Abstract
Purpose
P-wave parameters including P-wave dispersion (P d) have been examined in general population to predict development of atrial fibrillation (AF). But data on end-stage renal disease (ESRD) population are limited. P index (Pi) and interatrial block (IAB) as novel parameters may more accurately predict AF and have not been previously investigated in ESRD patients. We aimed to evaluate these novel ECG parameters in ESRD patients.
Methods
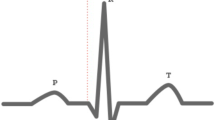
Eighty-six HD, 47 CAPD, and 43 age- and gender-matched control subjects were enrolled in the study. P-wave duration was measured in all 12-leads of the surface ECG. The standard deviation of the P-wave duration across the 12 ECG leads was accepted as a Pi. P-wave duration above and equal to 110 ms was defined as IAB. All P-wave parameters were evaluated digitally by two observers.
Results
Pi was found to be significantly different among the groups in ANOVA. In post hoc analysis, P i was increased in HD group compared with the control group (p = 0.01). Also, P i tended to increase in CAPD group compared with controls (p = 0.06). The effect of ESRD on P i was independent of age, gender, and systolic blood pressure in univariate covariant analysis. The prevalence of IAB was 61, 55, and 32 % in patients with HD, CAPD, and controls, respectively (p = 0.001). P d was significantly higher in HD group compared with healthy controls. However, Pd values of CAPD patients did not show significant difference compared with controls.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrated that IAB frequency and Pi were increased in patients with ESRD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vazquez E, Sanchez-Perales C, Lozano C, Garcia-Cortes MJ, Borrego F, Guzman M, Perez P, Pagola C, Borrego MJ, Perez V (2003) Comparison of prognostic value of atrial fibrillation versus sinus rhythm in patients on long-term hemodialysis. Am J Cardiol 92(7):868–871
Vazquez E, Sanchez-Perales C, Borrego F, Garcia-Cortes MJ, Lozano C, Guzman M, Gil JM, Borrego MJ, Perez V (2000) Influence of atrial fibrillation on the morbido-mortality of patients on hemodialysis. Am Heart J 140(6):886–890
Abbott KC, Trespalacios FC, Taylor AJ, Agodoa LY (2003) Atrial fibrillation in chronic dialysis patients in the United States: risk factors for hospitalization and mortality. BMC Nephrol 4:1
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos JE (2001) P-wave dispersion: a novel predictor of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 6(2):159–165
Perez MV, Dewey FE, Marcus R, Ashley EA, Al-Ahmad AA, Wang PJ, Froelicher VF (2009) Electrocardiographic predictors of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 158(4):622–628. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2009.08.002
Szabo Z, Kakuk G, Fulop T, Matyus J, Balla J, Karpati I, Juhasz A, Kun C, Karanyi Z, Lorincz I (2002) Effects of haemodialysis on maximum P wave duration and P wave dispersion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(9):1634–1638
Ozben B, Toprak A, Koc M, Sumerkan M, Tanrikulu AM, Papila-Topal N, Kefeli US, Cincin AA, Baykan O, Fak AS (2009) P wave dispersion increases during hemodialysis sessions. Nephron Clin Pract 112(3):c171–c176. doi:10.1159/000214213
Taskapan MC, Senel S, Ulutas O, Aksoy Y, Sahin I, Kosar F, Taskapan H (2007) Brain natriuretic peptide and P wave duration in dialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 39(2):603–608. doi:10.1007/s11255-007-9191-0
Mansia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Struijker Boudier HA, Zanchetti A (2007) 2007 ESH-ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Blood Press 16(3):135–232. doi:10.1080/08037050701461084
Schneditz D, Daugirdas JT (2001) Compartment effects in hemodialysis. Semin Dial 14(4):271–277
Ariyarajah V, Asad N, Tandar A, Spodick DH (2005) Interatrial block: pandemic prevalence, significance, and diagnosis. Chest 128(2):970–975. doi:10.1378/chest.128.2.970
Kitkungvan D, Spodick DH (2009) Interatrial block: is it time for more attention? J Electrocardiol 42(6):687–692. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2009.07.016
Agarwal YK, Aronow WS, Levy JA, Spodick DH (2003) Association of interatrial block with development of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 91(7):882
Jairath UC, Spodick DH (2001) Exceptional prevalence of interatrial block in a general hospital population. Clin Cardiol 24(8):548–550
Centurion OA (2009) Clinical implications of the P wave duration and dispersion: relationship between atrial conduction defects and abnormally prolonged and fractionated atrial endocardial electrograms. Int J Cardiol 134(1):6–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.072
Aytemir K, Ozer N, Atalar E, Sade E, Aksoyek S, Ovunc K, Oto A, Ozmen F, Kes S (2000) P wave dispersion on 12-lead electrocardiography in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 23(7):1109–1112
Tezcan UK, Amasyali B, Can I, Aytemir K, Kose S, Yavuz I, Kursaklioglu H, Isik E, Demirtas E, Oto A (2004) Increased P wave dispersion and maximum P wave duration after hemodialysis. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 9(1):34–38
Drighil A, Madias JE, El Mosalami H, El Badaoui N, Mouine B, Fadili W, Ramdani B, Bennis A (2007) Impact of hemodialysis on P-wave amplitude, duration, and dispersion. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 7(2):85–96
Ozmen N, Cebeci BS, Kardesoglu E, Atasoyu EM, Unver S, Celik T, Aparci M, Dincturk M (2007) Relationship between P-wave dispersion and effective hemodialysis in chronic hemodialysis patients. Med Princ Pract 16(2):147–150. doi:10.1159/000098369
Atar I, Konas ND, Uyar M, Atar A, Bozbas H, Gulmez H et al (2007) Pwave dispersion in chronic renal failure patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. TAPE 5(1):46–52
Yazici M, Ozdemir K, Altunkeser BB, Kayrak M, Duzenli MA, Vatankulu MA, Soylu A, Ulgen MS (2007) The effect of diabetes mellitus on the P-wave dispersion. Circ J 71(6):880–883
Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Herpen G, Stricker BH, Stijnen T, Lip GY, Witteman JC (2006) Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J 27(8):949–953. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi825
Tuncer M, Fettser DV, Gunes Y, Batyraliev TA, Guntekin U, Gumrukchuoglu Kh A, Eryonucu B, Guler N, Sidorenko BA (2008) Comparison of effects of nebivolol and atenolol on P-wave dispersion in patients with hypertension. Kardiologiia 48(4):42–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solak, Y., Gul, E.E., Kayrak, M. et al. Electrocardiographic P-wave characteristics in patients with end-stage renal disease: P-index and interatrial block. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 511–517 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0187-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0187-z