Abstract
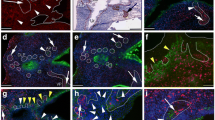
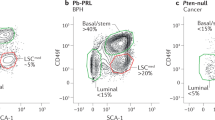
To establish a method for efficient and relatively easy isolation of a cell population containing epithelial prostate stem cells, we developed two transgenic mouse models, K5/CFP and K18/RFP. In these models, promoters of the cytokeratin 5 (Krt5) and the cytokeratin 18 (Krt18) genes regulate cyan and red fluorescent proteins (CFP and RFP), respectively. CFP and RFP reporter protein fluorescence allows for visualization of K5+ and K18+ epithelial cells within the cellular spatial context of the prostate gland and for their direct isolation by FACS. Using these models, it is possible to test directly the stem cell properties of prostate epithelial cell populations that are positively selected based on expression of cytoplasmic proteins, K5 and K18. After validating appropriate expression of the K5/CFP and K18/RFP transgenes in the developing and adult prostate, we demonstrate that a subset of CFP-expressing prostate cells exhibits stem cell proliferation potential and differentiation capabilities. Then, using prostate cells sorted from double transgenic mice (K5/CFP + K18/RFP), we compare RNA microarrays of sorted K5+K18+ basal and K5−K18+ luminal epithelial cells, and identify genes that are differentially expressed. Several genes that are over-expressed in K5+ cells have previously been identified as potential stem cell markers. These results suggest that FACS isolation of prostate cells from these mice based on combining reporter gene fluorescence with expression of potential stem cell surface marker proteins will yield populations of cells enriched for stem cells to a degree that has not been attained by using cell surface markers alone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn S, Joyner AL (2005) In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to sonic hedgehog. Nature 437:894–897
Avilion AA, Nicolis SK, Pevny LH, Perez L, Vivian N, Lovell-Badge R (2003) Multipotent cell lineages in early mouse develpment depend on sox2 function. Genes Dev 17:126–140
Bhatia B, Tang S, Yang P, Doll A, Aumueller G, Newman RA, Tang DG (2005) Cell-autonomous induction of functional tumor suppressor 15-lipoxygenase 2 (15-lox2) contributes to replicative senescence of human prostate progenitor cells. Oncogene 24:3583–3595
Bonkhoff H, Stein U, Remberger K (1994) The proliferative function of basal cells in the normal and hyperplastic human prostate. Prostate 24:114–118
Bruen KJ, Campbell CA, Schooler WG, de Serres S, Cairns BA, Hultman CS, Meyer AA, Randell SH (2004) Real-time monitoring of keratin 5 expression during burn re-epithelialization. J Surg Res 120:12–20
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell Cycle 127:469–480
Collins AT, Habib FK, Maitland NJ, Neal DE (2001) Identification and isolation of human prostate epithelial stem cells based on a2b1-integrin expression. J Cell Sci 114:3865–3872
Cunha GR, Donjacour PS, Coole S, Mee S, Bigsby RM, Higgins SJ, Sugimura Y (1987) The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocr Rev 8:338–362
De Marzo AM, Nelson WG, Meeker AK, Coffey DS (1998) Stem cell features of benign and malignant prostate epithelial cells. J Urol 160:2381–2392
English HF, Stanten RJ, Isaacs JT (1987) Response of glandular versus basal rat ventral prostatic epithelial cells to androgen withdrawal and replacement. Prostate 10:163–178
Evans GS, Chandler JA (1987) Cell proliferation studies in the rat prostate: Ii. The effects of castration and androgen-induced regeneration upon basal and secretory cell proliferation. Prostate 11:339–351
Garraway LA, Lin D, Signoretti S, Waltregny D, Dilks J, Bhattacharya N, Loda M (2003) Intermediate basal cells of the prostate: In vitro and in vivo characterization. Prostate 55:206–218
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown MR, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG, Liu S, Schott A, Hayes D, Birbaum D, Wicha MS, Dontu G (2007) Aldh1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 1:555–567
Gleiberman AS, Michurina T, Encinas JM, Roig JL, Krasnov P, Balordi F, Fishell G, Rosenfeld MG, Enikolopov G (2008) Genetic approaches identify adult pituitary stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6332–6337
Goldstein AS, Lawson DA, Cheng D, Sun W, Garraway LA, Witte ON (2008) Trop2 identifies a subpopulation of murine and human prostate basal cells with stem cell characteristics. Proc Nal Acad Sci USA 105:20882–20887
Goldstein AS, Huang J, Guo C, Garraway IP, Witte ON (2010) Identification of a cell of origin for human prostate cancer. Science 329:568–571
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA, Lander ES (2009) Indentification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 138:645–659
Hebbard L, Steffen A, Zawadzki V, Fieber C, Howells N, Moll J, Ponta H, Hofmann M, Sleeman J (2000) Cd44 expression and regulation during mammary gland development and function. J Cell Sci 113:2619–2630
Hogan B, Costantini F, Lacy E (1986) Manipulating the mouse embryo. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor
Huang EH, Hynes MJ, Zhang T, Ginestier C, Dontu G, Appelman H, Fields JZ, Wicha MS, Boman BM (2009) Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a marker for normal and malignant human colonic stem cells (sc) and tracks sc overpopulation during colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 69:3382–3389
Isaacs JT (1987) Control of cell proliferation and cell death in normal and neoplastic prostate: A stem cell model. In: Roger CH, Coffey DC, Cunha GR (eds) Benign prostatic hyperplasia, vol II. NIH publication N. 87–2881. Bethesda, MD, pp 85–94
Kurita T, Medina RT, Mills AA, Cunha GR (2004) Role of p63 and basal cells in the prostate. Development 131:4955–4964
Lawson DA, Xin L, Lukacs RU, Cheng D, Witte ON (2007) Isolation and functional characterization of murine prostate stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:181–186
Leong KG, Wang B-E, Johnson L, Gao W-Q (2008) Generation of a prostate from a single adult stem cell. Nature 456:804–808
Liang CC, You LR, Chang JL, Tsai TF, Chen CM (2009) Transgenic mice exhibiting inducible and spontaneous cre activities driven by a bovine keratin 5 promoter that can be used for the conditional analysis of basal epithelial cells in multiple organs. J Biomed Sci 16:2–9
Morris RJ, Fischer SM, Klein-Szanto AJP, Slaga TJ (1990) Subpopulations of adult murine epidermal basal cells sedimented on density gradients. Cell Tissue Kinet 23:587–602
Morris RJ, Liu Y, Marles L, Yang Z, Trempus C, Li S, Lin JS, Sawicki JA, Cotsarelis G (2004) Capturing and profiling adult hair follicle stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 22:411–417
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol G, Vecchi M, Ronsoni S, Bernard L, Viale G, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (2010) Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell 140:62–73
Peng W, Anderson DG, Bao Y, Padera RF Jr, Langer R, Sawicki JA (2007) Nanoparticulate delivery of suicide DNA to murine prostate and prostate tumors. Prostate 67:855–862
Povsic TJ, Zavodni KL, Kelly FL, Zhu S, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Dong C, Peterson ED (2007) Circulating progenitor cells can be reliably identified on the basis of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:2243–2248
Richardson GD, Robson CN, Lang SH, Neal DE, Maitland NJ, Collins AT (2004) Cd133, a novel marker for human prostatic epithelial stem cells. J Cell Sci 117:3539–3545
Sawicki JA, Rothman CJ (2002) Evidence for stem cells in cultures of mouse prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 50:46–53
Tran CP, Lin C, Yamashiro J, Reiter RE (2002) Prostate stem cell antigen is a marker of late intermediate prostate epithelial cells. Mol Cancer Res 1:113–121
Tsujimura A, Fujita K, Komori K, Takao T, Miyagawa Y, Takada S, Matsumiya K, Nonomur N, Okuyama A (2007) Prostatic stem cell marker identified by cdna microarray in mouse. J Urol 178:686–691
van Leenders G, Dijkman H, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa C, Ruiter D, Schalken J (2000) Demonstration of intermediate cells during human prostate epithelial differentiation in situ and in vitro using triple-staining confocal scanning microscopy. Lab Invest 80:1251–1258
Verhagen AP, Ramaekers FC, Aalders TW, Schaafsma HE, Debruyne FM, Schalken JA (1992) Colocalization of basal and luminal cell-type cytokeratins in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res 52:6182–6187
Wang X, Kruithof-de Julio M, Economides KD, Walker D, Yu H, Halili MV, Hu YP, Price SM, Abate-Shen C, Shen MM (2009) A luminal epithelial stem cell that is a cell of origin of prostate cancer. Nature 461:495–502
Wen F, Cecena G, Munoz-Ritchie V, Fuchs E, Chambon P, Oshima RG (2003) Expression of conditional cre recombinase in epithelial tissues of transgenic mice. Genesis 35:100–106
Yang A, Schweitzer R, Sun D, Kaghad M, Walker N, Bronson RT, Tabin C, Sharpe A, Caput D, Crum C, McKean F (1999) P63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature 398:714–718
Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M, Abrahamsson A, Blum J, Kwon HY, Kim J, Chute JP, Rizzieri D, Munchhof M, Van Arsdale T, Beachy PA, Reya T (2009) Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 458:776–779
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis (Memorial Sloane Kettering Cancer Center, NY) for providing the plasmid pCX/mRFP, and Robert G. Oshima (UCSD) for providing the plasmid pK18iresEGFP. We thank Gwendolyn Gilliard, Jiping Chen, and Narumi Furuuchi for excellent technical support, James Oesterling for assistance with FACS analysis, and Mindy George-Weinstein for reading the manuscript and for discussions. This work was supported by NIH grant CA115527 (JAS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, W., Bao, Y. & Sawicki, J.A. Epithelial cell-targeted transgene expression enables isolation of cyan fluorescent protein (CFP)-expressing prostate stem/progenitor cells. Transgenic Res 20, 1073–1086 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-010-9478-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-010-9478-2