Abstract
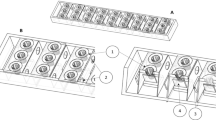
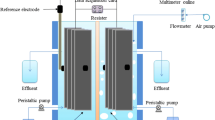
In this study, five two-chambered microbial fuel cells (MFCs) were hydraulically connected in series to constitute a MFC stack, which was integrated into a sink drain pipe for kitchen wastewater treatment. Performances of the MFC stack operating with artificial and real wastewater were studied. Considering the practical application, the voltage response to different flow rates and temperatures of the substrate was also investigated. It was found that the MFC stack could achieve a reasonable performance, with an average open circuit voltage of 3.44 ± 0.02 V, a peak power of 45.74 ± 1.39 mW (i.e. 809.27 mW/m2) and a coulombic efficiency of 78.2 ± 3.6 %. The MFC performance was disturbed by the flushing process, but could recover after a few minutes. The results also suggest that the MFC stack can operate after flushing by the substrate at 50 °C, above which irreversible performance deterioration was observed. The proposed MFC stack is expected to serve as a potential power source for lighting and low-power devices, especially in off-grid rural areas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.E. Logan, Microbial Fuel Cells (Wiley, London, 2008)
S. Atkinson, Membr. Technol. 2006, 8 (2006)
B.E. Logan, B. Hamelers, R. Rozendal, U. Schröder, J. Keller, S. Freguia, P. Aelterman, W. Verstraete, K. Rabaey, Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 5181 (2006)
B.E. Logan, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85, 1665 (2010)
H. Liu, R. Ramnarayanan, B.E. Logan, Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 2281 (2004)
K. Rabaey, P. Clauwaert, P. Aelterman, W. Verstraete, Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 8077 (2005)
Z. He, S.D. Minteer, L.T. Angenent, Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 5262 (2005)
L. Zhang, J. Li, X. Zhu, D. Ye, Q. Liao, Chem. Eng. J. 223, 623 (2013)
X. Zhu, L. Zhang, J. Li, Q. Liao, D. Ye, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38, 15716 (2013)
F. Zhang, Z. Ge, J. Grimaud, J. Hurst, Z. He, Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 4941 (2013)
Y. Kim, M.C. Hatzell, A.J. Hutchinson, B.E. Logan, Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 4662 (2011)
B.H. Kim, I.S. Chang, G.M. Gadd, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76, 485 (2007)
B. Wang, J.-I. Han, Biotechnol. Lett. 31, 387 (2009)
L. Zhuang, Y. Zheng, S. Zhou, Y. Yuan, H. Yuan, Y. Chen, Bioresour. Technol. 106, 82 (2012)
L. Zhuang, Y. Yuan, Y. Wang, S. Zhou, Bioresour. Technol. 123, 406 (2012)
L. Zhuang, S. Zhou, Electrochem. Commun. 11, 937 (2009)
S.-E. Oh, B.E. Logan, J. Power Sources 167, 11 (2007)
A. Dekker, A.T. Heijne, M. Saakes, H.V.M. Hamelers, C.J.N. Buisman, Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 9038 (2009)
R.A. Rozendal, H.V.M. Hamelers, K. Rabaey, J. Keller, C.J.N. Buisman, Trends Biotechnol. 26, 450 (2008)
A. Janicek, Y. Fan, H. Liu, Biofuels 5, 79 (2014)
K. Scott, C. Murano, G. Rimbu, J. Appl. Electrochem. 37, 1063 (2007)
Y. Hong, D.F. Call, C.M. Werner, B.E. Logan, Biosens. Bioelectron. 28, 71 (2011)
S.E. Oh, J.R. Kim, J.-H. Joo, B.E. Logan, Water Sci. Technol. 60, 1311 (2009)
R.A. Rozendal, H.V.M. Hamelers, C.J.N. Buisman, Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 5206 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural and Science Foundation of China (No. 51376203), the National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (No. 51325602), the National Natural and Science Foundation of China (No.51276208) and Overseas, Hong Kong & Macao Scholars Collaborated Research Fund (No.51428601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, D., Deng, B., Li, J. et al. Electricity production of a microbial fuel cell stack integrated into a sink drain pipe. Res Chem Intermed 42, 7689–7700 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2654-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2654-0