Abstract
Background
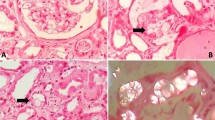
KIM-1 staining is upregulated in proximal tubule-derived renal cell carcinoma (RCC) including clear renal cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma, but not in chromophobe RCC (distal tubular tumor). This study was designed to prospectively examine urine KIM-1 level before and 1 month after removal of renal tumors.
Patients and design
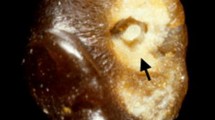
A total of 19 patients were eventually enrolled in the study based on pre-operative imaging studies. Pre-operative and follow-up (1 month) urine KIM-1 levels were measured. The urine KIM-1 levels (uKIM-1) were then normalized to urine creatinine levels (uCr). Renal tumors were also stained for KIM-1 using immunohistochemical techniques.
Results
The KIM-1-negative staining group included 7 cases, and the KIM-1-positive group consisted of 12 cases. The percentage of KIM-1-positive staining RCC cells ranged from 10 to 100 %, and the staining intensity ranged from 1+ to 3+. In both groups, serum creatinine levels were both significantly elevated after nephrectomy. In the KIM-1-negative group, uKIM-1/uCr remained at a similar level before (0.37 ± 0.1 ng/mg Cr) and after nephrectomy (0.32 ± 0.01 ng/mg Cr). However, in the KIM-1-positive group, elevated uKIM-1/uCr at 1.20 ± 0.31 ng/mg Cr was significantly reduced to 0.36 ± 0.1 ng/mg Cr, which was similar to the pre-operative uKIM-1/uCr (0.37 ± 0.1 ng/mg Cr) in the KIM-1-negative group.
Conclusion
Our small but prospective study showed significant reduction in uKIM-1/uCr after nephrectomy in the KIM-1 positive group, suggesting that urine KIM-1 may serve as a surrogate biomarker for kidney cancer and a non-invasive pre-operative measure to evaluate the malignant potential of renal masses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59(4):225–249
Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H, Hession CA, Cate RL et al (1998) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem 273(7):4135–4142
Ichimura T, Hung CC, Yang SA, Stevens JL, Bonventre JV (2004) Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286(3):F552–F563
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62(1):237–244
van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, Bakker SJ, van Goor H, Stegeman CA (2007) Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J Pathol 212(2):209–217
Zhang PL, Rothblum LI, Han WK, Blasick TM, Potdar S, Bonventre JV (2008) Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in transplant biopsies is a sensitive measure of cell injury. Kidney Int 73(5):608–614
Ichimura T, Asseldonk EJ, Humphreys BD, Gunaratnam L, Duffield JS, Bonventre JV (2008) Kidney injury molecule-1 is a phosphatidylserine receptor that confers a phagocytic phenotype on epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 118(5):1657–1668
de Borst MH, van Timmeren MM, Vaidya VS, de Boer RA, van Dalen MB, Kramer AB et al (2007) Induction of kidney injury molecule-1 in homozygous Ren2 rats is attenuated by blockade of the renin-angiotensin system or p38 MAP kinase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292(1):F313–F320
Kramer AB, van Timmeren MM, Schuurs TA, Vaidya VS, Bonventre JV, van Goor H et al (2009) Reduction of proteinuria in adriamycin-induced nephropathy is associated with reduction of renal kidney injury molecule (Kim-1) over time. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296(5):F1136–F1145
Vaidya VS, Ramirez V, Ichimura T, Bobadilla NA, Bonventre JV (2006) Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: a sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney tubular injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290(2):F517–F529
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P et al (2008) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 73(7):863–869
Han WK, Alinani A, Wu CL, Michaelson D, Loda M, McGovern FJ et al (2005) Human kidney injury molecule-1 is a tissue and urinary tumor marker of renal cell carcinoma. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(4):1126–1134
Lin F, Zhang PL, Yang XJ, Shi J, Blasick T, Han WK et al (2007) Human kidney injury molecule-1 (hKIM-1): a useful immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing renal cell carcinoma and ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 31(3):371–381
Morrissey JJ, London AN, Lambert MC, Kharasch ED (2011) Sensitivity and specificity of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 for the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Nephrol 34(5):391–398
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI et al (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150(9):604–612
Endre ZH, Pickering JW, Walker RJ, Devarajan P, Edelstein CL, Bonventre JV et al (2011) Improved performance of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in the critically ill by stratification for injury duration and baseline renal function. Kidney Int 79(10):1119–1130
Holness CL, Simmons DL (1993) Molecular cloning of CD68, a human macrophage marker related to lysosomal glycoproteins. Blood 81(6):1607–1613
Saito N, Pulford KA, Breton-Gorius J, Masse JM, Mason DY, Cramer EM (1991) Ultrastructural localization of the CD68 macrophage-associated antigen in human blood neutrophils and monocytes. Am J Pathol 139(5):1053–1059
Vaidya VS, Ozer JS, Dieterle F, Collings FB, Ramirez V, Troth S et al (2010) Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):478–485
Liangos O, Perianayagam MC, Vaidya VS, Han WK, Wald R, Tighiouart H et al (2007) Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(D)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(3):904–912
Schworer CM, Zhang PL, Gerhard GS, Lin F (2009) Mutations in the mucin binding domain of the human kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) gene are present in renal epithelial neoplasms. Mod Pathol 22(Suppl 1):192A
Ichimura T, Brooks CR, Bonventre JV (2012) Kim-1/Tim-1 and immune cells: shifting sands. Kidney Int 81(9):809–811
Tanaka M, Suzuki Y, Shirato I, Takahara H, Shibata T, Sugaya T et al (2008) Tubular epithelial cells have the capacity to transdifferentiate into CD68-positive macrophage-like cells by oxidative stress. Inflamm Res 57(12):593–600
Zhu L, Yang X, Ji Y, Chen W, Guan W, Zhou SF et al (2009) Up-regulated renal expression of TNF-alpha signalling adapter proteins in lupus glomerulonephritis. Lupus 18(2):116–127
Gloghini A, Rizzo A, Zanette I, Canal B, Rupolo G, Bassi P et al (1995) KP1/CD68 expression in malignant neoplasms including lymphomas, sarcomas, and carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol 103(4):425–431
Sridhar S, Botbol Y, Macian F, Cuervo AM (2012) Autophagy and disease: always two sides to a problem. J Pathol 226(2):255–273
Cox TM, Cachon-Gonzalez MB (2012) The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases. J Pathol 226(2):241–254
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Beaumont Health System and Geisinger Health System for funding the internal grants and National Institutes of Health awards DK 39773, DK 72381 and DK 38452 (to J.V.B.). Authors appreciate excellent assistance from Ms. Sharon K. Hick.
Conflict of interest
J.V.B is a co-inventor of KIM-1 patents that are assigned to Partners HealthCare and licensed by Partners to Johnson & Johnson, Sekisui Medical, Biogen Idec and a number of research reagent companies. J.V.B. is a consultant for Sekisui Medical.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P.L., Mashni, J.W., Sabbisetti, V.S. et al. Urine kidney injury molecule-1: a potential non-invasive biomarker for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 379–388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0522-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0522-z