Abstract
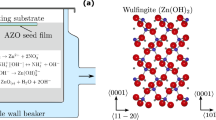
Bunches of ZnO nanowires have been synthesized by hydrothermal process with the assistance of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. The obtained bunches of ZnO nanowires are hexagonal wurtzite structures, and they exhibit orange visible emission ~600 nm. It seems the orange emission ~600 nm is due to the presence of Zn(OH)2 on the surface of ZnO nanowires. On the basis of material information provided by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and photoluminescence, a growth mechanism is proposed for the formation of bunches of ZnO nanowires.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu JT, Odom TW, Lieber CM (1999) Acc Chem Res 32:435. doi:10.1021/ar9700365
Hiruma K, Yazawa M, Katsuyama T, Ogawa K, Haraguchi K, Koguchi M (1995) J Appl Phys 77:447. doi:10.1063/1.359026
Keem K, Kim H, Kim GT, Lee JS, Min B, Cho K, Sung MY, Kim S (2004) Appl Phys Lett 84:4376. doi:10.1063/1.1756205
Arnold MS, Avouris P, Pan ZW, Wang ZL (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:659. doi:10.1021/jp0271054
Huang MH, Mao S, Feick H, Yan HQ, Wu YY, Kind H, Weber E, Russo R, Yang PD (2001) Science 292:1897. doi:10.1126/science.1060367
Lee CJ, Lee TJ, Lyu SC, Zhang Y, Ruh H, Lee HJ (2002) Appl Phys Lett 81:3648. doi:10.1063/1.1518810
Park WI, Jun YH, Jung SW, Yi GC (2003) Appl Phys Lett 82:964. doi:10.1063/1.1544437
Wang ZL (2004) Mater Today 7:26. doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(04)00286-X
Park JH, Choi HJ, Choi YJ, Sohn SH, Park JG (2004) J Mater Chem 14:35
Park JH, Choi HJ, Park JG (2004) J Cryst Growth 263:237. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2003.11.106
Boyle DS, Govender K, O’Brien P (2002) Chem Commun (Camb) 1:80. doi:10.1039/b110079n
Hung C-H, Whang W-T (2003) Mater Chem Phys 82:705. doi:10.1016/S0254-0584(03)00331-6
Sun XM, Chen X, Deng ZX, Li YD (2002) Mater Chem Phys 78:99. doi:10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00310-3
Guo L, Ji YL, Xu HB, Simon P, Wu ZY (2002) J Am Chem Soc 124:14864. doi:10.1021/ja027947g
Yang JL, An SJ, Park WI, Yi GC, Choi W (2004) Adv Mater 16:1661. doi:10.1002/adma.200306673
Li ZQ, Ding Y, Xiong YJ, Yang Q, Xie YI (2004) Chem Eur J 10:5823. doi:10.1002/chem.200400498
Coley JF, Stecker L, Ono Y (2005) Nanotechnology 16:292. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/16/2/020
Yadav RS, Pandey AC (2007) J Exp Nanosci 2:177. doi:10.1080/17458080701474242
Lao JY, Huang JY, Wang DZ, Ren ZF (2002) Nano Lett 2:1287. doi:10.1021/nl025753t
Sun Z, Liu L, Zhang L, Jia D (2006) Nanotechnology 17:2266. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/9/032
Sun XM, Chen X, Deng ZX, Li YD (2002) Mater Chem Phys 78:99. doi:10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00310-3
Zhang H, Yang D, Ji Y, Ma X, Xu J, Que D (2004) J Phys Chem B 13:108
Ge J, Tang B, Zhuo L, Shi Z (2006) Nanotechnology 17:1316. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/5/025
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Prof. Ramesh Chandra, IIT, Roorkee, India for the SEM observations and Dr. Manvendra Kumar, IUAC, Delhi for PL observation. They also wish to express their gratitude to all the scientific members of Nanophosphor Application Centre, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India. This work was financially supported by DST, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, R.S., Pandey, A.C. Hydrothermal synthesis and optical study of bunches of ZnO nanowires. Struct Chem 20, 847–850 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-009-9482-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-009-9482-4