Abstract
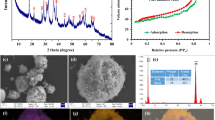
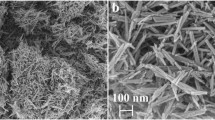
The performance and mechanism of mechanochemical activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by cryptomelane-type manganese octahedral molecular sieve (OMS-2) prepared by a refluxing method for degradation of Acid Orange 7 (AO7) have been demonstrated. Grinding of OMS-2 and PMS in presence of a small amount of H2O for a short time induced a much higher AO7 degradation efficiency compared with the OMS-2 + PMS system without pretreatment. Such degradation can also be efficiently performed by this system over a wide range of solution pH and for different organic dyes. For other manganese oxides such as OMS-2 prepared by a solvent-free method, amorphous manganese oxides, and γ-MnO2, with coexistence of Mn(III) and Mn(IV) species, great enhancement of catalytic activity was also observed. Characterization of the ground OMS-2 by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) suggested that, during grinding, low-valent manganese species are oxidized to Mn(IV) species, representing the main active species for AO7 degradation. The produced SO −·4 and HO· radicals from Mn(III) and the rest of the PMS also take part in the degradation reaction, although their contribution is limited. In addition, the influence of some key factors including the water content and time on the grinding and AO7 degradation was explored. The results of this study provide deep insight into mechanochemical activation of PMS with manganese oxides for enhanced degradation of pollutants in aqueous solution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.L. James, C.J. Adams, C. Bolm, D. Braga, P. Collier, T. Friscic, F. Grepioni, K.D.M. Harris, G. Hyett, W. Jones, A. Krebs, J. Mack, L. Maini, A.G. Orpen, I.P. Parkin, W.C. Shearouse, J.W. Steed, D.C. Waddell, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 413 (2012)
G.-W. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 7668 (2013)
Q. Tan, J. Li, Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 5849 (2015)
A. Fischer, C. Ney, G. Kickelbick, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 5701 (2013)
A. Nasser, U. Mingelgrin, Appl. Clay Sci. 67–68, 141 (2012)
X. Guo, D. Xiang, G. Duan, P. Mou, Waste Manag. 30, 4 (2010)
G. Cagnetta, J. Robertson, J. Huang, K. Zhang, G. Yu, J. Hazard. Mater. 313, 85 (2016)
S. Lu, J. Huang, Z. Peng, X. Li, J. Yan, Chem. Eng. J. 195–196, 62 (2012)
S. Deng, S. Kang, N. Feng, J. Zhu, B. Yu, X. Xie, J. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater. 333, 116 (2017)
P. Di Leo, M.D.R. Pizzigallo, V. Ancona, F. Di Benedetto, E. Mesto, E. Schingaro, G. Ventruti, J. Hazard. Mater. 244–245, 303 (2013)
A. Nasser, G. Sposito, M.A. Cheney, Colloids Surf., A 163, 117 (2000)
P. Di Leo, M.D.R. Pizzigallo, V. Ancona, F. Di Benedetto, E. Mesto, E. Schingaro, G. Ventruti, J. Hazard. Mater. 201–202, 148 (2012)
A. J., D.A. J., P.W. G., Phys. Status Solidi B 3, 2275 (1963)
W. Zhang, H. Wang, H. Jun, M. Yu, F. Wang, L. Zhou, G. Yu, Chem. Eng. J. 239, 185 (2014)
X. Liu, X. Zhang, K. Zhang, C. Qi, Chemosphere 150, 551 (2016)
J. Wang, S. Wang, Chem. Eng. J. 334, 1502 (2018)
P. Hu, M. Long, Appl. Catal. B 181, 103 (2016)
C. Tan, N. Gao, Y. Deng, J. Deng, S. Zhou, J. Li, X. Xin, J. Hazard. Mater. 276, 452 (2014)
S. Luo, L. Duan, B. Sun, M. Wei, X. Li, A. Xu, Appl. Catal. B 164, 92 (2015)
L. Duan, B. Sun, M. Wei, S. Luo, F. Pan, A. Xu, X. Li, J. Hazard. Mater. 285, 356 (2015)
J. Li, J. Fang, L. Gao, J. Zhang, X. Ruan, A. Xu, X. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. 402, 352 (2017)
A. Iyer, H. Galindo, S. Sithambaram, C. King’ondu, C.-H. Chen, S.L. Suib, Appl. Catal., A 375, 295 (2010)
R. Wang, J. Li, Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 4282 (2010)
V.P. Santos, O.S.G.P. Soares, J.J.W. Bakker, M.F.R. Pereira, J.J.M. Órfão, J. Gascon, F. Kapteijn, J.L. Figueiredo, J. Catal. 293, 165 (2012)
K. Selvakumar, S.M. Senthil Kumar, R. Thangamuthu, G. Kruthika, P. Murugan, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39, 21024 (2014)
X. Du, Y. Zhang, I. Hussain, S. Huang, W. Huang, Chem. Eng. J. 313, 1023 (2017)
M. Wei, L. Gao, J. Li, J. Fang, W. Cai, X. Li, A. Xu, J. Hazard. Mater. 316, 60 (2016)
J. Wan, L. Zhou, H. Deng, F. Zhan, R. Zhang, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 407, 67 (2015)
C.K. Remucal, M. Ginder-Vogel, Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 16, 1247 (2014)
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support provided by the Science and Technology Research Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (D20181706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, P., Wang, M., Wei, Y. et al. Mechanochemical formation of highly active manganese species from OMS-2 and peroxymonosulfate for degradation of dyes in aqueous solution. Res Chem Intermed 45, 935–946 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3653-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3653-0