Abstract
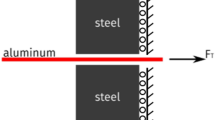
Tribofilms formed during dry sliding usually exhibit a nanocrystalline structure and complicated composition. In the present study, tribofilms consisting mainly of a solid lubricant, namely graphite nanoparticles, are considered. Systems providing such tribofilms are candidates for anti-friction applications. Since sliding action always leads to mixing of the materials at both sides of the tribological interface, it was of major interest to study the impact of different amounts of a hard constituent, SiC in the considered case, within the soft matrix systematically. Furthermore, the impact of normal pressure was considered. A mechanically mixed layer was observed for the whole range of normal pressures and SiC volume fractions. The calculated coefficient of friction decreased significantly with increasing thickness of this layer but was only marginally affected by SiC volume fraction, which is good news for anti-friction applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Jacobson, S., Hogmark, S.: Tribofilms—on the crucial importance of tribologically induced surface modifications. In: Nikas, G.K. (ed.) Recent Developments in Wear Protection, Friction and Lubrication, pp. 197–225. Research Signpost, Kerala, India (2010)
Österle, W., Dmitriev, A.I., Kloß, H.: Possible impacts of third body nanostructure on friction performance during dry sliding determined by computer simulation based on the method of movable cellular automata. Tribol. Int. 48, 128–136 (2012)
Dmitriev, A.I., Smolin, A.Y., Psakhie, S.G., Österle, W., Kloß, H., Popov, V.L.: Computer modeling of local tribological contacts by the example of the automotive brake friction pair. Phys. Mesomech. 11, 73–84 (2008)
Österle, W., Prietzel, C., Kloß, H., Dmitriev, A.I.: On the role of copper in brake friction materials. Tribol. Int. 43, 2317–2326 (2010)
Österle, W., Dmitriev, A.I., Orts-Gil, G., Schneider, T., Ren, H., Sun, X.: Verification of nanometre-scale modelling of tribofilm sliding behaviour. Tribol. Int. 62, 155–162 (2013)
Dmitriev, A.I., Österle, W.: Modelling the sliding behaviour of tribofilms forming during automotive braking: impact of loading parameters and property range of constituents. Tribol. Lett. (2013). doi:10.1007/s11249-013-0274-z
Österle, W., Dmitriev, A.I., Kloß, H.: Does ultra-mild wear play any role in dry friction applications, such as automotive braking? Faraday Discuss. 156, 159–171 (2012)
Milman, Y.V., Gridneva, I.V., Golubenko, A.A.: Construction of stress-strain curves for brittle materials by indentation in a wide temperature range. Sci. Sinter. 39, 67–75 (2007)
Österle, W., Orts-Gil, G., Gross, T., Deutsch, C., Hinrichs, R., Vasconcellos, M.A.Z., Zoz, H., Yigit, D., Sun, X.: Impact of high energy ball milling on the nanostructure of magnetite-graphite and magnetite–graphite–molybdenum disulphide blends. Mater. Char. 36, 28–38 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), Contract No. OS77/19-1 and supported by the Russian Academy of Science (SB RAS), Program No. III.23.2.4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Österle, W., Dmitriev, A.I. & Kloß, H. Assessment of Sliding Friction of a Nanostructured Solid Lubricant Film by Numerical Simulation with the Method of Movable Cellular Automata (MCA). Tribol Lett 54, 257–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-013-0287-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-013-0287-7