Abstract
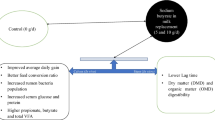
The study aimed to analyze the impact of calcium butyrate supplementation in calf starter on growth performance indices associated with early rumen development to decrease the volume of milk or milk replacer feeding and enhance early starter intake in Holstein calves. For this purpose, twelve Holstein calves were randomly assigned into three treatments (n = 4/treatment); a control without coated calcium butyrate, T1, and T2 treatments supplemented with coated calcium butyrate 3 g and 6 g per day/head, respectively. Body weight was measured at days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, and 56 of the trial, and the average daily weight gain and feed conversion ratio were determined. Blood samples were collected at 14, 28, 42, and 56 days of trial for serological parameters. Gut morphometry was performed at the end of trial at slaughtering by collecting duodenal samples. Furthermore, the meat was also evaluated for its quality parameters including pH and tenderness after slaughtering. The results indicated that the feed intake, average daily weight gain, feed conversion ratio, and gut morphometric parameters involving villus height and crypts depth of calves were improved in coated calcium butyrate–supplemented groups. Furthermore, the supplementation of calf starter with coated calcium butyrate significantly enhanced serum concentrations of glucose and total protein. Besides, Beta hydroxy butyrate (BHBA) levels of blood were also found to be elevated in both treatment groups. However, it was revealed that coated calcium butyrate supplementation had no significant effect on meat quality parameters. In conclusion, the supplementation of calf starter with coated calcium butyrate could improve calf performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and further available from the corresponding author if needed.
References
Ahmad, S.; Yousaf, M.S.; Tahir, S.K.; Mustafa, G.; Majeed, K.A.; Rashid, M.A.; Zaneb, H.; Mustafa, R.; Rehman, H., 2022. Effects of co-supplementation of β-galacto-oligosaccharides and methionine on production performance, blood metabolites, and gut histomorphometry in broilers. Pakistan Veterinary Journal, 42, 173-178.
Annison, E.; Leng, R.; Lindsay, D.; White, R.R., 1963. The metabolism of acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid in sheep. Biochemical Journal 88, 248-252.
Augenlicht, L.H.; Anthony, G.M.; Church, T.L.; Edelmann, W.; Kucherlapati, R.; Yang, K.; Lipkin, M.; Heerdt, B.G., 1999. Short-chain fatty acid metabolism, apoptosis, and Apc-initiated tumorigenesis in the mouse gastrointestinal mucosa. Cancer research 59, 6005-6009.
Chen, D.; Tang, Q.; Su, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, K.; Zhong, G., 2021a. Rumen microbial community and functions of rumen bacteria under different feeding regime. Pakistan Veterinary Journal 41, 341-346.
Chen, D.; Zhong, G.; Su, H.; ur Rahman, M.A.; Chen, K.; Tang, J.; Li, F., 2021. Physiological variation in ruminal microbiota under altered energy levels in starter ration of suckling Angus calves. Pakistan Veterinary Journal 41, 409-413.
Chishti, G.; Felix, T., 2020. Effects of supplemental calcium butyrate on lamb growth, plasma metabolites, and hepatic gluconeogenic and inflammatory gene expression changes. Animal feed science and technology 270, 114678.
Davarmanesh, A.; Nasri, M.F.; Firouzabad, A.K.; Montazer-Torbati, M., 2015. Effect of Ca-butyrate and Oleobiotec (a flavoring agent) supplemented starter on the performance of Holstein dairy calves. The Journal of Agricultural Science 153, 1506-1513.
Ferreira, L.; Bittar, C.M.M., 2011. Performance and plasma metabolites of dairy calves fed starter containing sodium butyrate, calcium propionate or sodium monensin. Animal 5, 239.
Gibson, P.R.; Kilias, D.; Rosella, O.; Day, J.M.; Abbott, M.; Finch, C.F.; Young, G.P., 1998. Effect of topical butyrate on rectal epithelial kinetics and mucosal enzyme activities. Clinical Science 94, 671-676.
Gorka, P.; Kowalski, Z.; Pietrzak, P.; Kotunia, A.; Kiljanczyk, R.; Flaga, J.; Holst, J.; Guilloteau, P.; Zabielski, R., 2009. Effect of sodium butyrate supplementation in milk replacer and starter diet on rumen development in calves. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 4, 10-11.
Gorka, P.; Kowalski, Z.; Pietrzak, P.; Kotunia, A.; Jagusiak, W.; Holst, J.J.; Guilloteau, P.; Zabielski, R., (2011a). Effect of method of delivery of sodium butyrate on rumen development in newborn calves. Journal of Dairy Science 94, 5578-5588.
Gorka, P.; Kowalski, Z.; Pietrzak, P.; Kotunia, A.; Jagusiak, W.; Zabielski, R., (2011b). Is rumen development in newborn calves affected by different liquid feeds and small intestine development? Journal of Dairy Science94, 3002-3013.
Guilloteau, P.; Zabielski, R.; David, J.-C.; Blum, J.W.; Morisset, J.A.; Biernat, M.; Woliński, J.; Laubitz, D.; Hamon, Y., 2009. Sodium-butyrate as a growth promoter in milk replacer formula for young calves. Journal of Dairy Science 92, 1038-1049.
Guilloteau, P.; Savary, G.; Jaguelin-Peyrault, Y.; Romé, V.; Le Normand, L.; Zabielski, R., 2010. Dietary sodium butyrate supplementation increases digestibility and pancreatic secretion in young milk-fed calves. Journal of Dairy Science 93, 5842-5850.
Gul, S.T.; Alsayeqh, A.F., 2022. Probiotics as an alternative approach to antibiotics for safe poultry meat production. Pakistan Veterinary Journal 42, 285-291.
Guzman, C.E.; Bereza‐Malcolm, L.T.; De Groef, B.; Franks, A.E., 2016. Uptake of milk with and without solid feed during the monogastric phase: effect on fibrolytic and methanogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract of calves. Animal science journal 87, 378-388.
Heerdt, B.G.; Houston, M.A.; Augenlicht, L.H., 1994. Potentiation by specific short-chain fatty acids of differentiation and apoptosis in human colonic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer research 54, 3288-3294.
Heinrichs A.J. and Lesmeister K.E., 2004. Rumen development in the dairy calf, (Nottingham University Press, Nottingham)
Hill, T.; Bateman Ii, H.; Aldrich, J.; Schlotterbeck, R., 2010. Effect of milk replacer program on digestion of nutrients in dairy calves. Journal of Dairy Science93, 1105-1115.
Hur, S.; Ye, B.; Lee, J.; Ha, Y.; Park, G.; Joo, S.T., 2004. Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on color and lipid oxidation of beef patties during cold storage. Meat science 66, 771-775.
Khan, M.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Ki, K.; Park, S.; Ha, J.; Choi, Y., 2007. Starch source evaluation in calf starter: i. Feed consumption, body weight gain, structural growth, and blood metabolites in Holstein calves. Journal of dairy science90, 5259-5268.
Kik, M.J.; Huisman J.; Van Der Poel A.F.; Mouwen J.M., 1990. Pathologic changes of the small intestinal mucosa of pigs after feeding phaseolus vulgaris beans. Veterinary Pathology 27(5) 329-334. https://doi.org/10.1177/030098589002700504
Klein, R.; Kincaid, R.; Hodgson, A.; Harrison, J.; Hillers, J.; Cronrath, J., 1987. Dietary fiber and early weaning on growth and rumen development of calves. Journal of Dairy Science 70, 2095-2104.
Lane, M.; Jesse, B.W., 1997. Effect of volatile fatty acid infusion on development of the rumen epithelium in neonatal sheep. Journal of Dairy Science 80, 740-746.
Lesmeister, K.; Heinrichs, A.J., 2005. Effects of adding extra molasses to a texturized calf starter on rumen development, growth characteristics, and blood parameters in neonatal dairy calves. Journal of Dairy Science 88, 411-418.
Lu, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y.M., 2008. Effects of sodium butyrate on the growth performance, intestinal microflora and morphology of weanling pigs. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences 17, 568-578.
Malau-Aduli, A.E.O.; Balogun, R.O.; Otto, J.R.; Verma, S.; Wehella, M.; Jones, D., 2020. Novel encapsulated calcium butyrate supplement enhances on-farm dairy calf growth performance and body conformation in a pasture-based dairy production system. Animals 10, 1380.
Mentschel, J.; Leiser, R.; Mülling, C.; Pfarrer, C.; Claus, R.J., 2001. Butyric acid stimulates rumen mucosa development in the calf mainly by a reduction of apoptosis. Archives of animal nutrition 55, 85-102.
Moreira, T.S.; Marques, K.O.; Guimarães, K.C.; Marchesin, W.A.; Bilego, U.O.; Freitas, N.F., 2016. Duodenal histology and carcass quality of feedlot cattle supplemented with calcium butyrate and Bacillus subtilis. Animal sciences 38, 61-7
Nazari, M.; Karkoodi, K.; Alizadeh, A., 2012. Performance and physiological responses of milk-fed calves to coated calcium butyrate supplementation. South African Journal of Animal Science 42, 296-303.
Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B., 2017. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Reviews in aquaculture 9, 342-368.
Pender, S.L.; Quinn, J.J.; Sanderson, I.R.; MacDonald, T.T., 2000. Butyrate upregulates stromelysin-1 production by intestinal mesenchymal cells. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 279, G918-G924.
Pereira, G.R.; Barcellos, J.O.J.; Sessim, A.G.; Tarouco, J.U.; Feijó, F.D.; Braccini Neto, J.; Prates, Ê.R.; Canozzi, M.E.A., 2017. Relationship of post-weaning growth and age at puberty in crossbred beef heifers. Brazilian Journal of Animal Science 46, 413-420.
Pineda-Quiroga, C.; Atxaerandio, R.; Ruiz, R.; García-Rodríguez, A., 2017. Effects of dry whey powder alone or combined with calcium butyrate on productive performance, duodenal morphometry, nutrient digestibility, and ceca bacteria counts of broiler chickens. Livestock science 206, 65-70.
Prvulović, D.; Kosarcic, S.; Popovic, M.; Dimitrijevic, D.; Grubor-Lajsic, G., 2012. The influence of hydrated aluminosilicate on biochemical and haematological blood parameters, growth performance and carcass traits of pigs. Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances 11, 134-140.
Quigley III, J.; Smith, Z.; Heitmann, R., 1991. Changes in plasma volatile fatty acids in response to weaning and feed intake in young calves. Journal of Dairy Science74, 258-263.
Rabbani, G.; Albert, M.J.; Rahman, A.H.; Isalm, M.M.; Islam, K.N.; Alam, K., 1999. Short-chain fatty acids improve clinical, pathologic, and microbiologic features of experimental shigellosis. Journal of Infectious Diseases 179, 390-397.
Radojičić, B.; Joksimović-Todorović, M.; Bukvić, M.; Simeunović, P.; Kakishev, M.; Pračić, N., 2016. The influence of sodium propionate on blood glucose, insulin and cortisol concentrations in calves of different ages. Acta Veterinaria Brno 85, 127-132.
Rehman, A.; Jingdong, L.; Chandio, A.A.; Hussain, I., 2017. Livestock production and population census in Pakistan: determining their relationship with agricultural GDP using econometric analysis. Information processing in agriculture 4, 168-177.
Sakata, T.; Tamate, H.J., 1978. Rumen epithelial cell proliferation accelerated by rapid increase in intraruminal butyrate. Journal of Dairy Science 61, 1109-1113.
Seifdavati, J.; Seifzadeh, S.; Ramezani, M., 2020. Effects of microencapsulated sodium butyrate on performance, blood metabolites and nutrient digestibility of suckling Holstein calves. Journal of Animal Science Research 30, 73-83.
Serbester, U.; Çakmakçi, C.; Göncü, S.; Görgülü, M., 2014. Effect of feeding starter containing butyrate salt on pre-and post-weaning performance of early or normally weaned calves. Revue de medecine veterinaire 165, 44-48.
Ślusarczyk, K.; Strzetelski, J.; Furgał-Dierżuk, I., 2010. The effect of sodium butyrate on calf growth and serum level of β-hydroxybutyric acid. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences 19, 348-357.
Upadhaya, S.D.; Jiao, Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, I.H., 2020. Coated sodium butyrate supplementation to a reduced nutrient diet enhanced the performance and positively impacted villus height and faecal and digesta bacterial composition in weaner pigs. Animal feed science and technology265, 114534.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors participated in this study. The idea was conceived, and research was supervised by Abdur Rahman, Zafar Hayat, Syed Ehtisham ul Haque, and Saima. Material preparation, trial execution, and data collection were performed by Muhammad Furhan Arshad, Abdur Rahman, and Zeeshan Anwar. Data was analyzed by Shah Nawaz, Akhtar Rasool Asif, and Abdur Rahman. The first draft was written by Muhammad Furhan Arshad, Shah Nawaz, and Muawuz Ijaz. All authors read the final draft of the manuscript and approved it.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Jhang (protocol code 12057 on 03–02-2021). Consent to participate is not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, A., Arshad, M.F., Nawaz, S. et al. Impact of graded levels of coated calcium butyrate on growth performance and serological indices during pre-weaning stage in Holstein calves. Trop Anim Health Prod 55, 348 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-023-03768-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-023-03768-0