, Y., Lu, H., Pardos, Z.A., Heffernan, N.T.: Does time matter? modeling the effect of time with Bayesian knowledge tracing. In: Pechenizkiy, M., Calders, T., Conati, C., Ventura, S., Romero, C., Stamper, J. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining (2011)
Schulze, K.G., Shelby, R.N., Treacy, D.J., Wintersgill, M.C., Vanlehn, K., Gertner, A.: Andes: an intelligent tutor for classical physics. J. Electron. Publ. 6(1) (2000)
Tatsuoka, K.K.: Rule space: an approach for dealing with misconceptions based on item response theory. J. Educ. Meas. 20(4), 345–354 (1983)
van de Sande, B.: Properties of the bayesian knowledge tracing model. J. Educ. Data Min. 5(2), 1 (2013)
Vanlehn, K.: The behavior of tutoring systems. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 16(3), 227–265 (2006)
Von Luxburg, U.: A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 17(4), 395–416 (2007)
Wauters, K., Desmet, P., Van Den Noortgate, W.: Monitoring learners’ proficiency: weight adaptation in the Elo rating system. In: Pechenizkiy, M., Calders, T., Conati, C., Ventura, S., Romero, C., Stamper, J. (eds.) Proceedings of Educational Data Mining, pp 247–252 (2011)
Zirkle, D.M., Ellis, A.K.: Effects of spaced repetition on long-term map knowledge recall. J. Geogr. 109(5), 201–206 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelánek, R., Papoušek, J., Řihák, J. et al. Elo-based learner modeling for the adaptive practice of facts. User Model User-Adap Inter 27, 89–118 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-016-9185-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-016-9185-7