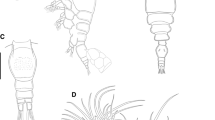
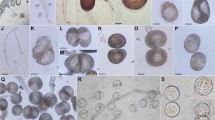
Abstract
The Ellobiopsidae are enigmatic parasites of crustaceans that have been grouped together exclusively on the basis of morphological similarities. Ultrastructural studies have revealed their affiliation within the alveolates, which was confirmed by the phylogenetic analysis of the ribosomal RNA gene (SSU rDNA) sequences of two species of Thalassomyces Niezabitowski, 1913. However, their precise systematic position within this group remains unresolved, since they could not be definitively allied with any particular alveolate group. To better determine the systematic position of ellobiopsids by molecular phylogeny, we sequenced the SSU rDNA from the type-species of the Ellobiopsidae, Ellobiopsis chattoni Caullery, 1910. We found E. chattoni infecting various copepod hosts, Acartia clausi Giesbrecht, Centropages typicus Kröyer and Clausocalanus sp., in the Bay of Marseille, NW Mediterranean Sea, which allowed us to study several stages of the parasite development. A single unicellular multinucleate specimen provided two different sequences of the SSU rDNA gene, indicating the existence of polymorphism at this locus within single individuals. Ellobiopsis Caullery, 1910 and Thalassomyces formed a very divergent and well-supported clade in phylogenetic analyses. This clade appears to be more closely related to the dinoflagellates (including the Syndiniales/Marine Alveolate Group II and the Dinokaryota) and Marine Alveolate Group I than to the other alveolates (Ciliophora, Perkinsozoa and Apicomplexa).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albaina, A., & Irigoien, X. (2006). Fecundity limitation of Calanus helgolandicus, by the parasite Ellobiopsis sp. Journal of Plankton Research, 28, 413–418.
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schaffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Alverson, A. J., & Kolnick, L. (2005). Intragenomic nucleotide polymorphism among small subunit (18S) rDNA paralogs in the diatom genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyta). Journal of Phycology, 41, 1248–1257.
Boschma, H. (1949). Ellobiopsidae. Discovery Report, 25, 281–314.
Boschma, H. (1959). Ellobiopsidae from the tropical West Africa. Atlantide Report, 5, 145–175.
Burreson, E. M., Dungan, C. F., & Reece, K. S. (2005). Molecular, morphological, and experimental evidence support the synonymy of Perkinsus chesapeaki and Perkinsus andrewsi. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 52, 258–270.
Cachon, J., & Cachon, M. (1987). Parasitic dinoflagellates. In F. J. R. Taylor (Ed.), The biology of dinoflagellates (pp. 571–610). Oxford: Blackwell.
Caullery, M. (1910). Ellobiopsis chattoni, n. g., n. sp., parasite de Calanus helgolandicus Claus, appartenant probablement aux Péridiniens. Bulletin Scientifique de la France et la Belgique, 44, 201–214.
Cavalier-Smith, T. (1993). Kingdom Protozoa and its 18 phyla. Microbiological Reviews, 57, 953–994.
Cavalier-Smith, T., & Chao, E. E. (2004). Protalveolae phylogeny and systematics and the origins of Sporozoa and dinoflagellates (phylum Myzozoa nom nov.). European Journal of Protistology, 40, 185–212.
Chatton, E. (1920). Les Péridiniens parasites. Morphologie, reproduction, éthologie. Archives de Zoologie Experimentale et Générale, 59, 1–475.
Chatton, E. (1952). Classe des Dinoflagellés ou Péridiniens. In P. Grassé (Ed.), Traité de Zoologie (Vol. 1, pp. 1309–1406). Paris: Masson et Cie.
Collin, B. (1913). Sur un Ellobiopside nouveau parasite des Nebalies (Parallobiopsis coutieri n. g., n. sp.). Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences, 156, 1332–1333.
Dick, M. W. (2001). Straminipilous fungi: Systematics of the peronosporomycetes, including accounts of the marine straminipilous protists, the plasmodiophorids, and similar organisms. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 654 pp.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792–1797.
Fukuda, Y., & Endoh, H. (2008). Phylogenetic analyses of the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans based on β-tubulin and Hsp90 genes. European Journal of Protistology, 44, 27–33.
Galt, J. H., & Whisler, H. C. (1970). Differentiation of flagellate spores in Thalassomyces Ellobiopsid parasite of marine Crustacea. Archiv für Mikrobiologie, 71, 295–303.
Grassé, P. P. (1952). Les Ellobiopsidae. In P. Grassé (Ed.), Traité de Zoologie (Vol. 1, pp. 1023–1030). Paris: Masson et Cie.
Gribble, K. E., & Anderson, D. M. (2007). High intraindividual, intraspecific, and interspecific variability in large-subunit ribosomal DNA in the heterotrophic dinoflagellates Protoperidinium, Diplopsalis, and Preperidinium (Dinophyceae). Phycologia, 46, 315–324.
Guillou, L., Viprey, M., Chambouvet, A., Welsh, R. M., Kirkham, A. R., Massana, R., et al. (2008). Widespread occurrence and genetic diversity of marine parasitoids belonging to Syndiniales (Alveolata). Environmental Microbiology, 10, 3349–3365.
Harada, A., Ohtsuka, S., & Horiguchi, T. (2007). Species of the parasitic genus Duboscquella are members of the enigmatic marine alveolate Group I. Protist, 158, 337–347.
Hovasse, R. (1926). “Parallobiopsis coutieri” Collin. Morphologie, cytologie, évolution, affinités des Ellobiopsidés. Bulletin Scientifique de la France et la Belgique, 60, 409–446.
Hovasse, R. (1952). Ellobiopsis fagei Hovasse, Ellobiopsidé parasite, en Méditerranée, de Clausocalanus arcuicornis Dana. Bulletin de l’Institut Océanographique, Monaco, 1016, 1–12.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2001). MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 754–755.
Jepps, M. W. (1937). On the protozoan parasites of Calanus finmarchicus in the Cycle Sea area. Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science, 79, 589–658.
Jobb, G., von Haeseler, A., & Strimmer, K. (2004). TREEFINDER: A powerful graphical analysis environment for molecular phylogenetics. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 4, 18.
Kim, S., Park, M. G., Kim, K. Y., Kim, C. H., Yih, W., Park, J. S., et al. (2008). Genetic diversity of parasitic dinoflagellates in the genus Amoebophrya and its relationship to parasite biology and biogeography. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 55, 1–8.
Lanave, C., Preparata, G., Saccone, C., & Serio, G. (1984). A new method for calculating evolutionary substitution rates. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 20, 86–93.
Lartillot, N., & Philippe, H. (2004). A Bayesian mixture model for across-site heterogeneities in the amino-acid replacement process. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 21, 1095–1109.
Leander, B. S., & Hoppenrath, M. (2008). Ultrastructure of a novel tube-forming, intracellular parasite of dinoflagellates: Parvilucifera prorocentri sp. nov. (Alveolata, Myzozoa). European Journal of Protistology, 44, 55–70.
López-García, P., Rodríguez-Valera, F., Pedrós-Alió, C., & Moreira, D. (2001). Unexpected diversity of small eukaryotes in deep-sea Antarctic plankton. Nature, 409, 603–607.
Mauchline, J. (1998). The biology of calanoid copepods. Advances in Marine Biology, 33, 1–710.
Moreira, D., & López-García, P. (2002). The molecular ecology of microbial eukaryotes unveils a hidden world. Trends in Microbiology, 10, 31–38.
Mori, K., Yamamoto, K., Teruya, K., Shiozawa, S., Yoseda, K., Sugaya, T., et al. (2007). Endoparasitic dinoflagellate of the genus Ichthyodinium infecting fertilized eggs and hatched larvae observed in the seed production of leopard coral grouper Plectropomus leopardus. Fish Pathology, 42, 49–57.
Niezabitowski, E. L. (1913). Die pfianzlichen Parasiten der Tiefsee-Decapoden-Gattung Pasiphaea. Kosmos, 38, 1563–1572.
Norén, F., Moestrup, O., & Rehnstam-Holm, A.-S. (1999). Parvilucifera infectans Norén et Moestrup sp. nov. (Perkinsozoa phylum nov.): A parasitic flagellate capable of killing toxic microalgae. European Journal of Protistology, 35, 233–254.
Philippe, H. (1993). MUST, a computer package of management utilities for sequences and trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 21, 5264–5272.
Reichenow, E. (1930). Parasitische Peridinea (einschließlich Ellobiopsidae). Die Tierwelt der Nord- und Ostsee, 19(2.d3), 85–100.
Rodríguez, F., Oliver, J. L., Marín, A., & Medina, J. R. (1990). The general stochastic model of nucleotide substitution. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 142, 485–501.
Rose, M. (1933). Copépodes pélagiques. Faune France, 26, 1–374.
Saitou, N., & Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406–425.
Schweikert, M., & Elbrächter, M. (2006). First ultrastructural investigations on Ellobiopsis spec. (incertae sedis) a parasite of copepods. Endocytobiosis Cell Research, 17, 73.
Shields, J. D. (1994). The parasitic dinoflagellates of marine crustaceans. Annual Review of Fish Diseases, 4, 241–271.
Silberman, J. D., Collins, A. G., Gershwin, L. A., Johnson, P. J., & Roger, A. J. (2004). Ellobiopsids of the genus Thalassomyces are alveolates. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 52, 246–252.
Skovgaard, A., Massana, R., Balague, V., & Saiz, E. (2005). Phylogenetic position of the copepod-infesting parasite Syndinium turbo (Dinoflagellata, Syndinea). Protist, 156, 413–423.
Théodoridès, J. (1989). Parasitology of marine zooplankton. Advances in Marine Biology, 25, 117–177.
Whisler, H. C. (1990). Incertae Sedis Ellobiopsida. In L. Margulis, J. O. Corliss, M. Melkonian, & D. J. Chapman (Eds.), Handbook of Protoctista (pp. 715–719). Boston: Jones & Bartlett.
Yamaguchi, A., Kawamura, H., & Horiguchi, T. (2006). A further phylogenetic study of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate genus, Protoperidinium (Dinophyceae) based on small and large subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Phycological Research, 54, 317–329.
Acknowledgements
This is a contribution to the project DIVERPLAN-MED supported by a post-doctoral grant to F.G. of the Ministerio Español de Educación y Ciencia No. 2007-0213. P.L.G. and D.M. acknowledge financial support from the French CNRS and the ANR Biodiversity project ‘Aquaparadox’. This is a part of SOMLIT (Service d’Observation en Milieu LITtoral) national grid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, F., López-García, P., Nowaczyk, A. et al. The crustacean parasites Ellobiopsis Caullery, 1910 and Thalassomyces Niezabitowski, 1913 form a monophyletic divergent clade within the Alveolata. Syst Parasitol 74, 65–74 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9199-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9199-1