Abstract
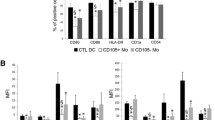
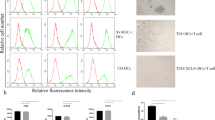
Dendritic cells (DCs) play an important role in anti-renal cell carcinoma (RCC) immunity. The aim of the study was to investigate effect of mimic RCC microenvironment on phenotype and function of DCs. We isolated conditioned media (CM) from supernatants of culturing RCC cells and adjacent non-RCC cells in patients. CD14+ monocytes were obtained from healthy donors. The monocytes derived DCs were treated by RCC CM and non-RCC CM. Maturation markers CD80, CD83, CD86, and HLA-DR on DCs were analyzed using flow cytometry, while the levels of IL-10, TGF-β, and IL12p70 in supernatants were examined by ELISA. The DCs migration treated with RCC CM and non-RCC CM was investigated using transwell assay. The DCs treated and allogenic T cells were co-cultured for detecting T-cell proliferation and change of phenotype on the T cells. Our results indicated that RCC CM inhibited the up-regulation of CD80,CD83, CD86, and HLA-DR in response to LPS in treated DCs and increased IL-10 and TGF-β secretion but reduced IL12p70 production. Moreover, the migration ability of DCs treated with RCC CM was also inhibited, compared to DCs treated with adjacent non-RCC CM. In addition, T-cell proliferation was suppressed in co-culture assay with DCs treated with RCC CM; proportion CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells were induced to increase. This study suggests that RCC CM can inhibit maturation of DCs and impair its function; moreover, DCs treated with RCC CM induce regulatory T cells increase, thus could contribute RCC escape from antitumor immunity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luczyńska E, Dyczek S, Heinze-Paluchowska S, Komorowski A, Pawlik T, Wysocki W, Klimek M (2013) Nephrectomy or nephron-sparing surgery: how to decide? Contemp Oncol (Pozn) 17(1):88–93
Kutikov A, Egleston BL, Canter D, Smaldone MC, Wong YN, Uzzo RG (2012) Competing risks of death in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma: a comorbidity based model. J Urol 188(6):2077–2083
Banchereau J, Palucka AK (2005) Dendritic cells as therapeutic vaccines against cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 5(4):296–306
Banchereau J, Steinman RM (1998) Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392(6673):245–252
Obryshev YV, Tran D, Killingsworth MC, Buckland M, Lord RV (2009) B Dendriti cell-associated immune inflammation of cardiac mucosa: a possible factor in the formation of Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 13(3):442–450
Halama N, Michel S, Kloor M, Zoernig I, Pommerencke T, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Schirmacher P, Weitz J, Grabe N, Jäger D (2009) The localization and density of immune cells in primary tumors of human metastatic colorectal cancer shows an association with response to chemotherapy. Cancer Immun 9:1
Kobayashi M, Suzuki K, Yashi M, Yuzawa M, Takayashiki N, Morita T (2007) Tumor infiltrating dendritic cells predict treatment response to immunotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 27(2):1137–1141
Hou MM, Chang JW, Pang ST, Chiang YJ, Shen YC, Liao SK, Hsieh JJ, Yeh KY, Chang NJ, Chuang CK (2010) Characterization of the response of dendritic cells and regulatory T cells to tumor antigens in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Chang Gung Med J 33(1):25–35
Troy AJ, Summers KL, Davidson PJ, Atkinson CH, Hart DN (1998) Minimal recruitment and activation of dendritic cells within renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 4(3):585–593
Troy AJ, Davidson PJ, Atkinson CH, Hart DN (1999) CD1a dendritic cells predominate in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder and kidney but are minimally activated. J Urol 161(6):1962–1967
Middel P, Brauneck S, Meyer W, Radzun HJ (2010) Chemokine-mediated distribution of dendritic cell subsets in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 10:578
Teng L, Liu L, Su Y, Yuan X, Li J, Fu Q, Chen S, Wang C (2011) Suppression of alloimmunity in mice by regulatory T cells converted with conditioned media. J Surg Res 171(2):797–806
Feijoó E, Alfaro C, Mazzolini G, Serra P, Peñuelas I, Arina A, Huarte E, Tirapu I, Palencia B, Murillo O, Ruiz J, Sangro B, Richter JA, Prieto J, Melero I (2005) Dendritic cells delivered inside human carcinomas are sequestered by interleukin-8. Int J Cancer 116(2):275–281
Michielsen AJ, Hogan AE, Marry J, Tosetto M, Cox F, Hyland JM, Sheahan KD, O’Donoghue DP, Mulcahy HE, Ryan EJ, O’Sullivan JN (2011) Tumour tissue microenvironment can inhibit dendritic cell maturation in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 6:e27944
Imai K, Minamiya Y, Koyota S, Ito M, Saito H, Sato Y, Motoyama S, Sugiyama T, Ogawa J (2012) Inhibition of dendritic cell migration by transforming growth factor-β1 increases tumor-draining lymph node metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:3
Baumgartner JM, Jordan KR, Hu LJ, Wilson CC, Banerjee A, McCarter MD (2012) DC maturation and function are not altered by melanoma-derived immunosuppressive soluble factors. J Surg Res 176(1):301–308
Marguti I, Yamamoto GL, da Costa TB, Rizzo LV, de Moraes LV (2009) Expansion of CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + T cells by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Immunology 127(1):50–61
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by scientific research program Grant (12531273) from Department of Education of Heilongjiang province.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lichen Teng and Yongsheng Chen have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, L., Chen, Y., Ding, D. et al. Immunosuppressive effect of renal cell carcinoma on phenotype and function of dendritic cells. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 915–920 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0595-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0595-8