Abstract
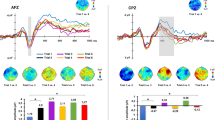
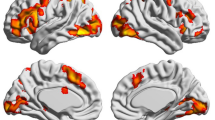
According to the Universal Writing System Constraint, all writing systems encode language, and thus reflect basic properties of the linguistic system they encode. According to a second universal, the Universal Phonological Principle, the activation of word pronunciations occurs for skilled readers across all writing systems. We review recent research that illustrates the implications of these two universal principles both across and within writing systems. Within the family of alphabetic systems, differences between Korean and English arise in the languages, rather than the orthographies, while the reverse appears to be true for German and English differences. Across writing systems, new Event Related Potentials (ERP) experiments show the robustness of phonology across Chinese and English systems and chart the time course of word reading in Chinese and English for Chinese bilinguals and for English speakers learning Chinese. The ERP results show differences between Chinese and English for both groups and suggest that the time course of word processes and the brain areas identified as sources for the ERP components differ both as a result of writing system and the skill of the reader. We propose the System Accommodation Hypothesis, that reading processes and the neural structures that support them accommodate to specific visual and structural features of a new writing system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Booth C.A. Perfetti (2002) ArticleTitleOnset and rime structure influences naming but not early word identification in children and adults Scientific Studies of Reading 6 IssueID1 1–23 Occurrence Handle10.1207/S1532799XSSR0601_01
J.A. Bowey J. Hansen (1994) ArticleTitleThe development of orthographic rimes as units of word recognition Journal of Experimental Child psychology 58 465–488 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jecp.1994.1045
M.W. Chee B. Weekes K.M. Lee C.S. Soon A. Schreiber J.J. Hoon et al. (2000) ArticleTitleOverlap and dissociation of semantic processing of Chinese characters, English words, and pictures: evidence from FMRI [In Process Citation] Neuroimage 12 IssueID4 392–403 Occurrence Handle10.1006/nimg.2000.0631 Occurrence Handle10988033
J. DeFrancis (1989) Visible speech: The diverse oneness of writing systems University of Hawaii Press Honolulu, HI, US
J.A. Fiez D.A. Balota M.E. Raichle S.E. Petersen (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of lexicality, frequency, and spelling-to-sound consistency on the functional anatomy of reading Neuron 24 205–218 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80833-8 Occurrence Handle10677038
J.A. Fiez S.E. Petersen (1998) ArticleTitleNeuroimaing studies of word reading Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95 914–921 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.95.3.914 Occurrence Handle9448259
S. Francis H. Kucera (1967) Computing Analysis of Present-day American English Brown University Press Providence, RI
D.L. Hung O.J.L. Tzeng A.K.Y. Tzeng (1992) Automatic activation of linguistic information in Chinese character recognition R. Frost (Eds) Orthography, phonology, morphology, and meaning North-Holland Amsterdam, Netherlands 119–130
Z.J. Koles (1998) ArticleTitleTrends in EEG source localization Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology: Evoked Potentials 106 127–137 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0013-4694(97)00115-6
M. Kutas S.A. Hillyard (1980) ArticleTitleEvent-related brain potentials to semantically inappropriate and surprisingly large words Biological Psychology 11 IssueID2 99–116 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0301-0511(80)90046-0 Occurrence Handle7272388
Y. Liu C.A. Perfetti L. Hart (2003) ArticleTitleERP evidence for the time course of graphic, phonological and semantic information in Chinese meaning and pronunciation decisions Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 29 IssueID6 1231–1247
Liu, Y., Perfetti, C. A., Wang, M. (2003, March). Learning to read in a new writing system: Evidence from event related potentials. Paper presented as a poster at the 10th Annual Meeting of Cognitive Neuroscience Society, New York, US.
R.D. Pascual Marqui C.M. Michel D. Lehmann (1994) ArticleTitleLow resolution electromagnetic tomography: A new method for localizing electrical activity in the brain International Journal of Psychophysiology 18 IssueID1 49–65 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0167-8760(84)90014-X Occurrence Handle7876038
E. Paulesu J.F. Démonet F. Fazio E. McCrory V. Chanoine N. Brunswick S.F. Cappa G. Cossu M. Habib C.D. Frith U. Frith (2001) ArticleTitleDyslexia: Cultural Diversity and Biological Unity Science 16 IssueID291 2165–2167 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1057179
C.A. Perfetti L. Bell (1991) ArticleTitlePhonemic activation during the first 40 ms of word identification: Evidence from backward masking and masked priming Journal of Memory and Language 30 473–485 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0749-596X(91)90017-E
C.A. Perfetti Y. Liu L.H. Tan (2002) How the mind meets the brain in reading: A comparative writing systems approach H.S.R. Kao C.K. Leong D.G. Gao (Eds) Cognitive Neuroscience Studies of the Chinese language Hong Kong University Press Hong Kong
C.A. Perfetti L.H. Tan (1998) ArticleTitleThe time course of graphic, phonological, and semantic activation in Chinese character identification Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 24 IssueID1 101–118
C.A. Perfetti S. Zhang (1995) ArticleTitleVery early phonological activation in Chinese reading Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 21 IssueID1 24–33
C.A. Perfetti S. Zhang I. Berent (1992) Reading in English and Chinese: Evidence for a “universal” phonological principle R. Frost (Eds) Orthography, phonology, morphology, and meaning North-Holland Amsterdam 227–248
M.D. Rugg (1984) ArticleTitleEvent-related potentials in phonological matching tasks Brain and Language 23 IssueID2 225–240 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0093-934X(84)90065-8 Occurrence Handle6518354
L.H. Tan H.-L. Liu C.A. Perfetti J.A. Spinks P.T. Fox J.-H. Gao (2001) ArticleTitleThe neural system underlying Chinese logograph reading NeuroImage 13 836–846 Occurrence Handle10.1006/nimg.2001.0749 Occurrence Handle11304080
L.H. Tan C.A. Perfetti (1998) ArticleTitlePhonological codes as early sources of constraint in Chinese word identification: A review of current discoveries and theoretical accounts Reading and Writing 10 IssueID3–5 165–200 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008086231343
L.H. Tan J.A. Spinks J.H. Gao H.L. Liu C.A. Perfetti J. Xiong et al. (2000) ArticleTitleBrain activation in the processing of Chinese characters and words: A functional MRI study Human Brain Mapping 10 IssueID1 16–27 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(200005)10:1<16::AID-HBM30>3.0.CO;2-M Occurrence Handle10843515
G.C. Orden ParticleVan (1987) ArticleTitleA ROWS is a ROSE: spelling, sound, and reading Memory and Cognition 15 IssueID3 181–198
Y. Xu A. Pollatsek M.C. Potter (1999) ArticleTitleThe activation of phonology during silent Chinese word reading Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 25 IssueID4 838–857
S. Zhang C.A. Perfetti (1993) ArticleTitleThe tongue-twister effect in reading Chinese Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 19 IssueID5 1082–1093
S. Zhang C.A. Perfetti H. Yang (1999) ArticleTitleWhole word, frequency-general phonology in semantic processing of Chinese characters Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 25 IssueID4 858–875
J.C. Ziegler A.M. Jacobs G.O. Stone (1996) ArticleTitleStatistical analysis of the bidirectional inconsistency of spelling and sound in French Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, Computers 28 504–515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research reported in this paper was made possible by National Science Foundation award BN0113243 to the first author.