Abstract
Purpose
To demonstrate the efficacy of combined rituximab and plasmapheresis (PP)/plasma exchange (PE) therapy for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in transplanted kidneys (ptFSGS).
Methods
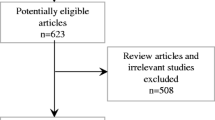
We searched MEDLINE, SCOPUS, and Cochrane Library for eligible publications. Only observational studies or clinical trials containing patients’ age > 18 years were included for full-text extraction.
Results
A total of eight observational studies (n = 85) were included in meta-analyses. With a median follow-up of 18 months (IQR 4.4), combination therapy of RTX-PP/PE in patients with ptFSGS resulted in overall remission rate of 72.7% (95% CI 52.3–86.6%) with a significant reduction of proteinuria and serum creatinine levels. Complete remission was 41.0%, while partial remission was 31.7%. The mean difference of serum creatinine levels between pre- and post-treatment was − 0.65 mg/dL (95% CI − 1.15 to − 0.14). The mean difference of the degree of proteinuria between pre- and post-treatment was − 4.79 g/day (95% CI − 7.02 to − 2.56). Subgroup analyses were performed after adjusted for study year, type of intervention, and primary pre-transplant lesion. Patients with recurrent FSGS tended have lesser reduction in the degree of proteinuria compared to patients with de novo FSGS. Incidence of serious adverse events with combined RTX-PP/PE therapy was 0.12 event/year.
Conclusion
We conclude that combined RTX-PP/PE therapy may be considered as an alternative treatment of ptFSGS in achieving remission by lowering proteinuria and serum creatinine levels. However, the efficacy of combined RTX-PP/PE therapy must be confirmed in randomized-controlled trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D'Agati V (1994) The many masks of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 46(4):1223–1241. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1994.388
Kitiyakara C, Eggers P, Kopp JB (2004) Twenty-one-year trend in ESRD due to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 44(5):815–825
Beaudreuil S, Lorenzo HK, Elias M, Nnang Obada E, Charpentier B, Durrbach A (2017) Optimal management of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 10:97–107. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijnrd.S126844
Choy BY, Chan TM, Lai KN (2006) Recurrent glomerulonephritis after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 6(11):2535–2542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01502.x
Cattran DC, Rao P (1998) Long-term outcome in children and adults with classic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis 32(1):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.1998.v32.pm9669427
Korbet SM (2002) Treatment of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 62(6):2301–2310. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00674.x
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K (2017) Rituximab for nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin Exp Nephrol 21(2):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-016-1313-5
Andresdottir MB, Ajubi N, Croockewit S, Assmann KJ, Hibrands LB, Wetzels JF (1999) Recurrent focal glomerulosclerosis: natural course and treatment with plasma exchange. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(11):2650–2656. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/14.11.2650
Davenport RD (2001) Apheresis treatment of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation: re-analysis of published case-reports and case-series. J Clin Apher 16(4):175–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/jca.10007
Damodar A, Mustafa R, Bhatnagar J, Panesar M, Gundroo A, Zachariah M, Blessios G, Tornatore K, Weber-Shrikant E, Venuto R (2011) Use of anti-CD20 antibody in the treatment of post-transplant glomerulonephritis. Clin Transplant 25(3):375–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01245.x
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Sterne JA, Hernan MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT, Boutron I, Carpenter JR, Chan AW, Churchill R, Deeks JJ, Hrobjartsson A, Kirkham J, Juni P, Loke YK, Pigott TD, Ramsay CR, Regidor D, Rothstein HR, Sandhu L, Santaguida PL, Schunemann HJ, Shea B, Shrier I, Tugwell P, Turner L, Valentine JC, Waddington H, Waters E, Wells GA, Whiting PF, Higgins JP ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. (1756–1833 (Electronic))
Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR (1991) Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 337(8746):867–872
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Kashgary A, Sontrop JM, Li L, Al-Jaishi AA, Habibullah ZN, Alsolaimani R, Clark WF (2016) The role of plasma exchange in treating post-transplant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 77 case-reports and case-series. BMC Nephrol 17(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-016-0322-7
Matalon A, Markowitz GS, Joseph RE, Cohen DJ, Saal SD, Kaplan B, D'Agati VD, Appel GB (2001) Plasmapheresis treatment of recurrent FSGS in adult renal transplant recipients. Clin Nephrol 56(4):271–278
Cravedi P, Kopp J, Fau-Remuzzi G, Remuzzi G. Recent progress in the pathophysiology and treatment of FSGS recurrence. (1600–6143 (Electronic))
Wei C, El Hindi S, Li J, Fornoni A, Goes N, Sageshima J, Maiguel D, Karumanchi SA, Yap HK, Saleem M, Zhang Q, Nikolic B, Chaudhuri A, Daftarian P, Salido E, Torres A, Salifu M, Sarwal M, Schaefer F, Morath C, Schwenger V, Zeier M, Gupta V, Roth D, Rastaldi M, Burke G, Ruiz P, Reiser J. Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. (1546–170X (Electronic))
McCarthy ET, Sharma M, Savin VJ. Circulating permeability factors in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. (1555–905X (Electronic))
de Oliveira JG, Xavier P, Carvalho E, Ramos JP, Magalhaes MC, Mendes AA, Faria V, Guerra LE (1999) T lymphocyte subsets and cytokine production by graft-infiltrating cells in FSGS recurrence post-transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(3):713–716. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/14.3.713
Kienzl-Wagner K, Waldegger S, Schneeberger S. Disease recurrence-the Sword of damocles in kidney transplantation for primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. (1664–3224 (Electronic))
Abbott KC, Sawyers E, Oliver J, Ko C, Kirk A, Welch P, Peters T, Agodoa LY. Graft loss due to recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in renal transplant recipients in the United States. (1523–6838 (Electronic))
Stegmayr B, Ptak J, Wikström B, Berlin G, Axelsson CG, Griskevicius A, Centoni P, Liumbruno G, Molfettini P, Audzijoniene J, Mokvist K, Sojka BN, Norda R, Knutson F, Ramlow W, Blaha M, Witt V, Evergren M, Tomaz J (2008) World apheresis registry 2003–2007 data. Transfus Apheres Sci 39(3):247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transci.2008.09.003
Rock G (2016) Note from the editor in chief. Transfus Apheres Sci 54(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transci.2016.01.002
D'Agati V (2003) Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol 23(2):117–134. https://doi.org/10.1053/snep.2003.50012
Valdivia P, Gonzalez Roncero F, Gentil MA, Jimenez F, Algarra G, Pereira P, Rivera M, Suner M, Cabello V, Toro J, Mateos J (2005) Plasmapheresis for the prophylaxis and treatment of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis following renal transplant. Transpl Proc 37(3):1473–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.02.061
Alasfar S, Matar D, Montgomery RA, Desai N, Lonze B, Vujjini V, Estrella MM, Manllo Dieck J, Khneizer G, Sever S, Reiser J, Alachkar N (2018) Rituximab and therapeutic plasma exchange in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis postkidney transplantation. Transplantation 102(3):e115–e120. https://doi.org/10.1097/tp.0000000000002008
Rodríguez-Ferrero M, Ampuero J, Anaya F (2009) Rituximab and chronic plasmapheresis therapy of nephrotic syndrome in renal transplantation patients with recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Transpl Proc 41(6):2406–2408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.06.044
Tsagalis G, Psimenou E, Nakopoulou L, Laggouranis A (2011) Combination treatment with plasmapheresis and rituximab for recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after renal transplantation. Artif Organs 35(4):420–425. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2010.01068.x
Alachkar N, Wei C, Arend LJ, Jackson AM, Racusen LC, Fornoni A, Burke G, Rabb H, Kakkad K, Reiser J, Estrella MM (2013) Podocyte effacement closely links to suPAR levels at time of posttransplantation focal segmental glomerulosclerosis occurrence and improves with therapy. Transplantation 96(7):649–656. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31829eda4f
Lionaki S, Vlachopanos G, Georgalis A, Liapis G, Skalioti C, Zavos G, Boletis JN (2015) Individualized scheme of immunoadsorption for the recurrence of idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in the graft: a single center experience. Ren Fail 37(5):777–783. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2015.1015366
Garrouste C, Canaud G, Büchler M, Rivalan J, Colosio C, Martinez F, Aniort J, Dudreuilh C, Pereira B, Caillard S, Philipponnet C, Anglicheau D, Heng AE (2017) Rituximab for recurrence of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation: clinical outcomes. Transplantation 101(3):649–656. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001160
Alachkar N, Li J, Matar D, Vujjini V, Alasfar S, Tracy M, Reiser J, Wei C (2018) Monitoring suPAR levels in post-kidney transplant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis treated with therapeutic plasma exchange and rituximab. BMC Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-1177-x
Koutroutsos K, Charif R, Moran L, Moss J, Cook T, Roufosse C, Pusey C, Taube D, Loucaidou M (2019) Successful management of post-transplant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with therapeutic plasma exchange and rituximab. Clin Exp Nephrol 23(5):700–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-019-01690-0
Acknowledgements
There is no institutional or national funding for this research.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PH and NG performed literature search, citation screening, and data collection. PH analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. PH and NG revised and edited the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
This study does not involve human participants and/or animals. Thus, ethical approval is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansrivijit, P., Ghahramani, N. Combined rituximab and plasmapheresis or plasma exchange for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adult kidney transplant recipients: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1377–1387 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02462-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02462-6