Abstract
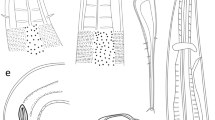
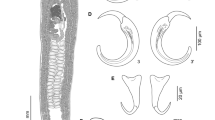
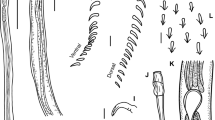
The dactylogyrid genus Rhinoxenus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) is composed of specialized monogeneans infecting the nasal cavities of freshwater fishes from the Neotropical region. This taxon currently comprises 11 species and is easily distinguished from other monogeneans by the absence of the dorsal bar, ventral anchor with inconspicuous roots covered by a sclerotized cap, dorsal anchor greatly modified into a needle-like shape, and hook pair 2 located into bilateral lobes of the trunk. Specimens of Rhinoxenus euryxenus and Rhinoxenus paranaensis were found infecting the nasal cavities of Serrasalmus marginatus and Serrasalmus maculatus, respectively, from the Paraná River basin in Brazil. For the first time, molecular data of Rhinoxenus spp. were obtained and used as a basis for phylogenetic analyses of the genus. Furthermore, our findings represent the first record of R. paranaensis in Brazil.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data will be available for consultation. Whenever necessary, they should be requested from the corresponding author. The specimens used for this work will be available in specialized scientific collections.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Acosta, A. A., Franceschini, L., Zago, A. C., Scholz, T. & Silva, R. J. (2017). Six new species of Heteropriapulus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from South American fishes with an amended diagnosis to the genus. Zootaxa, 4290, 459-482. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4290.3.3
Acosta, A. A., Scholz, T., Blasco-Costa, I., Alves, P. V. & Silva, R. J. (2018). A new genus and two new species of dactylogyrid monogeneans from gills of Neotropical catfishes (Siluriformes: Doradidae and Loricariidae). Parasitology International, 67, 4-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2017.09.012
Acosta, A. A., Mendoza-Palmero, C. A., da Silva, R. J. & Scholz, T. (2019). A new genus and four new species of dactylogyrids (Monogenea), gill parasites of pimelodid catfishes (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) in South America and the reassignment of Urocleidoides megorchis Mizelle et Kritsky, 1969. Folia Parasitologica, 66, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2019.004
Behrmann-Godel, J., Roch, S., & Brinker, A. (2014). Gill worm Ancyrocephalus percae (Ergens 1966) outbreak negatively impacts the Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis L. stock of Lake Constance, Germany. Journal of Fish Diseases, 37, 925-930. http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:bsz:352-259551
Boeger, W.A., Domingues, M.V. & Pavanelli, G.C. (1995). Neotropical Monogenoidea. 24. Rhinoxenus bulbovaginatus n. sp. (Dactylogyridae, Ancyrocephalinae) from the nasal cavity of Salminus maxillosus (Osteichthyes, Characidae) from the Rio Paraná, Paraná, Brazil, Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 90, 695-698.
Bush, A.O., Lafferty, K.D., Lotz, J.M. & Shostak, A.W. (1997). Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. The Journal of Parasitology, 83, 575–583. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227.
Cohen, S. C., Justo, M. C., & Kohn, A. (2013). South American Monogenoidea Parasites of Fishes, Amphibians and Reptiles, Oficina de livros, Rio de Janeiro.
Domingues, M.V. & Boeger, W.A. (2005). Neotropical Monogenoidea. 47. Phylogeny and coevolution of species of Rhinoxenus (Platyhelminthes, Monogenoidea, Dactylogyridae) and their Characiformes hosts (Teleostei, Ostariophysi) with description of four new species. Zoosystema, 27, 441-467. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5402419.
Eiras, J.D.C., Takemoto, R.M. & Pavanelli, G.C. (2000). Métodos de estudo e técnicas laboratoriais em parasitologia de peixes, In Métodos de estudo e técnicas laboratoriais em parasitologia de peixes, Eduem, 171.
Eiras, J.C., Takemoto, R.M., Pavanelli, G.C. & Adriano, E.A. (2011). About the biodiversity of parasites of freshwater fish from Brazil. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol., 31, 161–168.
Franceschini, L., Zago, A. C., Müller, M. I., Francisco, C. J., Takemoto, R. M., & Da Silva, R. J. (2017). Morphology and molecular characterization of Demidospermus spirophallus n. sp., D. prolixus n. sp. (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) and a redescription of D. anus in siluriform catfish from Brazil. Journal of Helminthology, 92, 228-243. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X17000256
Franceschini, L., Acosta, A. A., Zago, A. C., Müller, M. I., & Da Silva, R. J. (2020). Trinigyrus spp. (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from Brazilian catfishes: new species, molecular data and new morphological contributions to the genus. Journal of helminthology, 94, 126. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X20000097
Guindon, S. & Gascuel, O. (2003). A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 52, 696–704. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150390235520
Kimura, M. (1980). A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 111-120.
Kritsky, D.C., Boeger, W.A. & Thatcher, V. E. (1988) Neotropical Monogenea. 11. Rhinoxenus, new genus (Dactylogyridae: Ancyrocephalinae) with descriptions of three new species from the nasal cavities of Amazonian Characoidea. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 101, 87-94.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G. & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874.
Littlewood, D.T.J., Curini-Galletti, M. & Herniou, E.A. (2000). The interrelationships of Proseriata (Platyhelminthes: Seriata) tested with molecules and morphology. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 16, 449–466. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.2000.0802.
Lockyer, A.E., Olson, P.D. & Littlewood, D.T.J. (2003). Utility of complete large and small subunit rRNA genes in resolving the phylogeny of the Neodermata (Platyhelminthes): implications and a review of the cercomer theory. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 78, 155–171. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8312.2003.00141.x.
Luque, J.L., Pereira, F.B., Alves, P.V., Oliva, M.E. & Timi, J.T. (2017). Helminth parasites of South American fishes: current status and characterization as a model for studies of biodiversity. Journal of Helminthology. 91, 150–164. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X16000717.
Mendoza-Palmero,C.A., Blasco-Costa,I. & Scholz,T. (2015). Molecular phylogeny of Neotropical monogeneans (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea) from catfishes (Siluriformes). Parasites & Vectors, v. 8, p. 1-11, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0767-8
Mendoza-Palmero, C. A., Blasco-Costa, I., Hernández-Mena, D., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2017). Parasciadicleithrum octofasciatum n. gen., n. sp. (Monogenoidea: Dactylogyridae), parasite of Rocio octofasciata (Regan) (Cichlidae: Perciformes) from Mexico characterised by morphological and molecular evidence. Parasitology International, 66, 152-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2017.01.006
Mendoza-Palmero, C. A., Mendoza-Franco, E. F., Acosta, A. A., & Scholz, T. (2019). Walteriella ng (Monogenoidea: Dactylogyridae) from the gills of pimelodid catfishes (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) from the Peruvian Amazonia based on morphological and molecular data. Systematic Parasitology, 96, . 441-452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09866-8
Mendoza-Palmero, C. A., Acosta, A. A. & Scholz, T. (2022). Molecular phylogeny of Cosmetocleithrum Kritsky, Thatcher & Boeger, 1986 (Monogenoidea: Dactylogyridae), gill parasites of Neotropical catfishes (Siluriformes). Journal of Helminthology, 96, 56. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X2200044X
Miller, M.A., Pfeiffer, W. & Schwartz, T. (2010). Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. Workshop on Gateway Computing Environments, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1145/2016741.2016785.
Moreira, J., da Silva Carneiro, J., Ruz, E. J., & Luque, J. L. (2019). New species and records of Anacanthorus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) parasitizing serrasalmid fish (Characiformes) from Brazil, including molecular data. Acta parasitologica, 64, 449-455. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-019-00055-7
Nitta, M., & Nagasawa, K. (2016). Four alien monogeneans, including Trinigyrus peregrinus n. sp., parasitic on the invasive armored catfish Pterygoplichthys disjunctivus (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from Okinawa-jima Island, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Species Diversity, 21, 95-104. https://doi.org/10.12782/sd.21.2.095
Oliveira, G.S., Silva, R.J.., Vieira, F.E.G.. & Acosta, A.A. (2021). Urocleidoides spp.(Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from the gills of Parodon nasus (Characiformes: Parodontidae) from a Brazilian stream with descriptions of two new species. Zootaxa, 5081, 535-550. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5081.4.5
Pavanelli, G. C., Takemoto, R. M., & Eiras, J. D. C. (2013). Parasitologia de peixes de água doce do Brasil. Eduem, 249–272.
Plaisance, L., Rousset, V., Morand, S. & Littlewood, T.D.J. (2008). Colonization of Pacific islands by parasites of low dispersal ability: phylogeography of two monogenean species parasitizing butterflyfishes in the South Pacific Ocean. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 65–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01794.x.
Posada, D. (2008). jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 25, 1253–1256. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn083.
Rambaut, A. (2020). FigTree v1.4. Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics and Epidemiology. Retrived Febuary 20, 2023, from http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/
Ronquist, F. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180.
Rossin, M.A., Francesco, P.N., Irigoitia, M.M., Scarabotti, P.A., Taglioretti, V. & Timi, J.T. (2019). Rhinoxenus (Dactylogyridae) parasitizing piranhas (Serrasalmidae) at its southernmost limit of distribution (Paraná River, Argentina), with the description of two new species. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 91. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201920190711.
Santos Neto, J.F., Costa, N.G.S., Soares, G.B. & Domingues, M.V. (2019). Monogenoidean parasites of Acestrorhynchus falcatus (Characiformes: Acestrorhynchidae) from Pará, Brazil: species of Diaphorocleidus and Rhinoxenoides n. gen. (Monogenoidea: Dactylogyridae). Journal of Helminthology, 93, 208–219. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X18000019.
Šimková, A. Matějusová, I., & Cunningham, C. O. (2006). A molecular phylogeny of the Dactylogyridae sensu Kritsky & Boeger (1989) (Monogenea) based on the D1-D3 domains of large subunit rDNA. Parasitology, 133, 43-53. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182006009942
Wang, M., Yan, S., Brown, C. L., Shaharom-Harrison, F., Shi, S. F., & Yang, T. B. (2016). Phylogeography of Tetrancistrum nebulosi (Monogenea, Dactylogyridae) on the host of mottled spinefoot (Siganus fuscescens) in the South China Sea, inferred from mitochondrial COI and ND2 genes. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 27, 3865-3875. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2014.971240
WoRMS Editorial Board, World Register of Marine Species. (2023). Retrived March 20, 2023, from https://www.marinespecies.org
Wu, X. Y., Chilton, N. B., Zhu, X. Q., Xie, M. Q., & Li, A. X. (2005). Molecular and morphological evidence indicates that Pseudorhabdosynochus lantauensis (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) represents two species. Parasitology, 130, 669-677. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182004007152
Wu, X. Y., Zhu, X. Q., Xie, M. Q., & Li, A. X. (2006). The radiation of Haliotrema (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae: Ancyrocephalinae): molecular evidence and explanation inferred from LSU rDNA sequences. Parasitology, 132, 659-668. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200500956X
Yamada, F. H., Acosta, A. A., Yamada, P. D. O., Scholz, T., & Silva, R. J. (2018). A new species of Aphanoblastella Kritsky, Mendoza-Franco and Scholz, 2000 (Monogenea, Dactylogyridae) parasitic on heptapterid catfish (Siluriformes) in the Neotropical region. Acta Parasitologica, 63, 772-780. https://doi.org/10.1515/ap-2018-0092
Zago, A. C., Yamada, F. H., Yamada, P. O. F., Franceschini, L., Bongiovani, M. F., & Silva, R. J. (2020). Seven new species of Urocleidoides (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from Brazilian fishes supported by morphological and molecular data. Parasitology Research, v. 119, p. 3255-3283, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06831-z
Zago, A. C., Franceschini, L., Abdallah, V. D., Müller, M. I., Azevedo, R. K., & Silva, R. J. (2021). Morphological and molecular data of new species of Characithecium and Diaphorocleidus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from Neotropical characid fishes. Parasitology International, 84, 102406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2021.102406
Funding
We thank the agencies for the financial support to this study: FAPESP – São Paulo Research Foundation [grant number – #2020/05412-9; D.H.M.D.V.: 2019/19060-0; R.B.N.: 2019/26831-2; M.B.E.: 2021/12779-9; M.I.M.: 2017/16546-3], and CNPq - National Council for Scientific and Technological Development [grant number – M.M.O.P.: 161838/2021-9; R.J.S.: 311635/2021-0]; M.B.E. was also supported by the Pro-Rectory of Research (PROPG/PROPe – UNESP, Edital 04/2022].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by M.M.O.P, R.B.N, D.H.M.D.V, M.I.M, M.B.E, and R.J.S. The first version of the manuscript was written by M.M.O.P and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the use and care of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11230_2023_10102_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 31 KB) Supplementary information 1. List of monogeneans included in the phylogenetic analyses, with details of the host, locality, and GenBank accession numbers of sequences from the partial 28S rDNA. New sequences obtained for the present study are in bold.
11230_2023_10102_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Supplementary file2 (DOCX 75 KB) Supplementary information 2. Genetic divergence (expressed in %) estimated for partial sequences of the 28S rDNA (LSU) gene within species of Dactylogyridae retrieved from GenBank.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Osaki-Pereira, M.M., Narciso, R.B., Vieira, D.H.M.D. et al. Molecular phylogeny of two Rhinoxenus species (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from the nasal cavities of serrasalmids (Characiformes: Serrasalmidae) from Brazil. Syst Parasitol 100, 521–530 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10102-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10102-7