Abstract
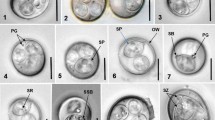
Thirty-eight faecal samples from the Plateau zokor, Myospalax baileyi Thomas, collected in the Haibei Area, Qinghai Province, China, were examined for the presence of coccidia (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Seventeen of 38 faecal samples (44.7%) were found to contain coccidian oöcysts representing four new species of Eimeria Schneider, 1875, and four of 17 (23.5%) infected zokors were concurrently infected with two or three of these eimerian species. The sporulated oöcysts of Eimeria myospalacensis n. sp. are ovoidal, 9.5–17.0 × 8.0–13.0 (mean 13.0 × 10.4) μm; a polar granule is present, oöcyst residuum is absent; sporocysts are ovoidal, 4.5–7.5 × 3.0–5.0 (mean 6.3 × 4.2) μm and have both a Stieda body and residuum. Oöcysts of Eimeria fani n. sp. are ellipsoidal to cylindroidal, 12.5–16.0 × 8.0–11.0 (mean 14.6 × 9.9) μm; a polar granule is present, but micropyle and residuum are lacking; sporocysts are ovoidal, 4.5–7.5 × 3.0–5.3 (mean 6.7 × 4.4) μm; a residuum and a Steida body are present. Oöcysts of Eimeria baileyii n. sp. are ellipsoidal, 15.0–23.0 × 12.0–18.0 (mean 18.2 × 13.7) μm; a polar granule is present but oöcyst residuum is absent; sporocysts are ovoidal, 8.0–11.0 × 5.0–7.0 (mean 9.5 × 5.9) μm and have both a Stieda body and residuum. Oöcysts of Eimeria menyuanensis n. sp. are ovoidal, 12.5–21.0 × 11.0–18.0 (mean 17.1 × 14.6) μm, with a distinct micropyle c.2.5 μm wide; a polar granule is present but a residuum is absent; sporocysts are ovoidal, 8.0–12.0 × 5.0–7.0 (mean 10.2 × 6.4) μm, and have both a Stieda body and residuum.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2013). American Veterinary Medical Association Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals. World Wide Web electronic publication, https://www.avma.org, version 01/2013.
Begall, S., Burda, H., & Schleich, C. E. (Eds.). (2007). Subterranean Rodents: News from Underground. Berlin - Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, pp. 1–9.
Cai, Z. Y., Zhang, T. Z., Ci, H. X., Tang, L. Z., Lian, X. M., Liu, J. Q., & Su, J. P. (2007). Mitochondrial phylogeography and genetic diversity of plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 27, 130–137. (In Chinese).
Couch, L., Duszynski, D. W., & Nevo, E. (1993). Coccidia (Apicomplexa), genetic diversity, and environmental unpredictability of four chromosomal species of the subterranean superspecies Spalax ehrenbergi (Mole-rat) in Israel. Journal of Parasitology, 79, 181–189.
Duszynski, D. W. (1999). Revisiting the code: Clarifying name-bearing types for photomicrographs of Protozoa. Journal of Parasitology, 85, 769–770.
Duszynski, D. W., & Wilber, P. G. (1997). A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in the Eimeriidae. Journal of Parasitology, 83, 333–336.
Fan, N. C., & Shi, Y. Z. (1982). A revision of the zokors of subgenus Eospalax. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 2, 183–199. (In Chinese).
Frey, J. K., Yates, T. L., Duszynski, D. W., Gannon, W. L., & Gardner, S. L. (1992). Designation and curatorial management of type host specimens (symbiotypes) for new parasite species. Journal of Parasitology, 78, 930–932.
Kang, M., Luo, J. Z., Chen, G., & Bai, Z. Y. (2004). A new species of Ransomus (Rhabditida: Stronglidae) of Myospalax baileyi. Acta Veterinaria Zootechnica Sinica, 35, 119–120. (In Chinese).
Koudela, B., Sumbera, R., & Sedlacek, F. (2000). Eimeria burdai sp.n. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae), a new parasite species from subterranean African silvery mole-rat, Heliophobius argenteocinereus. Folia Parasitologica, 47, 97–99.
Lambert, C. R., Gardner, S. L., & Duszynski, D. W. (1988). Coccidia (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the subterranean rodent Ctenomys opimus Wagner (Ctenomyidae) from Bolivia, South America. Journal of Parasitology, 74, 1018–1022.
Levine, N. D., Ivens, V., & Kruidenier, F. J. (1957). New species of Eimeria from Arizona rodents. Journal of Protozoology, 4, 80–88.
Modry, D., Jirku, M., & Sumbera, R. (2005). Three new species of Eimeria (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the Silvery mole-rat Heliophobius argenteocinereus Peters, 1846 (Rodentia: Bathyergidae) from Malawi. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1200–1203.
Norris, R. W., Zhou, K. Y., Zhou, C. Q., Yang, G., Kilpatrick, C. W., & Honeycutt, R. L. (2004). The phylogenetic position of the zokors (Myospalacinae) and comments on the families of muroids (Rodentia). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 31, 972–978.
Sayin, F. (1980). Eimeriidae of the herbivorous mole-rat, Spalax ehrenbergi Nehring. Journal of Protozoology, 27, 364–367.
Sayin, F., Dincer, S., & Meric, I. (1977). Coccidia (Protozoa: Eimeridae) of the herbivorous mole-rat, Spalax leucodon Nordmann. Journal of Protozoology, 24, 210–212.
Su, J. P., & Wang, Z. W. (1992). Studies on the population energetics of plateau zokor I. Average daily metabolic rate and burrowing metabolic rate. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 12, 200–206. (In Chinese).
Tang, L. Z., Zhang, T. Z., Lin, G. H., & Su, J. P. (2010). Phylogenetic discontinuity of Plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi Thomas) populations in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Polish Journal of Ecology, 58, 167–176.
Todd, K. S., & Tryon, C. A. (1970). Eimeria fitzgeraldi n. sp. from the northern Pocket gopher, Thomomys talpoides. Journal of Wildilife Diseases, 6, 107–108.
Veisov, A. (1975). Tri novykh vida koktsidii roda Eimeria iz gornogo ili belozobugo slepysha Spalax leucodon Nordman, 1840. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk Azerbaidzhanskoi SSR, 4, 82–85. (In Russian).
Wang, Z. L., Chen, Y., Yang, J., Chen, W. J., Zhang, Y. M., & Zhao, X. Q. (2012). cDNA cloning and expression of erythropoietin in the plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi) from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57, 997–1006.
Wang, Q. Y., Zhang, Y. M., Wei, W. H., & Bian, J. H. (2000). Food habit of the plateau zokor. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 20, 198–210. (In Chinese).
Wilson, D. E., & Reeder, D. M. (2005). Mammal species of the world (3rd ed.). Vol. 2. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, pp. 909–926.
Zhang, Y. M., Fan, N. C., & Zhou, W. Y. (1993). Study on the population ecology of the plateau zokors. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 4, 359–361. (In Chinese).
Zhou, W. Y., & Dou, F. M. (1990). Studies on activity and home range of plateau zokor. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 10, 31–39. (In Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 31170394 and 31370405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, YF., Nie, XH., Zhang, TZ. et al. Four new coccidia (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the Plateau zokor, Myospalax baileyi Thomas (Rodentia: Myospalacinae), a subterranean rodent from Haibei area, Qinghai Province, China. Syst Parasitol 87, 181–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-013-9466-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-013-9466-z