Abstract
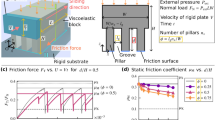
Numerous studies have proved the usefulness of surface patterning for the modification of tribological performances of sliding contacts. Here, we investigate the effects of patterning on the tribological properties of a slider over a solid substrate. We show that, depending on the numerical density of surface grooves, the tribological properties can change significantly. A low density of surface patterning leads to a decrease of static friction force, while a higher density weakens this effect. Contrary to static friction, kinetic friction shows a much weaker dependence on surface patterning. The decrease is related to a non-uniform distribution of surface stress induced by patterning. We believe these findings and approach to be relevant for technological applications and related optimal design.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etsion, I.: Improving tribological performance of mechanical components by laser surface texturing. Tribol. Lett. 17, 733 (2004)
Raeymaekers, B., Etsion, I., Talke, F.E.: Enhancing tribological performance of the magnetic tape/guide interface by laser surface texturing. Tribol. Lett. 27, 89 (2007)
Prodanov, N., Gachot, C., Rosenkranz, A., Mücklich, F., Müser, M.H.: Contact mechanics of laser-textured surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 50, 41–48 (2013)
Gachot, C., Rosenkranz, A., Reinert, L., Ramos-Moore, E., Souza, N., Müser, M.H., Mücklich, F.: Dry friction between laser-patterned surfaces: role of alignment, structural wavelength and surface chemistry. Tribol. Lett. 49, 193–202 (2013)
Pettersson, U., Jacobson, S.: Friction and wear properties of micro textured DLC coated surfaces in boundary lubricated sliding. Tribol. Lett. 17, 553 (2004)
Blatter, A., Maillat, M., Pimenov, S.M., Shafeev, G.A., Simakin, A.V.: Lubricated friction of laser micro-patterned sapphire flats. Tribol. Lett. 4, 237 (1998)
Mourier, L., Mazuyer, D., Lubrecht, A.A., Donnet, C.: Transient increase of film thickness in micro-textured EHL contacts. Tribol. Int. 39, 1745 (2006)
Persson, B.N.J.: On the mechanism of adhesion in biological systems. J. Chem. Phys. 118(16), 7614 (2003)
Persson, B.N.J., Albohr, O., Tartaglino, U., Volokitin, A.I., Tosatti, E.: On the nature of surface roughness with application to contact mechanics, sealing, rubber friction and adhesion. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 17, R1 (2005)
Scherge, M., Gorb, S.N.: Biological Micro- and Nanotribology: Nature’s Solutions. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Murarash, B., Itovich, Y., Varenberg, M.: Tuning elastomer friction by hexagonal surface patterning. Soft Matter 7, 5553 (2011)
Federle, W., Barnes, W.J.P., Baumgartner, W., Drechsler, P., Smith, J.M.: Wet but not slippery: boundary friction in tree frog adhesive toe pads. J. R. Soc. Interface 3, 689 (2006)
Borghi, A., Gualtieri, E., Marchetto, D., Moretti, L., Valeri, S.: Tribological effects of surface texturing on nitriding steel for high-performance engine applications. Wear 265, 1046 (2008)
Gualtieri, E., Pugno, N., Rota, A., Spagni, A., Lepore, E., Valeri, S.: Role of roughness parameters on the tribology of randomly nano-textured silicon surface. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 9244 (2011)
Pugno, N.: Nanotribology of Spiderman. In: Bellucci, S. (ed.) Physical Properties of Ceramic and Carbon Nanoscale Structures, pp. 111–136. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Gualtieri, E., Borghi, A., Calabri, L., Pugno, N., Valeri, S.: Increasing nanohardness and reducing friction of nitride steel by laser surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 42, 699 (2009)
Capozza, R., Fasolino, A., Ferrario, M., Vanossi, A.: Lubricated friction on nanopatterned surfaces via molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. B 77, 235432 (2008)
Braun, O.M., Barel, I., Urbakh, M.: Dynamics of transition from static to kinetic friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 194301 (2009)
Capozza, R., Rubinstein, S.M., Barel, I., Urbakh, M., Fineberg, J.: Stabilizing stick-slip friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 024301 (2011)
Capozza, R., Barel, I., Urbakh, M: Probing and tuning frictional aging at the nanoscale. Sci. Rep. 3, 1896 (2013)
Berthoud, P., Baumberger, T.: Shear stiffness of a solid–solid multicontact interface. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454, 1615 (1998)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Theory of Elasticity, Course of Theoretical Physics, vol. 7. Pergamon, New York (1986)
Greiner, C., Schafer, M., Pop, U., Gumbsch, P.: Contact splitting and the effect of dimple depth on static friction of textured surfaces. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 7986 (2014)
Capozza, R., Urbakh, M.: Static friction and the dynamics of interfacial rupture. Phys. Rev. B 86, 085430 (2012)
Acknowledgments
RC is supported by Sinergia Contract CRSII2136287/1, and by ERC Advanced Grant 320796—MODPHYSFRICT. This work is also supported by the COST Action MP1303. “Understanding and Controlling Nano and Mesoscale Friction”. NMP is supported by the European Research Council (ERC StG Ideas 2011 BIHSNAM n. 279985 on “Bio-Inspired hierarchical super-nanomaterials”, ERC PoC 2013-1 REPLICA2 n. 619448 on “Large-area replication of biological anti-adhesive nanosurfaces”, ERC PoC 2013-2 KNOTOUGH n. 632277 on “Super-tough knotted fibres”), by the European Commission under the Graphene Flagship (WP10 “Nanocomposites”, n. 604391) and by the Provincia Autonoma di Trento (“Graphene Nanocomposites”, n. S116/2012-242637 and reg.delib. n. 2266.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capozza, R., Pugno, N. Effect of Surface Grooves on the Static Friction of an Elastic Slider. Tribol Lett 58, 35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0510-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0510-9