Abstract
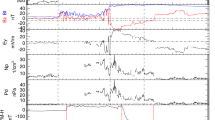
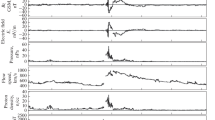
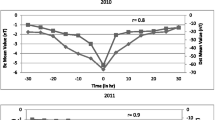
We investigate the influence of various solar wind parameters on the intensity of the associated major geomagnetic storm. SYM-Hmin was used to indicate the intensity of major geomagnetic storms, while \(I(B_{s})\), \(I(E_{y})\) and \(I(Q)\) were used to indicate the time integrals of the southward interplanetary magnetic field component (\(B_{s}\)), the solar wind electric field (\(E_{y}\)), and Q, which is the combination of \(E_{y}\) and the solar wind dynamic pressure, during the main phase of a major geomagnetic storm, respectively. We have found that the correlation coefficient (CC) between the time integral of solar wind parameters and the intensity of an associated major geomagnetic storm has a physical meaning, while the CC between the peak value of a given solar wind parameter and the intensity of an associated major geomagnetic storm has no physical meaning. We used 67 major geomagnetic storms that occurred between 1998 and 2006 to calculate the CC between SYM-Hmin and \(I(B_{s})\), the CC between SYM-Hmin and \(I(E_{y})\), and the CC between SYM-Hmin and \(I(Q)\). The derived CC between \(I(B_{s})\) and SYM-Hmin is 0.33, while the CC between \(I(E_{y})\) and SYM-Hmin is 0.57, and the CC between \(I(Q)\) and SYM-Hmin is 0.86, respectively. These values indicate that \(I(B_{s})\), \(I(E_{y})\) and \(I(Q)\) contribute in a small, moderate, and crucial way to the intensity of a major geomagnetic storm, respectively. For the solar wind to have a strong geoeffectiveness \(B_{s}\) plays a role, together the solar wind speed and density, but also the dynamic pressure > 3 nPa. Large and long duration \(B_{s}\) or \(E_{y}\) cannot ensure a major geomagnetic storm, if the solar wind dynamic pressure is much lower than 3 nPa.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673. DOI.
Burton, R.K., McPherron, R.L., Russell, C.T.: 1975, J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4204. DOI.
Chen, L.-B., Le, G.-M., Zhao, M.-X.: 2020, Res. Astron. Astrophys. 20, 36. DOI.
Choi, Y., Moon, Y.-J., Choi, S., Baek, J.-H., Kim, S.S., Cho, K.-S., Choe, G.S.: 2009, Solar Phys. 254, 311. DOI.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, A.L.C.: 2008, J. Geophys. Res. 113, A05221. DOI.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2008, Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L06S03. DOI.
Fenrich, F.R., Luhmann, J.G.: 1998, Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2999. DOI.
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1987, Planet. Space Sci. 35, 1101. DOI.
Gonzalez, W.D., Joselyn, J.A., Kamide, Y., Kroehl, H.W., Rostoker, G., Tsurutani, B.T., Vayliuma, V.M.: 1994, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771. DOI.
Ji, E.Y., Moon, Y.J., Kim, K.H., Lee, D.H.: 2010, J. Geophys. Res. 115, A10232. DOI.
Kane, R.P.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A02213. DOI.
Kane, R.P.: 2010, Planet. Space Sci. 58, 1792. DOI.
Kataoka, R., Fairfield, D.H., Sibeck, D.G., Rastätter, L., Fok, M.-C., Nagatsuma, T., Ebihara, Y.: 2005, Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L21108. DOI.
Lopez, R.E., Wiltberger, M., Hernandez, S., Lyon, J.G.: 2004, Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L08804. DOI.
Meng, X., Tsurutani, B.T., Mannucci, A.J.: 2019, J. Geophys. Res. 124, 3926. DOI.
O’Brien, T.P., McPherron, R.L.: 2000a, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3797. DOI.
O’Brien, T.P., McPherron, R.L.: 2000b, J. Geophys. Res. 105(A4), 7707. DOI.
Wang, C.B., Chao, J.K., Lin, C.-H.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108(A9), 1341. DOI.
Wanliss, J.A., Showalter, K.M.: 2006, J. Geophys. Res. 111, A02202. DOI.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2011, Space Weather 9, S07005. DOI.
Weigel, R.S.: 2010, J. Geophys. Res. 115, A09201. DOI.
Wu, C.-C., Lepping, R.P.: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107(A11), 1346. DOI.
Wu, C.C., Lepping, R.P.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 265. DOI.
Acknowledgements
We thank the ACE/SWEPAM instrument team and the ACE Science Center for providing the ACE data. We thank the Center for Geomagnetism and Space Magnetism, Kyoto University, for providing the SYM-H index. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41074132, 41274193, 41674166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, GM., Liu, GA. & Zhao, MX. Dependence of Major Geomagnetic Storm Intensity (\(\mathrm{Dst}\le -100\) nT) on Associated Solar Wind Parameters. Sol Phys 295, 108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01675-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01675-3