Abstract
Steviol glycosides (SGs) and gibberellins (GAs) share the same molecular basis. However, the coordination of their respective biosynthetic pathways is very intriguing. Thus, the present study aimed to investigate the role of plant growth regulators, gibberellic acid (GA3), chlorocholine chloride (CCC), and paclobutrazol (PBZ), on the metabolism of Stevia rebaudiana and identify possible ameliorates of the evaluated parameters when CCC and PBZ-treated plants were subsequently treated with GA3. For this, explants were cultured in the absence or presence of 2 mg L−1 GA3, CCC, or PBZ (Step 1). After 20 days, half explants incubated with CCC and PBZ were treated with 2 mg L−1 GA3 and the other half, as well as the rest of the explants, were sub-cultured in their respective initial conditions for 20 days (Step 2). GA3-treated plants showed increased stevioside and phenolic compounds content, as well as a downregulation of most of the SGs/GAs biosynthesis-related genes, with a more pronounced effect upstream of steviol. Following this trend, CCC downregulated some MEP pathway genes, including SrDXS, SrDXR, SrCDPS, and SrKS, and upregulated SrUGT6G1. PBZ also upregulated SrUGT76G1 and inhibited five genes of the MEP pathway and all genes coding for kaurenoid pathway enzymes. The obtained results highlight the capability of GA3 to reverse the negative effects of PBZ on the pattern of many transcripts and to additionally increase the stevioside content to levels comparable to those found in field-grown plants.
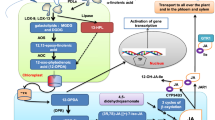
Graphic abstract

Key message
A feedback loop in in vitro cultured stevia plants in response to GA3, CCC and PBZ was demonstrated. GA3-treated plants showed increases in stevioside and phenolic compound contents.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CCC:
-
Chlorocholine chloride
- CDPS:
-
Copalyl diphosphate synthase
- CMK:
-
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase
- CMS:
-
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase
- DMAPP:
-
Dimethylallyl diphosphate
- DXR:
-
Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductase
- DXS:
-
Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase
- FLA:
-
Total soluble flavonoids
- GAs:
-
Gibberellins
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- GA2ox:
-
Gibberellin 2-oxidase
- GA20ox:
-
Gibberellin 20-oxidase
- GA3ox:
-
Gibberellin 3-oxidase
- GGDP:
-
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate
- GGDPS:
-
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase
- HDR:
-
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate reductase
- HDS:
-
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)–butenyl-4-diphosphate synthase
- IPP:
-
Isopentenyl diphosphate
- KAH:
-
Kaurenoic acid 13-hydroxylase
- KAO:
-
Kaurenoic acid oxidase
- KO:
-
Kaurene oxidase
- KS:
-
Kaurene synthase
- MCS:
-
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase
- MEP:
-
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4 phosphate
- MVA:
-
Mevalonate
- PBZ:
-
Paclobutrazol
- PGRs:
-
Plant growth regulators
- Reb-A:
-
Rebaudioside-A
- Reb-D:
-
Rebaudioside-D
- Reb-M:
-
Rebaudioside-M
- SGs:
-
Steviol glycosides
- STEV:
-
Stevioside
- TPC:
-
Total soluble phenol content
- UGT73E1:
-
UDP glucosyltransferase-73E1
- UGT74G1:
-
UDP glucosyltransferase-74G1
- UGT76G1:
-
UDP glucosyltransferase-76G1
- UGT85C2:
-
UDP glucosyltransferase-85C2
- UGT91D2:
-
UDP glucosyltransferase-91D2
References
Bondarev N, Reshetnyak O, Nosov A (2001) Peculiarities of diterpenoid steviol glycoside production in in vitro cultures of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00400-9
Brandle JE, Telmer PG (2007) Steviol glycoside biosynthesis. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.010
Chughtai MFJ, Imran P, Zahoor T et al (2020) Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Stevia rebaudiana as emerging sweetener; a way forward for sweetener industry. CYTA J Food . https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2020.1721562
Dey A, Paul S, Kundu S et al (2013a) Elevated antioxidant potential of chlorocholine chloride-treated in vitro grown Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1214-0
Dey A, Kundu S, Bandyopadhyay A et al (2013b) Efficient micropropagation and chlorocholine chloride induced stevioside production of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. CR Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2012.11.007
Fonouni-Farde C, McAdam E, Nichols D et al (2018) Cytokinins and the CRE1 receptor influence endogenous gibberellin levels in Medicago truncatula. Plant Signal Behav. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2018.1428513
Geuns JMC (2003) Stevioside. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(03)00426-6
Guleria P, Yadav SK (2013) Agrobacterium mediated transient gene silencing (AMTS) in Stevia rebaudiana: insights into steviol glycoside biosynthesis pathway. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074731
Hajihashemi S (2018) Physiological, biochemical, antioxidant and growth characterizations of gibberellin and paclobutrazol-treated sweet leaf (Stevia rebaudiana B) herb. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-017-0428-4
Hajihashemi S, Geuns JMC (2017) Steviol glycosides correlation to genes transcription revealed in gibberellin and paclobutrazol-treated Stevia rebaudiana. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-017-0399-5
Hajihashemi S, Geuns JMC, Ehsanpour AA (2013) Gene transcription of steviol glycoside biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under polyethylene glycol, paclobutrazol and gibberellic acid treatments in vitro. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1226-9
Hernández-García J, Briones-Moreno A, Blázquez MA (2020) Origin and evolution of gibberellin signaling and metabolism in plants. Semin Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.04.009
Humphrey TV, Richman AS, Menassa R et al (2006) Spatial organization of four enzymes from Stevia rebaudiana that are involved in steviol glycoside synthesis. Plant Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-5966-9
JECFA (2010) Steviol glycosides. In: Compendium of Food Additive Specifications. FAO JECFA Monographs 10:17-21
Karimi M, Ahmadi A, Hashemi J et al (2014) Effect of two plant growth retardants on steviol glycosides content and antioxidant capacity in Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni). Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1498-8
Karimi M, Hashemi J, Ahmadi A et al (2015) Opposing effects of external gibberellin and daminozide on Stevia growth and metabolites. Appl Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1310-7
Karimi M, Ahmadi A, Hashemi J et al (2019) Plant growth retardants (PGRs) affect growth and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under drought stress. S Afr J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2018.11.028
Kim D, Jeong SW, Lee CY (2003) Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00423-5
Kumar H, Kaul K, Bajpai-Gupta S et al (2012) A comprehensive analysis of fifteen genes of steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni). Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2011.10.015
Kundu S, Dey A, Bandyopadhyay A (2014) Stimulation of in vitro morphogenesis, antioxidant activity and over expression of kaurenoic acid 13-hydroxylase gene in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni by chlorocholine chloride. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1639-0
Ladygin VG, Bondarev NI, Semenova GA et al (2008) Chloroplast ultrastructure, photosynthetic apparatus activities and production of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana in vivo and in vitro. Biol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-008-0002-y
Lajara MA, López-Orenes A, Ferrer MA et al (2015) Long-term exposure treatments revert the initial SA-induced alterations of phenolic metabolism in grapevine cell cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0800-9
Li W, Zhou Y, You W et al (2018) Development of Photoaffinity Probe for the Discovery of Steviol Glycosides Biosynthesis Pathway in Stevia rebaudiana and Rapid Substrate Screening. ACS Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.8b00285
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
López-Orenes A, Ros-Marín AF, Ferrer MA et al (2013) Antioxidant capacity as a marker for assessing the in vitro performance of the endangered Cistus heterophyllus. Sci World. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/176295
Lucho SR, do Amaral MN, Milech C et al (2018a) Elicitor-induced transcriptional changes of genes of the steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9795-x
Lucho SR, do Amaral MN, Benitez LC et al (2018b) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies in Stevia rebaudiana in response to elicitor agents. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-018-0583-7
Lucho SR, do Amaral MN, Auller PA et al (2019) Salt stress-induced changes in in vitro cultured stevia rebaudiana bertoni: effect on metabolite contents antioxidant capacity and expression of steviol glycosides-related biosynthetic genes. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09937-6
Modi A, Litoriya N, Prajapati V et al (2014) Transcriptional profiling of genes involved in steviol glycoside biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni during plant hardening. Dyn Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.24157
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A Revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Olsson K, Carlsen S, Semmler A et al (2016) Microbial production of next-generation stevia sweeteners. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0609-1
Pazuki A, Aflaki F, Yücesan B et al (2019) Effects of cytokinins, gibberellic acid 3, and gibberellic acid 4/7 on in vitro growth, morphological traits, and content of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.02.009
Rademacher W (2016) Chemical regulators of gibberellin status and their application in plant production. Ann Plant Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119312994.apr0541
Richman A, Swanson A, Humphrey T et al (2005) Functional genomics uncovers three glucosyltransferases involved in the synthesis of the major sweet glucosides of Stevia rebaudiana. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02275.x
Rogach VV, Voytenko LV, Shcherbatiuk MM et al (2020) Morphogenesis, pigment content, phytohormones and productivity of eggplants under the action of gibberellin and tebuconazole. Regul Mech Biosyst. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.15421/022017
Totté N, Van den Ende W, Van Damme EJM et al (2003) Cloning and heterologous expression of early genes in gibberellin and steviol biosynthesis via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in Stevia rebaudiana. Can J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1139/b03-032
Ullah A, Munir S, Mabkhot Y et al (2019) Bioactivity profile of the diterpene isosteviol and its derivatives. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040678
Wang Y, Yao R (2020) Increased endogenous gibberellin level inhibits root growth of Pinus massoniana Lamb plantlets during long-term subculture. Vitro Cell Dev-Pl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-020-10067-y
Wang J, Li S, Xiong Z, Wang Y (2016) Pathway mining-based integration of critical enzyme parts for de novo biosynthesis of steviol glycosides sweetener in Escherichia coli. Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.111
Wölwer-Rieck U (2012) The Leaves of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni), Their Constituents and the Analyses Thereof: A Review. J Agric Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2044907
Yoneda Y, Shimizu H, Nakashima H et al (2018) Effect of treatment with gibberellin, gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitor, and auxin on steviol glycoside content in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Sugar Tech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-017-0561-3
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifíco e Tecnológico) for their financial support and research fellowship EJBB and VJB, as well as the FAPERGS (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul). This study was financed in part by CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil—Finance Code 001. This work was partially carried out at IBV (Instituto de Biotecnología Vegetal), UPCT (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: SRL and EJBB. Performed the experiments: SRL, CM, LA and MNA. Analysed the data: SRL, MNA and EJBB. Wrote the paper: SRL, AAC and EJBB. Corrected the manuscript: MAF, AAC, VJB and EJBB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Mohammad Faisal.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2021_2059_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the experimental conditions. Stevia mother plants grown in greenhouse (A), in vitro establishment (B and C) and multiplication (D) before applying treatments (E) (PDF 108 kb)
11240_2021_2059_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure 2 Agarose gel electrophoresis (1%) of PCR products amplified from Stevia rebaudiana under the effect of GA3 and its inhibitors PBZ and CCC after 40 days of in vitro growth. (A and B) Specificity of primer pairs used for RT-qPCR reactions. Lane 1 is 100pb DNA ladder; 2: DXS; 3: DXR; 4: CMS; 5: CMK; 6: MCS; 7: HDS; 8: HDR; 9: GGDPS; 10: CDPS; 11: KS; 12: KO; 13: KAH; 14: UGT85C2; 15: UGT74G1; 16: UGT76G1; 17: UGT73E1; 18: UGT91D2; 19: UBQ and C: Negative control (PDF 413 kb)
11240_2021_2059_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure 3 Specificity of the primers used for the RT-qPCR reactions in Stevia rebaudiana under the effect of GA3 and its inhibitors PBZ and CCC after 40 days of in vitro growth (PDF 261 kb)
11240_2021_2059_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure 4 Effect of GA3 and its inhibitors PBZ and CCC on growth and development of Stevia rebaudiana after 40 days of in vitro growth (PDF 857 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucho, S.R., do Amaral, M.N., Milech, C. et al. Gibberellin reverses the negative effect of paclobutrazol but not of chlorocholine chloride on the expression of SGs/GAs biosynthesis-related genes and increases the levels of relevant metabolites in Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 146, 171–184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02059-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02059-6