Abstract
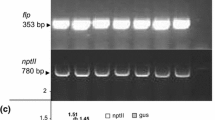
Oilseed rape is considered relatively recalcitrant for genetic modification. This work was performed to establish conditions for effective transformation and regeneration of commercially used cultivars Campino, Haydn, Heros, Hunter and Topas (Brassica napus L.). Cotyledonary petioles and hypocotyls (obtained from the seedlings grown under dark conditions) as a source of explants were used. Our experiments revealed that a lower selection pressure in combination with postponing of selection by 14 days after co-cultivation resulted in recovery of transgenic plants from all cultivars. Transformants were obtained with efficiency from 1 to 5.5%. Histochemically GUS-positive plants were analysed by PCR using primers corresponding to the internal fragments of gus and nptII genes. The transgenic nature was confirmed by Southern blot analyses using a specific nptII probe. This work enriches the list of oilseed rape cultivars available for genetic modification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi MR, Corral-Martinez P, Mousavi A, Salmanian AH, Moieni A, Segui-Simarro JM (2009) An efficient method for transformation of pre-androgenic, isolated Brassica napus microspores involving microprojectile bombardment and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Acta Physiol Plant 31:1313–1317
Abdollahi MR, Moieni A, Mousavi A, Salmanian AH (2011) High frequency production of rapeseed transgenic plants via combination of microprojectile bombardment and secondary embryogenesis of microspore-derived embryos. Mol Biol Rep 38:711–719
Bhowmik P, Dirpaul J, Polowick P, Ferrie AMR (2011) A high throughput Brassica napus microspore culture system: influence of percoll gradient separation and bud selection on embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org. doi:10.1007/s11240-009-9610-2:1-4
Boulter ME, Croy E, Simpson P, Shields R, Croy RRD, Shirsat AH (1990) Transformation of Brassica napus L (oilseed rape) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes: a comparison. Plant Sci 70:91–99
Cardoza V, Stewart CN (2003) Increased Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and rooting efficiencies in canola (Brassica napus L.) from hypocotyl segment explants. Plant Cell Rep 21:599–604
Charest PJ, Holbrook LA, Gabard J, Iyer VN, Miki BL (1988) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of thin cell layer explants from Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Gen 75:438–445
Chen JL, Beversdorf WD (1994) A combined use of microprojectile bombardment and DNA imbibition enhances transformation frequency of canola (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Gen 88:187–192
Chen Z, Greenblatt IM, Dellaporta SL (1992) Molecular analysis of Ac transposition and DNA replication. Genetics 130:665–676
Colby SM, Juncosa AM, Meredith CP (1991) Cellular differences in Agrobacterium susceptibility and regenerative capacity restrict the development of transgenic grapevines. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 116:356–361
Damgaard O, Jensen LH, Rasmussen OS (1997) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Brassica napus winter cultivars. Transgenic Res 6:279–288
De Block M, Debrouwer D (1991) 2 T-DNA’s co-transformed into Brassica napus by a double Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection are mainly integrated at the same locus. Theor Appl Gen 82:257–263
De Block M, Debrouwer D, Tenning P (1989) Transformation of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the expression of the bar and neo genes in the transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 91:694–701
Ferrie AMR, Möllers C (2011) Haploids and doubled haploids in Brassica spp. For genetic and genomic research. Plant Cell Tiss Org 104:375–386
Fry J, Barnason A, Horsch RB (1987) Transformation of Brassica napus with Agrobacterium tumefaciens based vectors. Plant Cell Rep 6:321–325
Ghnaya AB, Charles G, Branchard M (2008) Rapid shoot regeneration from thin cell layer explants excised from petioles and hypocotyls in four cultivars Brassica napus L. Plant Cell Tiss Org 92:25–30
Guerche P, Charbonnier M, Jouanin L, Tourneur C, Paszkowski J, Pelletier G (1987) Direct gene transfer by electroporation in Brassica napus. Plant Sci 52:111–116
Hong HP, Gerster JL, Datla RSS, Albani D, Scoles G, Keller W, Robert LS (1997) The promoter of a Brassica napus polygalacturonase gene directs pollen expression of beta-glucuronidase in transgenic Brassica plants. Plant Cell Rep 16:373–378
Huo R, Wang Y, Ma LL, Qiao JQ, Shao M, Gao XW (2010) Assessment of inheritance pattern and agronomic performance of transgenic rapeseed having harpinXooc-encoding hrf2 gene. Transgenic Res 19:841–847
Hüsken A, Baumert A, Milkowski C, Becker HC, Strack D, Mollers C (2005a) Resveratrol glucoside (piceid) synthesis in seeds of transgenic oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Gen 111:1553–1562
Hüsken A, Baumert A, Strack D, Becker HC, Möllers C, Milkowski C (2005b) Reduction of sinapate ester content in transgenic oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by dsRNAi-based suppression of BnSGT1 gene expression. Mol Breeding 16:127–138
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) Gus fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kamal GB, Illich KG, Asadollah A (2007) Effects of genotype explant type and nutrient medium components on canola (Brassica napus L.) shoot in vitro organogenesis. Afr J Biotechnol 6:861–867
Khan MR, Rashid H, Ansar M, Chaudry Z (2003) High frequency shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer in Canola (Brassica napus). Plant Cell Tiss Org 75:223–231
Khan I, Ali W, Takar ZA Frooqi A, Sikandar WA (2010) Increased regeneration efficiency of Brassica napus L. cultivars Star, Westar and Cyclone from hypocotyle and cotyledonary explants. Available from Nature Precedings http://hdl.handle.net/10101/npre.2010.4781.1
Kong FM, Li J, Tan XL, Zhang LL, Zhang ZY, Qi CK, Ma XK (2009) A new time-saving transformation system for Brassica napus. Afr J Biotechnol 8:2497–2502
Kopertekh L, Broer I, Schiemann J (2009) Developmentally regulated site-specific marker gene excision in transgenic B napus plants. Plant Cell Rep 28:1075–1083
Li X, Ahlman A, Yan X, Lindgren H, Zhu LH (2010) Genetic transformation of the oilseed crop Crambe abyssinica. Plant Cell Tiss Org 100:149–156
Liu H, Guo X, Naeem MS, Liu D, Xu L, Zhang W, Tang G, Zhou W (2010) Transgenic Brassica napus L. lines carrying a two gene construct demonstrate enhanced resistance against Plutella xylostella and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Cell Tiss Org. doi 10.1007/s11240-010-9902-6
Miki B, Huang B, Bird S, Kemble R, Simmonds D, Keller W (1989) A procedure for the microinjection of plant cells and protoplasts. Methods Cell Sci 12:139–144
Moloney MM, Walker JM, Sharma KK (1989) High efficiency transformation of Brassica napus using Agrobacterium vectors. Plant Cell Rep 8:238–242
Murashige I, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 15:473–497
Nath UK, Wilmer JA, Wallington EJ, Becker HC, Möllers C (2009) Increasing erucic acid content through combination of endogenous low polyunsaturated fatty acids alleles with Ld-LPAAT + Bn-fae1 transgenes in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Gen 118:765–773
Ovesná J, Ptáček L, Opatrný Z (1993) Factors influencing the regeneration capacity of oilseed rape and cauliflower in transformation experiments. Biol Plant 35:107–112
Pandian A, Hurlstone C, Liu Q, Singh S, Salisbury P, Green A (2006) Agrobacterium- mediated transformation protocol to overcome necrosis in elite Australian Brassica juncea lines. Plant Mol Biol Rep 24:103a–103i
Pechan PM (1989) Successful cocultivation of Brassica napus microspores and proembryos with Agrobacterium. Plant Cell Rep 8:387–390
Peng Q, Hu Y, Wei R, Zhang Y, Guan CY, Ruan Y, Liu CL (2010) Simultaneous silencing of FAD2 and FAE1 genes affects both oleic acid and erucic acid contents in Brassica napus seeds. Plant Cell Rep 29:317–325
Pua EC, Mehrapalta A, Nagy F, Chua NH (1987) Transgenic plants of Brassica napus L. Bio-Technol 5:815–817
Radke SE, Andrews BM, Moloney MM, Crouch ML, Kridl JC, Knauf VC (1988) Transformation of Brassica napus L. using Agrobacterium tumefaciens: developmentally regulated expression of a reintroduced napin gene. Theor Appl Gen 75:685–694
Reiss E, Schubert J, Scholze P, Kramer R, Sonntag K (2009) The barley thaumatin-like protein HV-TLP8 enhances resistance of oilseed rape plants to Plasmodiophora brassicae. Plant Breed 128:210–212
Salaj T, Moravcikova J, Vookova B, Salaj J (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissues of hybrid firs (Abies spp.) and regeneration of transgenic emblings. Biotechnol Lett 31:647–652
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York. ISBN 0-87969-309-6
Schröder M, Dixelius C, Rahlen L, Glimelius K (1994) Transformation of Brassica napus by using the aadA gene as selectable marker and inheritance studies of the marker genes. Physiol Plantarum 92:37–46
Shi Y, Xu G, Warrington TB, Murdoch GK, Kazala EC, Snyder CL, Weselake RJ (2008) Microspore-derived cell suspension cultures of oilseed rape as a system for studying gene expression. Plant Cell Tiss Org 92:131–139
Spangenberg G, Neuhaus G, Schweiger HG (1986) Expression of foreign genes in a higher plant cell after electrofusion-mediated cell reconstruction of a microinjected karyoplast and a cytoplast. Eur J Cell Biol 42:236–238
Tang GX, Zhou WJ, Li HZ, Mao BZ, He ZH, Yoneyama K (2003) Medium, explant and genotype factors influencing shoot regeneration in oilseed Brassica spp. J Agron Crop Sci 189:351–358
Wallbraun M, Sonntag K, Eisenhauer C, Krzcal G, Wang YP (2009) Phosphomannose-isomerase (pmi) gene as a selectable marker for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rapeseed. Plant Cell Tiss Org 99:345–351
Wang J, Chen Z, Du J, Sun Y, Liang Y (2005) Novel insect resistance in Brassica napus developed by transformation of chitinase and scorpion toxin genes. Plant Cell Rep 24:549–555
Wang M, Liu M, Li D, Wu J, Li X, Yang Y (2010) Overexpression of FAD2 promotes seed germination and hypocotyl elongation in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Tiss Org 102:205–211
Weselake RJ, Shah S, Tang MG, Quant PA, Snyder CL, Furukawa-Stoffer TL, Zhu WM, Taylor DC, Zou JT, Kumar A, Hall L, Laroche A, Rakow G, Raney P, Moloney MM, Harwood JL (2008) Metabolic control analysis is helpful for informed genetic manipulation of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) to increase seed oil content. J Expl Bot 59:3543–3549
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: Characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12832–12836
Zhang Y, Singh MB, Swoboda I, Bhalla PL (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and generation of male sterile lines of australian canola. Aust J Agr Res 56:353–361
Zhang Y, Xu J, Han L, Wei W, Guan Z, Cong L, Chai T (2006) Efficient shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Brassica juncea. Plant Mol Biol Rep 24:255a–255i
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Bodil Jørgensen and Beata Dedicova for their advice concerning oilseed rape transformation. This work was funded by the Slovak Grant Agency VEGA project No. 2-0062-11 and by EEA Financial Mechanism SAV-EHP-2008-02-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boszoradova, E., Libantova, J., Matusikova, I. et al. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of economically important oilseed rape cultivars. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 107, 317–323 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9982-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9982-y