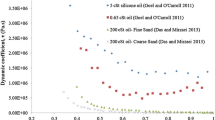
Abstract
The dynamic capillary effect, which is a common phenomenon of two-phase flow in porous media, has crucial importance in various fields. Several factors, such as permeability, grain size, temperature, fluid properties, and saturation conditions, have a significant impact on the observed dynamic capillary effect. This review systematically analyzes the influence of three categories of factors on the dynamic capillary effect, including properties of porous media and fluids, as well as certain external factors. The main conclusions of available researches are presented and analyzed for each influencing factor. The possible reasons for controversial results are discussed as well. This review shows that the pore throat size of porous media has the greatest impact on the dynamic capillary effect, which can lead to a variation of up to nearly five orders of magnitude in the value of the dynamic capillary coefficient. Meanwhile, the grain size, fracture aperture, and temperature cause the variation of the dynamic capillary coefficient by one or two orders of magnitude. The effect of other factors on the dynamic capillary effect is relatively weakened. Finally, the future perspectives, concluding remarks, and recommendations are presented.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, J., Ghaedi, M., Riazi, M.: A new numerical approach for investigation of the effects of dynamic capillary pressure in imbibition process. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 162, 44–54 (2018)
Abidoye, L.K., Das, D.B.: Scale dependent dynamic capillary pressure effect for two-phase flow in porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 74, 212–230 (2014)
Abidoye, L.K., Das, D.B.: Artificial neural network modeling of scale-dependent dynamic capillary pressure effects in two-phase flow in porous media. J. Hydroinf. 17(3), 446–461 (2015)
Abidoye, L.K., Das, D.B.: Impacts of dynamic capillary pressure effects in supercritical CO2–water flow: experiments and numerical simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 136, 103504 (2020)
Bhattarai, S.P., Midmore, D.J., Su, N.: Sustainable Irrigation to Balance Supply of Soil Water, Oxygen, Nutrients and Agro-Chemicals, pp. 253–286. Springer, Dordrecht (2010)
Bottero, S., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Kleingeld, P.J., et al.: Nonequilibrium capillarity effects in two-phase flow through porous media at different scales. Water Resour. Res. 47(10), W10505 (2011)
Brooks, R.H., Corey, A.T.: Hydraulic properties of porous media and their relation to drainage design. Trans. ASAE 7(1), 26–0028 (1964)
Cai, J.C., Jin, T.X., Kou, J.S., et al.: Lucas–washburn equation-based modeling of capillary-driven flow in porous systems. Langmuir 37(5), 1623–1636 (2021)
Camps-Roach, G., O’Carroll, D.M., Newson, T.A., et al.: Experimental investigation of dynamic effects in capillary pressure: grain size dependency and upscaling. Water Resour. Res. 46(8), W08544 (2010)
Cao, Y.X., Tang, M.M., Zhang, Q., et al.: Dynamic capillary pressure analysis of tight sandstone based on digital rock model. Capillarity 3(2), 28–35 (2020)
Chen, L.: Hysteresis and dynamic effects in the relationship between capillary pressure, saturation, and air-water interfacial area in porous media. PhD thesis. The University of Oklahoma, (2006)
Chen, L., Wang, M.Y., Kang, Q.J., et al.: Pore scale study of multiphase multicomponent reactive transport during CO2 dissolution trapping. Adv. Water Resour. 116, 208–218 (2018)
Chen, L., He, A., Zhao, J.L., et al.: Pore-scale modeling of complex transport phenomena in porous media. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 88, 100968 (2022)
Civan, F.: Temperature dependency of dynamic coefficient for nonequilibrium capillary pressure-saturation relationship. AIChE J. 58(7), 2282–2285 (2012)
Dahle, H.K., Celia, M.A., Hassanizadeh, S.M.: Bundle-of-tubes model for calculating dynamic effects in the capillary-pressure-saturation relationship. Transp. Porous Media 58, 5–22 (2005)
Das, D.B., Mirzaei, M.: Experimental measurement of dynamic effect in capillary pressure relationship for two-phase flow in weakly layered porous media. AIChE J. 59(5), 1723–1734 (2013)
Das, D.B., Mirzaei, M., Widdows, N.: Non-uniqueness in capillary pressure–saturation–relative permeability relationships for two-phase flow in porous media: Interplay between intensity and distribution of random micro-heterogeneities. Chem. Eng. Sci. 61(20), 6786–6803 (2006)
Das, D.B., Gauldie, R., Mirzaei, M.: Dynamic effects for two-phase flow in porous media: fluid property effects. AIChE J. 53(10), 2505–2520 (2007)
Das, D.B., Thirakulchaya, T., Deka, L., et al.: Artificial neural network to determine dynamic effect in capillary pressure relationship for two-phase flow in porous media with micro-heterogeneities. Environ. Process. 2(1), 1–18 (2015)
Diamantopoulos, E., and W. Durner: Dynamic nonequilibrium of water flow in porous media: a review. Vadose Zone J. 11(3), vzj2011.0197 (2012)
Elkhoury, J.E., Brodsky, E.E., Agnew, D.C.: Seismic waves increase permeability. Nature 441, 1135–1138 (2006)
Ershadnia, R., Wallace, C.D., Soltanian, M.R.: CO2 geological sequestration in heterogeneous binary media: effects of geological and operational conditions. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 4(4), 392–405 (2020)
Ferrari, A., Lunati, I.: Direct numerical simulations of interface dynamics to link capillary pressure and total surface energy. Adv. Water Resour. 57, 19–31 (2013)
Gielen, T., Hassanizadeh, S., Leijnse, A., et al.: Dynamic effects in multiphase flow: a pore-scale network approach. In: Upscaling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media. Springer, pp. 217–236 (2005)
Gielen, T.W.J.: Dynamic effect in two-phase flow in porous media: a pore-scale network approach. PhD thesis. Delft University of Technology, (2007).
Goel, G., O’Carroll, D.M.: Experimental investigation of nonequilibrium capillarity effects: fluid viscosity effects. Water Resour. Res. 47(9), W09507 (2011)
Goel, G., Abidoye, L.K., Chahar, B.R., et al.: Scale dependency of dynamic relative permeability–satuartion curves in relation with fluid viscosity and dynamic capillary pressure effect. Environ. Fluid Mech. 16, 945–963 (2016)
Hamida, T., Babadagli, T.: Analysis of capillary interaction and oil recovery under ultrasonic waves. Transp. Porous Media 70, 231–255 (2007)
Hamzehpour, H., Asgari, M., Sahimi, M.: Acoustic wave propagation in heterogeneous two-dimensional fractured porous media. Phys. Rev. E 93(6), 063305 (2016)
Hanspal, N.S., Das, D.B.: Dynamic effects on capillary pressure–saturation relationships for two-phase porous flow: implications of temperature. AIChE J. 58(6), 1951–1965 (2012)
Hassanizadeh, S.M., Celia, M.A., Dahle, H.K.: Dynamic effect in the capillary pressure–saturation relationship and its impacts on unsaturated flow. Vadose Zone J. 1(1), 38–57 (2002)
Iassonov, P., Beresnev, I.: Mobilization of entrapped organic fluids by elastic waves and vibrations. SPE J. 13(4), 465–473 (2008)
Joekar-Niasar, V., Hassanizadeh, S.M.: Effect of fluids properties on non-equilibrium capillarity effects: dynamic pore-network modeling. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 37(2), 198–214 (2011)
Joekar-Niasar, V., Hassanizadeh, S.M.: Analysis of fundamentals of two-phase flow in porous media using dynamic pore-network models: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(18), 1895–1976 (2012)
Joekar-Niasar, V., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Dahle, H.: Non-equilibrium effects in capillarity and interfacial area in two-phase flow: dynamic pore-network modelling. J. Fluid Mech. 655, 38–71 (2010)
Li, H.T., Li, Y., Chen, S.N., et al.: Effects of chemical additives on dynamic capillary pressure during waterflooding in low permeability reservoirs. Energy Fuels 30(9), 7082–7093 (2016)
Li, Y., Li, H.T., Cai, J.C., et al.: The dynamic effect in capillary pressure during the displacement process in ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs. Capillarity 1(2), 11–18 (2018)
Li, Y., Li, H.T., Chen, S.N., et al.: Two-phase fluid flow characterizations in tight rock: a fractal bundle of capillary tubes model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58(45), 20806–20814 (2019a)
Li, Y., Liu, C., Li, H.T., et al.: A comprehensive modelling investigation of dynamic capillary effect during non-equilibrium flow in tight porous media. J. Hydrol. 584, 124709 (2020a)
Li, Y., Li, H.T., Chen, S.N., et al.: Investigation of the dynamic capillary pressure during displacement process in fractured tight rocks. AIChE J. 66(1), e16783 (2020b)
Li, Y., Li, H.T., Chen, S.N., et al.: Capillarity characters measurement and effects analysis in different permeability formations during waterflooding. Fuel 194, 129–143 (2017)
Li, Y., Luo, H.W., Li, H.T., et al.: Dynamic capillarity during displacement process in fractured tight reservoirs with multiple fluid viscosities. Energy Sci. Eng. 8(2), 300–311 (2020c)
Li, Y., Luo, H.W., Li, H.T., et al.: A brief review of dynamic capillarity effect and its characteristics in low permeability and tight reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 189, 106959 (2020d)
Li, Y., Li, H.W., Chen, S.N., et al.: Dynamic capillarity during the water flooding process in fractured low permeability reservoirs. International Petroleum Technology Conference in Beijing, China, 26 – 28 March 2019b
Liu, H., Zhu, Z., Patrick, W., et al.: Pore-scale numerical simulation of supercritical CO2 migration in porous and fractured media saturated with water. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 4(4), 419–434 (2020)
Liu, W.D.: Imbibition of Surfactant System. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (2007)
Lo, W.C., Yang, C.C., Hsu, S.Y., et al.: The dynamic response of the water retention curve in unsaturated soils during drainage to acoustic excitations. Water Resour. Res. 53(1), 712–725 (2017)
Lovoll, G., Jankov, M., Måløy, K.J., et al.: Influence of viscous fingering on dynamic saturation-pressure curves in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 86, 305–324 (2011)
Manthey, S., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Helmig, R.: Macro-scale dynamic effects in homogeneous and heterogeneous porous media. In Upscaling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media. Springer, pp. 121–145 (2005)
Mayer, A., Miller, C.: A compositional model for simulating multiphase flow, transport and mass transfer in groundwater systems. In Computational Methods in Subsurface Hydrology; Proceedings 8th International Conference; Venice 1990. Springer-Verlag and Computational Mechanics Publications, pp. 217–222 (1990)
Mirzaei, M., Das, D.B.: Dynamic effects in capillary pressure–saturations relationships for two-phase flow in 3D porous media: implications of micro-heterogeneities. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62(7), 1927–1947 (2007)
Mirzaei, M., Das, D.B.: Experimental investigation of hysteretic dynamic effect in capillary pressure–saturation relationship for two-phase flow in porous media. AIChE J. 59(10), 3958–3974 (2013)
Oung, O., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Bezuijen, A.: Two-phase flow experiments in a geocentrifuge and the significance of dynamic capillary pressure effect. J Porous Media 8(3), 247–257 (2005)
Sabatier, J.M., Hess, H., Arnott, W.P., et al.: In situ measurements of soil physical properties by acoustical techniques. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 54(3), 658–672 (1990)
Sakaki, T., O’Carroll, D.M., Illangasekare, T.H.: Direct quantification of dynamic effects in capillary pressure for drainage–wetting cycles. Vadose Zone J. 9(2), 424–437 (2010)
Spencer, C.W.: Review of characteristics of low-permeability gas reservoirs in western United States. AAPG Bull. 73(5), 613–629 (1989)
Stauffer, F.: Time dependence of the relations between capillary pressure, water content and conductivity during drainage of porous media, pp. 3–35. In IAHR symposium on scale effects in porous media, Thessaloniki, Greece (1978)
Tang, M.M., Lu, S.F., Zhan, H.B., et al.: The effect of a microscale fracture on dynamic capillary pressure of two-phase flow in porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 113, 272–284 (2018)
Tian, L., Feng, B., Zheng, S.X., et al.: Performance evaluation of gas production with consideration of dynamic capillary pressure in tight sandstone reservoirs. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 141(2), 022902 (2019)
Tsai, Y.Z., Liu, Y.T., Wang, Y.L., et al.: Effects of the grain size on dynamic capillary pressure and the modified green-ampt model for infiltration. Geofluids 2018, 8946948 (2018)
Tu, X., Ooms, G., Van Der Tu, F.: Experimental evidence of ultrasonic stimulation of brine-oil flow through a porous rock in laboratory conditions. Transp. Porous Media 70, 323–333 (2007)
Washburn, E.W.: The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys. Rev. 17(3), 273–283 (1921)
Wildenschild, D., Hopmans, J.W., Simunek, J.: Flow rate dependence of soil hydraulic characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 65(1), 35–48 (2001)
Xu, M., Liu, H.H.: Prediction of immiscible two-phase flow properties in a two-dimensional Berea sandstone using the pore-scale lattice Boltzmann simulation. Eur. Phys. J. E 41, 124 (2018)
Yang, Y.F., Cai, S.B., Yao, J., et al.: Pore-scale simulation of remaining oil distribution in 3D porous media affected by wettability and capillarity based on Volume of Fluid method. Int. J. Multip. Flow 143, 103746 (2021)
Zhang, H.Y., He, S.L., Jiao, C.Y., et al.: The influence of dynamic capillary pressure on the seepage of ultra-low permeability reservoir. Open Pet. Eng. J. 7, 55–63 (2014)
Zhang, T., Li, Y.T., Sun, S.Y., et al.: Accelerating flash calculations in unconventional reservoirs considering capillary pressure using an optimized deep learning algorithm. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 195, 107886 (2020)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42172159) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 2462019YJRC011 and CUGGC04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist that are relevant to the contents of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Mao, Y., Yang, L. et al. A Comprehensive Review of Factors Affecting Dynamic Capillary Effect in Two-Phase Flow. Transp Porous Med 144, 33–54 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01723-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01723-x