Abstract
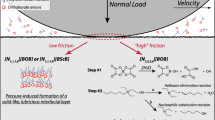
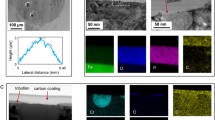
The tribological behaviour and surface interactions of Ti6Al4V sliding against AISI 52100 steel have been studied in the presence of three commercial methylimidazolium (mim) room-temperature ionic liquids (ILs) containing the same anion, bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide, [(CF3SO2)2N] (Tf2N), and cations with increasing alkyl chain length, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium [C2mim], 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium [C4mim] and 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium [C8mim]. Increasing alkyl chain length increases viscosity whilst reducing the onset temperature for thermal degradation in air, the surface tension and the molecular polarity of the ILs. At room temperature, the tribological performance of the three ILs has been compared with that of a mineral oil (MO). The results show the reduction of the running-in period for the ILs with respect to the MO. In contrast with previously described results for IL lubrication, wear rates for Ti6Al4V at room temperature increase as the alkyl chain length of the ILs increases. The maximum wear reduction, of a 39%, with respect to MO is obtained for the [C2mim] cation, with only two carbon atoms on the lateral chain. This was the IL selected for the tests at 100 °C. At this temperature, the reduction of the mean friction coefficient with respect to the MO is higher than 50%, whilst the wear rate of Ti6Al4V is reduced by 78%. The friction-sliding distance records for the IL at 100 °C show sharp transitions, related to formation of wear debris and surface interactions between the Tf2N anion and the aluminium present in the Ti6Al4V alloy. Surface tribolayers and wear debris have been studied by SEM–EDX observations and XPS analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minami, I.: Ionic liquids in tribology. Molecules 14, 2286–2305 (2009)
Zhou, F., Liang, Y.M., Liu, W.M.: Ionic liquid lubricants: designed chemistry for engineering applications. Chem Soc Rev 28, 2590–2599 (2009)
Bermudez, M.D., Jimenez, A.E., Sanes, J., Carrion, F.J.: Ionic liquids as advanced lubricant fluids. Molecules 14, 2888–2908 (2009)
Torimoto, T., Tsuda, T., Okazaki, K., Kuwawata, S.: New frontiers in materials science opened by ionic liquid. Adv. Mater. 22, 1196–1221 (2010)
Jin, C.M., Ye, C.F., Phillips, B.S., Zabinski, J.S., Liu, X.Q., Liu, W.M., Shreeve, J.M.: Polyethylene glycol functionalized dicationic ionic liquids with alkyl or polyfluoroalkyl substituents as high temperature lubricants. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 1529–1535 (2006)
Phillips, B.S., John, G., Zabinski, J.S.: Surface chemistry of fluorine containing ionic liquids on steel substrates at elevated temperature using Mossbauer spectroscopy. Tribol. Lett. 26, 85–91 (2007)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Ionic liquids as lubricants for steel-aluminium contacts at low and elevated temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 26, 53–60 (2007)
Zeng, Z., Phillips, B.S., Xiao, J.C., Shreeve, J.M.: Polyfluoroalkyl, polyethylene glycol, 1,4-bismethylenebenzene or 1,4-bismethylene-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzene bridged functionalized dicationic ionic liquids: synthesis and properties as high temperature lubricants. Chem. Mater. 20, 2719–2726 (2008)
Yao, M.H., Liang, Y.M., Xia, Y.Q., Zhou, F., Liu, X.Q.: High temperature tribological properties of 2-substituted imidazolium ionic liquids for Si3N4-steel contacts. Tribol. Lett. 32, 73–79 (2008)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Iglesias, P.: Lubrication of Inconel 600 with ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 42, 1744–1751 (2009)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Tribol. Lett. 33, 111–126 (2009)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Part 2. Friction, wear and surface interactions at high temperature. Tribol. Lett. 37, 431–443 (2010)
Mu, Z.G., Zhou, F., Zhang, S.X., Liang, Y.M., Liu, W.M.: Effect of the functional groups in ionic liquid molecules on the friction and wear behavior of aluminium alloy in lubricated aluminium-on-steel contact. Tribol. Int. 38, 725–731 (2005)
Mu, Z.G., Wang, X.X., Zhang, S.X., Liang, Y.M., Bao, M., Liu, W.M.: Investigation of tribological behavior of Al-Si alloy against steel lubricated with ionic liquids of 1-diethylphosphonyl-n-propyl-3-alkylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 130, Art. No. 034501 (2008)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Iglesias, P., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G.: 1-N-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids as neat lubricants and lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts. Wear 260, 766–782 (2006)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G.: Room temperature ionic liquids as lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts: influence of sliding velocity, normal load and temperature. Wear 261, 347–359 (2006)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Imidazolium ionic liquids as additives of the synthetic ester propylene glycol dioleate in aluminium-steel lubrication. Wear 265, 787–798 (2008)
Qu, J., Truhan, J.J., Dai, S., Luo, H., Blau, P.J.: Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 22, 207–214 (2006)
Qu, J., Blau, P.J., Sheng, D., Huimin, L., Meyer, J.M., Truhan, J.J.: Tribological characteristics of aluminium alloys sliding against steel lubricated by ammonium and imidazolium ionic liquids. Wear 267, 1226–1231 (2009)
Iglesias, P., Bermudez, M.D., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G.: Friction and wear of aluminium-steel contacts lubricated with ordered fluids. Neutral and ionic liquid crystals as oil additives. Wear 256, 386–392 (2004)
Moulder, J.F., Stickle, W.F., Sobol, P.E., Bomben, K.D.: Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Perkin Elmer, Eden Prairie (1992)
Xie, G., Liu, S., Guo, D., Wang, Q., Luo, J.: Investigation of the running-in process and friction coefficient under the lubrication of ionic liquid/water mixture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 6408–6414 (2009)
Caporali, S., Bardi, U., Lavacchi, A.: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and low energy ion scattering studies on 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 151, 4–8 (2006)
Gonbeau, D., Guimon, C., Pfister-Guillouzo, G., Lavasseur, A., Meunier, G., Dormoy, R.: XPS study of thin films of titanium oxysulfides. Surf. Sci. 254, 81–89 (1991)
Xue, H., Verma, R., Schreeve, J.M.: Review of ionic liquids with fluorine-containing anions. J Fluor Chem 127, 159–176 (2006)
Nooruddin, N.S., Wahlbeck, P.G., Carper, W.R.: Molecular modelling of ionic liquid tribology: semi-empirical bonding and molecular structure. J Mol Struc Theochem 822, 1–7 (2007)
Kamimura, H., Kubo, T., Mori, S.: Effect and mechanism of additives for ionic liquids as new lubricants. Tribol. Int. 40, 620–625 (2007)
Minami, I., Watanabe, N., Nanao, H., Mori, S., Fukumoto, K., Ohno, H.: Aspartic acid-derived wear-preventing and friction-reducing agents for ionic liquids. Chem. Lett. 37, 300–301 (2008)
Bardi, U., Chenakin, S.P., Caporali, S., Lavacchi, A., Perissi, I., Tolstogouzov, A.: Surface modification of industrial alloys induced by long-term interaction with an ionic liquid. Surf. Interface. Anal. 38, 1768–1772 (2006)
Minami, I., Kamimura, H., Mori, S.: Thermo-oxidative stability of ionic liquids as lubricating fluids. J. Synth. Lubr. 24, 135–147 (2007)
Wakai, C., Oleinikova, A., Ott, M., Weingärtner, H.: How polar are ionic liquids? Determination of the static dielectric constat of an imidazolium-based ionic liquid by microwave dielectric spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B Lett. 109, 17028–17030 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by MICINN (Spain), EU FEDER program (MAT2008-01670), and by the Programa de Generación de Conocimiento Científico de Excelencia de la Fundación Séneca de la Región de Murcia (08596/PI/08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez, A.E., Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic Liquids as Lubricants of Titanium–Steel Contact. Part 3. Ti6Al4V Lubricated with Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Different Alkyl Chain Lengths. Tribol Lett 40, 237–246 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9633-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9633-1