Abstract
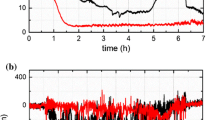
Reciprocating sliding wear experiments were conducted on cold-sprayed pure aluminum and Al–22.6 wt% Al2O3 coatings using a custom-built in situ tribometer. Using a transparent sapphire counterface for the wear tests, the dynamic behavior of third body material in the contact was optically observed. The presence of Al2O3 particles led to greater stability of the transfer films adhering to the sapphire counterface, as well as greater stability of the friction coefficient and lower wear rates. Ex situ microanalysis of material in the wear tracks and transfer films suggests that the presence of Al2O3 particles promoted strain localization during sliding. This produced more uniform third body microstructures and protected the underlying aluminum matrix from deformation, which slowed the rate of transfer to the counterface.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, J.R. (ed.): Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys, chapter Corrosion Behavior, pp 579–622. ASM Specialty Handbook. ASM International (1993)
Clyne, T.W., Withers, P.J.: An Introduction to Metal Matrix Composites, Chapter 9: Fabrication Processes, pp. 318–360. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993)
Deuis, R.L., Subramanian, C., Yellup, J.M.: Dry sliding wear of aluminium composites: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 57, 415–435 (1997)
Venkataraman, B., Sundararajan, G.: The sliding wear behaviour of Al-SiC particulate composites: I. Macrobehaviour. Acta Mater. 44(2), 451–460 (1996)
Alpas, A.T., Zhang, J.: Effect of microstructure (particulate size and volume fraction) and counterface material on the sliding wear resistance of particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 25A, 969–983 (1994)
Irissou, E., Legoux, J.-G., Arsenault, B., Moreau, C.: Investigation of Al-Al2O3 cold spray coating formation and properties. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 16(5–6), 661–668 (2007)
Evans, A., San Marchi, C., Mortensen, A.: Metal Matrix Composites, pp. 9–38. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2003)
Spencer, K., Fabijanic, D.M., Zhang, M.-X.: The use of Al-Al2O3 cold spray coatings to improve the surface properties of magnesium alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 204, 336–344 (2009)
Tao, Y., Xiong, T., Sun, C., Jin, H., Hao, D., Li, T.: Effect of Al-Al2O3 on the properties of cold sprayed Al-Al2O3 composite coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(1), 261–266 (2009)
U.S. Department Of Defense Manufacturing Process Standard MIL-STD-3021, “Materials Deposition, Cold Spray,” 2008
Assadi, H., Gärtner, F., Stoltenhoff, T., Kreye, H.: Bonding mechanism in cold gas spraying. Acta Mater. 51, 4379–4394 (2003)
Gärtner, F., Stoltenhoff, T., Schmidt, T., Kreye, H.: The cold spray process and its potential for industrial applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 15(2), 223–232 (2006)
Irissou, E., Legoux, J.-G., Ryabinin, A., Jodoin, B., Moreau, C.: Review on cold spray process and technology: part I-intellectual property. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 17(4), 495–516 (2008)
Champagne, V.K.: The Cold Spray Materials Deposition Process: Fundamentals and Applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge (2007)
Papyrin, A., Kosarev, V., Klinkov, K.V., Alkhimov, A., Fomin, V.M.: Cold Spray Technology. Elsevier, Oxford (2006)
Champagne, V.K.: The repair of magnesium rotorcraft components by cold spray. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 8, 164–175 (2008)
Kim, H.J., Windl, W., Rigney, D.A.: Structure and chemical analysis of aluminium wear debris: experiments and ab initio simulations. Acta Mater. 55, 6489–6498 (2007)
Blau, P.J.: Mechanisms for transitional friction and wear behavior of sliding metals. Wear 72, 55–66 (1981)
Cocks, M.: Interaction of sliding metal surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 33(7), 2152–2161 (1962)
Antler, M.: Processes of metal transfer and wear. Wear 7, 181–203 (1964)
Prasad, S.V., Michael, J.R., Majumdar, B.S., Battaile, C.C.: On the evolution of friction- induced microstructures in single crystal nickel. Microsc. Microanal. 14(Suppl 2), 906–907 (2008)
Venkataraman, B., Sundararajan, G.: The sliding wear behaviour of Al-SiC particulate composites: II. The characterization of subsurface deformation and correlation with wear behaviour. Acta Mater. 44(2), 451–460 (1996)
Shockley, J.M., Strauss, H.W., Chromik, R.R., Brodusch, N., Gauvin, R., Irissou, E., Legoux, J.-G.: In situ tribometry of cold-sprayed Al-Al2O3 composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 215, 350–356 (2013)
Berthier, Y.: Wear: Materials, Mechanisms and Practice, Chapter 7: Third-Body Reality: Consequences and Use of the Third-Body Concept to Solve Friction and Wear Problems, pp. 291–316. Wiley, New York (2005)
Biswas, S.K.: Wear: Materials, Mechanisms and Practice, Chapter 3: Wear of Metals: A Material Approach, pp. 21–36. Wiley, New York (2005)
Godet, Maurice: The third-body approach: a mechanical view of wear. Wear 100, 437–452 (1984)
Godet, M.: Third-bodies in tribology. Wear 136(1), 29–45 (1990)
Descartes, S., Berthier, Y.: Rheology and flows of solid third bodies: background and application to an MoS1:6 coating. Wear 253, 546–556 (2002)
Chromik, R.R., Baker, C.C., Voevodin, A.A., Wahl, K.J.: In situ tribometry of solid lubricant nanocomposite coatings. Wear 262(9), 1239–1252 (2007)
Strauss, H.W., Chromik, R.R., Hassani, S., Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E.: In situ tribology of nanocomposite Ti-Si-C-H coatings prepared by PE-CVD. Wear 272(1), 133–148 (2011)
Stoyanov, P., Strauss, H.W., Chromik, R.R.: Scaling effects between micro- and macro-tribology for a Ti-MoS2 coating. Wear 274–275, 149–161 (2012)
Singer, I.L., Dvorak, S.D., Wahl, K.J., Scharf, T.W.: Role of third bodies in friction and wear of protective coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 21(5), S232–S240 (2003)
Chromik, R.R., Strauss, H.W., Scharf, T.W.: Materials phenomena revealed by in situ tribometry. JOM 64(1), 35–43 (2012)
Oliver, W.C., Pharr, G.M.: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sending indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564–1586 (1992)
Rigney, D.A.: Transfer, mixing, and associated chemical and mechanical processes during the sliding of ductile materials. Wear 245(1), 1–9 (2000)
Berthier, Y., Godet, M., Brendle, M.: Velocity accommodation in friction. Tribol. Trans. 32, 490–496 (1989)
Wang, Y., Rainforth, W.M., Jones, H., Lieblich, M.: Dry wear behaviour and its relation to microstructure of novel 6092 aluminium alloy-Ni3Al powder metallurgy composite. Wear 251, 1421–1432 (2001)
Rigney, D.A., Chen, L.H., Naylor, M.G.S., Rosenfield, A.R.: Wear processes in sliding systems. Wear 100, 195–219 (1984)
Wahl, K.J., Chromik, R.R., Lee, G.Y.: Quantitative in situ measurement of transfer film thickness by a Newton‘s rings method. Wear 264, 731 (2008)
Kim, H.-J., Emge, A., Karthikeyan, S., Rigney, D.A.: Effects of tribooxidation on sliding behavior of aluminum. Wear 259, 501–505 (2005)
Rainforth, W.M.: Microstructural evolution at the worn surface: a comparison of metals and ceramics. Wear 245, 162–177 (2000)
Li, J., Elmadagli, M., Gertsman, V.Y., Alpas, A.T.: FIB and TEM characterization of subsurfaces of an Al–Si alloy (A390) subjected to sliding wear. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 421, 317–327 (2006)
Venkataraman, B., Sundararajan, G.: Correlation between the characteristics of the mechanically mixed layer and wear behaviour of aluminium, Al-7075 alloy and Al-MMCs. Wear 245, 22–38 (2000)
Farhat, Z.N., Ding, Y., Northwood, D.O., Alpas, A.T.: Effect of grain size on friction and wear of nanocrystalline aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 206, 302–313 (1996)
Barnoush, A., Welsch, M.T., Vehoff, H.: Correlation between dislocation density and pop-in phenomena in aluminum studied by nanoindentation and electron channeling contrast imaging. Scripta Mater. 63, 465–468 (2010)
Buckley, D.H.: Ceramic microstructure and adhesion. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A3(3), 762 (1985)
Pepper, S.V.: Shear strength of metal-sapphire contacts. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 801 (1976)
Johnson, K.H., Pepper, S.V.: Molecular-orbital model for metal-sapphire interfacial strength. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 6634 (1982)
Siegel, D.J., Hector Jr, L.G., Adams, J.B.: Adhesion, atomic structure, and bonding at the Al(111)/α-Al2O3(0001) interface: a first principles study. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter. Mater. Phys. 65(8), 854151–8541519 (2002)
Valiev, R.Z., Islamgaliev, R.K., Alexandrov, I.V.: Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog. Mater Sci. 45, 103–189 (2000)
Apps, P.J., Bowen, J.R., Prangnell, P.B.: The effect of coarse second-phase particles on the rate of grain refinement during severe deformation processing. Acta Mater. 51, 2811–2822 (2003)
Mahato, A., Verma, N., Jayaram, V., Biswas, S.K.: Severe wear of a near eutectic aluminium-silicon alloy. Acta Mater. 59, 6069–6082 (2011)
Descartes, S., Desrayaud, C., Rauch, E.F.: Inhomogeneous microstructural evolution of pure iron during high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 3666–3675 (2011)
Gutierrez-Urrutia, I., Munoz-Morris, M.A., Morris, D.G.: Contribution of microstructural parameters to strengthening in an ultrafine-grained Al-7% Si alloy processed by severe deformation. Acta Mater. 55, 1319–1330 (2007)
Gutierrez-Urrutia, I., Munoz-Morris, M.A., Puertas, I., Luis, C., Morris, D.G.: Influence of processing temperature and die angle on the grain microstructure produced by severe deformation of an Al-7% Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 475, 268–278 (2008)
Fleck, N.A., Muller, G.M., Hutchison, J.W.: Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. Acta Metall. Mater. 42, 475–487 (1994)
Perrin, C., Rainforth, W.M.: The effect of alumina fibre reinforcement on the wear of an Al–4.3% Cu alloy. Wear 181–183, 312–324 (1995)
Sannino, A.P., Rack, H.J.: Dry sliding wear of discontinuously reinforced aluminum composites: review and discussion. Wear 189, 1–19 (1995)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Canadian Foundation for Innovation (CFI) project No. 8246 for the cold-spray equipment, the CFI Leader’s Opportunity Fund project No. 13029 for the in situ tribometer and nanoindentation equipment, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) Discovery Grants Program for the operational funding of this project. JMS acknowledges partial financial support from the McGill Engineering Doctoral Award (MEDA) program. Thanks are also due to the CLYM (Center Lyonnais de Microscopie, http://clym.insa-lyon.fr) for the access to the FIB/SEM (Zeiss NVision 40) and to N. Blanchard, A. Descamps-Mandine, Th. Douillard, and B. Van De Moortèle for the technical help. CLYM is supported by CNRS, le Grand Lyon, and le Conseil Régional Rhône-Alpes (France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shockley, J.M., Descartes, S., Irissou, E. et al. Third Body Behavior During Dry Sliding of Cold-Sprayed Al-Al2O3 Composites: In Situ Tribometry and Microanalysis. Tribol Lett 54, 191–206 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0326-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0326-z