Abstract
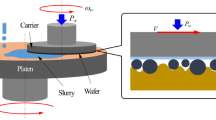
The material removal in chemical–mechanical planarization/polishing (CMP) of copper involves both chemical and mechanical effects. The roles of chemical corrosion, abrasive wear, and their synergistic effects on the material removal mechanism were studied by electrochemical analysis and nano-scratching method using atom force microscopy, respectively. Combining with the results of CMP experiments, dominant factors (chemistry and mechanics) in slurries within the range of pH 3.0–10.0 were assessed. Consequently, a removal mechanism map of copper CMP depending on pH values was constructed. In the alkaline slurry, the wear–corrosion effect predominated in the material removal at pH 8.0 and 9.0; while the copper removal mechanism changed to corrosion–wear action in the acidic slurry from pH 4.0 to 6.0, and good surface quality was also obtained. The results and the strategies provide thorough understanding of the material removal mechanism and further optimization of the CMP process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdyyeva, T.K., Emery, S.B., Sokolov, I.Y.: In situ AFM study of surface layer removal during copper CMP. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 6, G91–G94 (2003)
Zantye, P.B., Kumar, A., Sikder, A.K.: Chemical mechanical planarization for microelectronics applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 45, 89–220 (2004)
Nanz, G., Camilletti, L.E.: Modeling of chemical-mechanical polishing—a review. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 8, 382–389 (1995)
Singh, R.K., Bajaj, R.: Advances in chemical-mechanical planarization. MRS Bull. 27, 743–751 (2002)
Krishnan, M., Nalaskowski, J.W.: Chemical mechanical planarization: slurry chemistry, materials, and mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 110, 178–204 (2010)
Preston, F.W.: The theory and design of plate glass polishing machines. J. Soc. Glass Technol. 11, 214–256 (1927)
Paul, E., Kaufman, F., Brusic, V., Zhang, J., Sun, F., Vacassy, R.: A model of copper CMP. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, G322–G328 (2005)
Cook, L.M.: Chemical processes in glass polishing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 120, 152–171 (1990)
Kaufman, F.B., Thompson, D.B., Broadie, R.E., Jaso, M.A., Guthrie, W.L., Pearson, D.J., Small, M.B.: Chemical-mechanical polishing for fabricating patterned W metal features as chip interconnects. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 3460–3465 (1991)
Zhao, Y.W., Chang, L., Kim, S.H.: A mathematical model for chemical- mechanical polishing based on formation and removal of weakly bonded molecular species. Wear 254, 332–339 (2003)
Luo, J.F., Dornfeld, D.A.: Material removal mechanism in chemical mechanical polishing: theory and modeling. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 14, 112–133 (2001)
Fu, G.H., Chandra, A., Guha, S., Subhash, G.: A plasticity-based model of material removal in chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP). IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 14, 406–417 (2001)
Qin, K., Moudgil, B., Park, C.W.: A chemical mechanical polishing model incorporating both the chemical and mechanical effects. Thin Solid Films 446, 277–286 (2004)
Choi, S., Tripathi, S., Doyle, F.M., Dornfeld, D.A.: Integrated tribo-chemical modeling of copper CMP. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1157, E02–E03 (2009)
Choi, S., Tripathi, S., Dornfeld, D.A., Doyle, F.M.: Copper CMP modeling: millisecond scale adsorption kinetics of BTA in glycine-containing solutions at pH 4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, H1153–H1159 (2010)
Du, T., Tamboli, D., Desai, V., Seal, S.: Mechanism of copper removal during CMP in acidic H2O2 slurry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, G230–G235 (2004)
Singh, R.K., Lee, S.M., Choi, K.S., Basim, G.B., Choi, W.S., Chen, Z., Moudgil, B.M.: Fundamentals of slurry design for CMP of metal and dielectric materials. MRS Bull. 27, 752–760 (2002)
Lin, J.F., Chern, J.D., Chang, Y.H., Kuo, P.L., Tsai, M.S.: Analysis of the tribological mechanisms arising in the chemical mechanical polishing of copper-film wafers. J. Tribol.-Trans. ASME 126, 185–199 (2004)
Che, W., Bastawros, A., Abhijit, C.: Synergy between chemical dissolution and mechanical abrasion during chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 867, 275–280 (2005)
Ziomek-Moroz, M., Miller, A., Hawk, J., Cadien, K., Li, D.Y.: An overview of corrosion–wear interaction for planarizing metallic thin films. Wear 255, 869–874 (2003)
Watson, S.W., Friedersdorf, F.J., Madsen, B.W., Cramer, S.D.: Methods of measuring wear corrosion synergism. Wear 181, 476–484 (1995)
Choi, W.: Study of interfacial interaction during chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) of dielectric silicon dioxide. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville (2003)
Xu, G., Liang, H., Zhao, J., Li, Y.: Investigation of copper removal mechanisms during CMP. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, G688–G692 (2004)
Pandija, S., Roy, D., Babu, S.V.: Chemical mechanical planarization of copper using abrasive-free solutions of oxalic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 102, 144–151 (2007)
Kim, Y.J., Kwon, O.J., Kang, M.C., Kim, J.J.: Effects of the functional groups of complexing agents and Cu oxide formation on Cu dissolution behaviors in Cu CMP Process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, H190–H196 (2011)
Gorantla, V.R.K., Goia, D., Matijevic, E., Babu, S.V.: Role of amine and carboxyl functional groups of complexing agents in slurries for chemical mechanical polishing of copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, G912–G916 (2005)
Aksu, S., Doyle, F.M.: Electrochemistry of copper in aqueous glycine solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, B51–B57 (2001)
Hariharaputhiran, M., Zhang, J., Ramarajan, S., Keleher, J.J., Li, Y.Z., Babu, S.V.: Hydroxyl radical formation in H2O2-amino acid mixtures and chemical mechanical polishing of copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 3820–3826 (2000)
Lu, J., Garland, J.E., Pettit, C.M., Babu, S.V., Roy, D.: Relative roles of H2O2 and glycine in CMP of copper studied with impedance spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, G717–G722 (2004)
Liao, C., Guo, D., Wen, S., Luo, J.: Effects of chemical additives of CMP slurry on surface mechanical characteristics and material removal of copper. Tribol. Lett. 45, 309–317 (2012)
Jindal, A., Babu, S.V.: Effect of pH on CMP of copper and tantalum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, G709–G716 (2004)
Antonijevic, M.M., Petrovic, M.B.: Copper corrosion inhibitors: a review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 3, 1–28 (2008)
Tamilmani, S., Huang, W., Raghavan, S., Small, R.: Potential-pH diagrams of interest to chemical mechanical planarization of copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, G638–G642 (2002)
Ihnfeldt, R., Talbot, J.B.: Effect of CMP slurry chemistry on copper nanohardness. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, H412–H420 (2008)
Tripathi, S., Doyle, F.M., Dornfeld, D.A.: Fundamental mechanisms of copper CMP—passivation kinetics of copper in CMP slurry constituents. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 1157 E06–02 (2009)
Lee, S.M., Choi, W., Craciun, V., Singh, R.K.: Transient electrochemical measurements during copper chemical mechanical polishing. In: Boning, D. (ed.) Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, pp. 127–132. Materials research society, Warrendale (2003)
Li, J., Lu, X., He, Y., Luo, J.: Modeling the chemical-mechanical synergy during copper CMP. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, H197–H202 (2011)
Di Vece, M., Kelly, J.J.: Electrochemical study of hydrogen diffusion in yttrium hydride switchable mirrors. J. Alloy. Compd. 356, 156–159 (2003)
Sulyma, C.M., Goonetilleke, P.C., Roy, D.: Analysis of current transients for voltage pulse-modulated surface processing: application to anodic electro-dissolution of copper for electrochemical mechanical planarization. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 1189–1198 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors would greatly appreciate the financial support of the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (50825501), Science Fund for Creative Research Groups (51021064), and the financial support of National Science and Technology Major Project (2008ZX02104-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Liu, Y., Lu, X. et al. Material Removal Mechanism of Copper CMP from a Chemical–Mechanical Synergy Perspective. Tribol Lett 49, 11–19 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-0037-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-0037-2