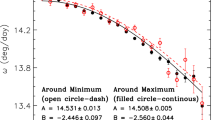Abstract
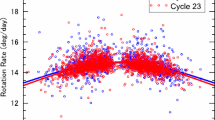
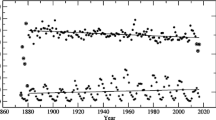
The solar equatorial rotation rate, determined from sunspot group data during the period 1879–2004, decreased over the last century, whereas the level of activity has increased considerably. The latitude gradient term of the solar rotation shows a significant modulation of about 79 year, which is consistent with what is expected for the existence of the Gleissberg cycle. Our analysis indicates that the level of activity will remain almost the same as the present cycle during the next few solar cycles (i.e., during the current double Hale cycle), while the length of the next double Hale cycle in sunspot activity is predicted to be longer than the current one. We find evidence for the existence of a weak linear relationship between the equatorial rotation rate and the length of sunspot cycle. Finally, we find that the length of the current cycle will be as short as that of cycle 22, indicating that the present Hale cycle may be a combination of two shorter cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder, H. L.: 1977, Introduction to Probability and Statistics (6th edn.), Freeman, San Fransisco.
Antia, H. M. and Basu, S.: 2000, Astrophys. J. 541, 442.
Balthasar, H. and Wöhl, H.: 1980, Astron. Astrophys. 92, 111.
Balthasar, H., Vázquez, M., and Wöhl, H.: 1986, Astron. Astrophys. 155, 87.
Beer, J., Tobias, S., and Weiss, N.: 1998, Solar Phys. 181, 237.
Bonev, B. P., Penev, K. M., and Sello, S.: 2004, Astrophys. J. 605, L81.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1988, Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 230, 535.
Dicke, R. H.: 1988, Solar Phys. 115, 171.
Eddy, J. A.: 1976, Science 192, 1189.
Eddy, J. A., Gilman, P. A., and Trotter, D. E.: 1976, Solar Phys. 46, 3.
Georgieva, K., Kirov, B., Javaraiah, J., and Krasteva, R.: 2005, Planet. Space Sci. 53, 197.
Gleissberg, W.: 1942, Astrophys. J. 96, 234.
Gnevyshev, M. N. and Ohl, A. I.: 1948, Astron. Zh. 25(1), 18.
Gokhale, M. H. and Javaraiah, J.: 1990, Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 243, 241.
Gokhale, M. H. and Javaraiah, J.: 1995, Solar Phys. 156, 157.
Hathaway, D. H. and Wilson, R. M.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 357, 271.
Hathaway, D. H. and Wilson, R. M.: 2005, Solar Phys. 224, 5.
Hathaway, D. H., Wilson, R. M., and Reichmann, E. J.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104(A10), 22375.
Hathaway, D. H., Nandy, D., Wilson, R. M., and Reichmann, E. J.: 2003, Astrophys. J. 589, 665 (Erratum: 2004, Astrophys. J. 602, 543).
Hiremath, K. M. and Mandi, P. I.: 2004, New Astronomy 9, 651.
Javaraiah, J.: 2003a, Solar Phys. 212, 23.
Javaraiah, J.: 2003b, Astron. Astrophys. 401, L9.
Javaraiah, J. and Gokhale, M. H.: 1995, Solar Phys. 158, 173.
Javaraiah, J., Bertello, L., and Ulrich, R. K.: 2005, Astrophys. J. 626, 479.
Juckett, D.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 399, 731.
Komm, R. W., Howard, R. F., and Harvey, J.: 1993, Solar Phys. 143, 19.
LaBonte, B. J. and Howard, R. F.: 1982, Solar Phys. 75, 161.
Lassen, K. and Friis-Christensen, E.: 1995, J. Atmos. Terrest. Phys. 57, 835.
Mendoza, B.: 1999, Solar Phys. 188, 237.
Nesme-Ribes, E., Ferreria, E. N., Sadourny, R., Le Truet, H., and Li, Z. X.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18,923.
Schüssler, M. and Schmitt, D.: 2004, Astron. Astrophys. 421, 349.
Obridko, V. N. and Shelting, B. D.: 2001, Solar Phys. 201, 1.
Solanki, S. K., Krivova, N. A., Schüssler, M., and Fligge, M.: 2002, Astron. Astrophys. 396, 1029.
Solanki, S. K., Usoskin, I. G., Kromer, B., Schüssler, M., and Beer, J.: 2004, Nature 431, 1084.
Rozelot, J. P.: 2001, J. Atmos. Solar–Terrest. Phys. 63, 375.
Ulrich, R. K. and Boyden, J. E.: 2005, Astrophys. J. 620, L123.
Usoskin, I. G., Mursula, K., and Kovaltsov, G. A.: 2000, Astron. Astrophys. 354, L33.
Usoskin, I. G., Mursula, K., and Kovaltsov, G. A.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 403, 743.
Vaquero, J. M., Sánchez-Bajo, F., and Gallego, M. C.: 2002, Solar Phys. 207, 219.
Ward, F.: 1966, Astrophys. J. 145, 416.
Wilson, R. M.: 1988, Solar Phys. 117, 269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presently working for the Mt. Wilson Solar Archive Digitization Project at UCLA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javaraiah, J., Bertello, L. & Ulrich, R.K. Long-Term Variations in Solar Differential Rotation and Sunspot Activity. Sol Phys 232, 25–40 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-8776-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-8776-y