Abstract
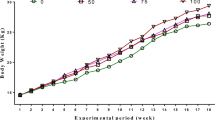
A feeding trial of 10 weeks duration was undertaken on laying hens (n = 240) to evaluate feeding value of rice distiller’s dried grains with soluble (rDDGS) with or without enzyme supplementation (α-amylase, β-glucanase, xylanase, carboxymethylcellulase, pectinase, proteinase, α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, lipase, and phytase), following 4 × 2 factorial design, on egg production, nutrient utilization, and cost economics of egg production. The birds were randomly assigned to eight dietary treatments with 30 birds/treatment. The birds were housed individually in layer cages and each bird was taken as an experimental unit. Eight experimental diets were prepared by incorporating four levels (0, 50, 75, and 100 g/kg) of rDDGS with and without enzyme supplementation. The results revealed a significant (P < 0.01) increase of egg mass, feed intake, egg production, and body weight gain in dietary treatments with up to 75 g rDDGS though the values were statistically similar to the hens fed 100 g rDDGS. Enzyme supplementation resulted in significant (P < 0.01) improvement of egg mass, egg production, feed conversion ratio (FCR) per dozen eggs, FCR per kilogramme egg mass, and net FCR. The significantly (P < 0.01) higher yolk index was observed at 100 g rDDGS level, while shell thickness improved significantly (P < 0.01) up to 75 g rDDGS level. No significant effect of rDDGS inclusion was observed on shape index, albumin index, and Haugh unit. Enzyme supplementation significantly improved the shell thickness and yolk colour of eggs. Nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorus retention and dry matter metabolizability did not show any significant treatment effects. There was significant (P < 0.01) reduction in feed-cost per kilogramme egg mass or per dozen eggs with the increased DDGS levels and dietary enzyme supplementation. It was concluded that rDDGS can be used up to 100 g/kg diet of laying hens along with enzyme supplementation for better productivity of layer hens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Hack, M.E. and Mahgoub, S., 2015. Mitigating harmful emissions from laying hens manure and enhancing productive performance through feeding of DDGS with or without Bacillus spp. In Proceedings of the International Conference Industrial waste and Wastewater Treatment and Valorization, May 21-23, 2015, President Hotel, Athens, Greece.
Bolu, S.A., Alli, O.I. and Esuola, P.O., 2012. Response of broilers to graded levels of distillers dried grain. Sustainable Agricultural Research, 1(1), 147-150.
Buchanan, N.P., Kimbler, L.B. and Parsons, A.S., 2007. The effects of non-starch polysaccharide enzyme addition and dietary energy restriction on performance and carcass quality of organic broiler chickens. Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 16, 1-12.
Cheon, Y.J., Lee, H.L., Shin, M.H., Jang, A. and Lee, S.K., 2008. Effects of corn distiller’s dried grains with solubles on production and egg quality in laying hens. Asian-Australian Journal of Animal Science, 21, 1318-1323.
Costa, F.G.P., Goulart, C.C., Figueiredo, D.F., Oliveira, C.F.S. and Silva, J.H.V., 2008 Economic and environmental impact of using exogenous enzymes on poultry feeding. International Journal of Poultry Science, 7(4), 311-314.
Deniz, G., Gencoglu, H., Gezen, S.S., Turkmen, I.I., Orman, A. and Kara, C., 2013. Effects of feeding corn distiller's dried grains with solubles with and without enzyme cocktail supplementation to laying hens on performance, egg quality, selected manure parameters, and feed cost. Livestock Science, 152(2), 174-181.
F.A.O., 2003. Poultry nutrition and feeds. Animal Production and Health Division, FAO, Rome, Italy. http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/themes/en/poultry/AP_nutrition.html.
Ghazalah, A.A., Abd-Elsamee, M.O. and AL-Arami, A.A., 2011. Use of distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) as replacement for yellow corn in laying hen diets. Egyptian Poultry Science, 31, 191-202.
Govt. of India, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, 2016. Area, production and yield of principal crops. In: Agricultural Statistics at a glance 2016. Govt. of India Controller of Publication, pp 87-88.
Hill, F.W. and Anderson, D.L., 1958. Comparison of metabolizable energy and productive energy determination with the chicks. Journal of Nutrition, 64, 587-603.
Jung, B. and Batal, A., 2009. The nutrient digestibility of high-protein corn distillers dried grains and the effect of feeding various levels on the performance of laying hens. Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 18, 741-751.
Lilburn, M.S. and Jensen, L.S., 1984. Evaluation of corn fermentation solubles as a feed ingredient for laying hens. Poultry Science, 63, 542-547.
Lumpkins, B., Batal, A. and Dale, N., 2005. Use of distillers dried grains plus solubles in laying hen diets. Journal of Applied Poultry Science, 14, 25-31.
Mandal, A.B., 2014. Alternate poultry feed resources for sustainable poultry meat and egg production. In XXXI Annual conference of Indian poultry science association and national symposium on “Poultry production for global trade” Namakkal p. 37-45.
Masadeh, M.K., Scheideler, S.E. and Hanford, K.J., 2011. Dried distillers grains with soluble in laying hen diets. Poultry Science, 90, 1960-1966.
Masadeh, M.K., Purdum, S.E. and Hanford, K.J., 2012. Distillers dried grains with solubles in pullet diets. Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 21(3), 531-539.
Noll, S.E., Parsons, C.M. and Doxier, III, W.A.. 2007. Formulating poultry diets with DDGS-How far can we go? In ‘Proceedings 5th Mid Atlantic Nutrition Conference’. (Ed. Zimmerman NG) pp. 91-99. University of Maryland, College Park, USA.
Olofintoye, O.R. and Bolu, S.A., 2013. Effects of corn distillers dried grains on the performance and egg quality of laying hen. Animal Research International, 10, 1665-1672.
Pescatore, A.J., Rossi, P., Cantor, A.H., Pierce, J.L., Ao, T., Macalintal, L.M., Ford, M.J., King, W.D. and Gillespie, H.D., 2011. The use of distillers dried grains with solubles in post peak diets for laying hens. Poultry Science, 90(1) (Abstract).
Pineda, L., Roberts, S., Kerr, B., Kwakkel, R., Verstegen, M. and Bregendahl, K., 2008. Maximum dietary content of corn dried distiller’s grains with solubles in diets for laying hens: Effects on nitrogen balance, manure excretion, egg production and egg quality. Animal Industry Report: A.S. Leaflet R2334. Iowa State University Digital press.https://doi.org/10.31274/ans_air-180814-121
Roberson, K.D., Kalbfleisch, J.L., Pan, W. and Charbeneau, R.A., 2005. Effect of corn distiller’s dried grains with solubles at various levels on performance of laying hens and egg yolk colour. International Journal of Poultry Science, 4(2), 44-51.
Romero, C., Abdallh, M.E., Powers, W., Angel, R. and Applegate, T.J., 2012. Effect of dietary adipic acid and corn dried distillers grains with solubles on laying hen performance and nitrogen loss from stored excreta with or without sodium bisulfate. Poultry Science, 91, 1149-1157.
Sastry, V.R.B., Kamra, D.N. and Pathak, N.N., 1999. Laboratory Manual of Animal Nutrition. CAS in Animal Nutrition, IVRI, Izatnagar.
Saunders, J.A. and Rosentrater, K.A., 2009. Survey of US fuel ethanol plants. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3277-3284.
Shalash, S.M.M., Ali, M.N., Sayed El-Gabry, H.E. and Shabaan, M., 2009. Novel method for improving the utilization of corn dried distillers grains with solubles in broiler diets. International Journal of Poultry Science, 8, 545-552.
Shurson, J.C., Santos, C., Aguirre, J. and Hernandez, S., 2003. Effects of feeding Babcock B300 laying hens conventional Sanfandila layer diets compared to diets containing 10% Norgold DDGS on performance and egg Quality. A commercial field trial sponsored by the Minnesota Corn Research and Promotion Council and the Minnesota Department of Agriculture.
Sun, H., Lee, E.J., Samaraweera, H., Persia, M. and Dong, U.A., 2013. Effects of increasing concentrations of corn distillers dried grains with solubles on chemical composition and nutrient content of egg. Poultry Science, 92, 233-242.
Swiatkiewicz, S. and Koreleski, J., 2006. Effect of maize distillers dried grains with soluble and dietary enzyme supplementation on the performance of laying hens. Journal of Animal and Feed Science, 5, 252-260.
Swiatkiewicz, S. and Koreleski, J., 2008. The use of distillers dried grains with soluble (DDGS) in poultry nutrition. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 64, 257-265.
Acknowledgements
The authors are sincerely thankful to the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India, for providing DST-INSPIRE fellowship to the first author for her Ph.D. research. The research did not receive any specific funding from any agency.
Funding
This work did not receive financial support from any agency
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The experimental procedures on the birds were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. The approval number of the research work, provided by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) of Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar, is (341/05/ab18/CPCSEA).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S.L., Tyagi, P.K., Mir, N.A. et al. Feeding value of rice distiller’s dried grains with solubles as protein supplement in diet of laying hens. Trop Anim Health Prod 52, 1229–1237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02122-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02122-7