Abstract
Background and aims
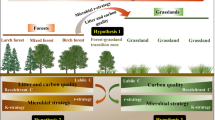
Irrigation-maintained artificial oases (AO) in arid regions of northwestern China provide vital human settlement sites. Recent human population increases has caused rapid AO expansion, mainly through transforming natural grassland to arable and afforested land. Here, we assessed how soil biodiversity is affected by various AO expansion strategies, each representing historical land-use regimes.
Methods
We sampled six dominant functional groups of soil biota, covering multiple trophic levels: macrofauna consumers (predators and insect herbivores), mesofauna decomposers (Oribatida and Collembola), and microbial decomposers (bacteria and fungi). Sampling was carried out in three AO sites of northwestern China, each containing distinct land uses: natural grasslands (NG; non-irrigated), shrub (Haloxylon ammodendron) plantations (SP; non-irrigated), tree (Populus gansuensis) plantations (TP; irrigated), and arable lands (AL; irrigated).
Results
The conversion of NG to SP, TP, and AL eliminated or reduced the abundance of some NG-adapted taxa. Their replacements were exotic species better suited for anthropogenic habitats. As a result, community composition shifted in all six functional groups, with greater differences between NG and TP and AL than between NG and SP. Based on taxonomic gains and losses within each group, we determined that NG to SP conversion positively affected diversity among predators, Collembola, and fungi, but negatively affected diversity of insect herbivores and Oribatida. Bacterial diversity remained unaffected. However, converting NG to TP and AL significantly promoted diversity in all six functional groups, although effect sizes differed.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that different AO expansion strategies differentially affected the diversity and structure of belowground communities, which in turn, cascaded down to ecosystem functioning differently. These findings not only contribute to a better understanding of how the diversity and community composition within soil food-webs respond to land-use change but also provide key insights into the development of management strategies for AO ecosystems in drylands to mitigate the negative impact of land-use change on soil biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew DR, Fitak RR, Munguia-Vega A, Racolta A, Martinson VG, Dontsova K (2012) Abiotic factors shape microbial diversity in Sonoran Desert soils. Appl Environ Microb 78:7527–7537
Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 515:505–511
Barnes AD, Jochum M, Mumme S, Haneda NF, Farajallah A, Widarto TH, Brose U (2014) Consequences of tropical land use for multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nat Commun 5: 5351. doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6351
Böhm SM, Wells K, Kalko EKV (2011) Top-down control of herbivory by birds and bats in the canopy of temperate broad-leaved oaks (Quercus robur). PLoS ONE 6:e17857. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017857
Brockett BFT, Prescott CE, Grayston SJ (2010) Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol Biochem 44:9–20
Buchmann CM, Schurr FM, Nathan R, Jeltsch F (2013) Habitat loss and fragmentation affecting mammal and bird communities-the role of interspecific competition and individual space use. Ecol Inform 14:90–98
Byrnes JEK, Gamfeldt L, Isbell F, Duffy JE, Lefcheck JS, Griffin JN, Hector A, Cardinale BJ, Hooper DU, Dee LE (2014) Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: challenges and solutions. Methods Ecol Evol 5:111–124
Cai WZ, Pang XF, Hua BZ, Liang GW, Song DL (2011) General Entomology, second edn. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Cheng GD, Li X, Zhao WZ, Xu ZM, Feng Q, Xiao SC, Xiao HL (2014) Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River basin. Natl Sci Rev 1:413–428
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER V6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth, UK
Connolly J, Bell T, Bolger T, Brophy C, Timothee Carnus T, Finn JA, Kirwan L, Isbell F, Levine J, Lüscher A, Picasso V, Roscher C, Sebastia MT, Suter M, Weigelt A (2013) An improved model to predict the effects of changing biodiversity levels on ecosystem function. J Ecol 101:344–355
Darby BJ, Neher DA, Housman DC, Belnap J (2011) Few apparent short-term effects of elevated soil temperature and increased frequency of summer precipitation on the abundance and taxonomic diversity of desert soil micro- and meso-fauna. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1474–1481
De Groot GA, Jagers op Akkerhuis GAJM, Dimmers WJ, Charrier X, Faber JH (2016) Biomass and diversity of soil mite functional groups respond to intensification of land management, potentially affecting soil ecosystem services. Front Environ Sci 4:15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2016.00015
De Vries FT, Thébault E, Liiri M, Birkhofer K, Tsiafouli MA, Bjørnlund L, Jørgensen HB, Brady MV, Christensen S, de Ruiter PC, d'Hertefeldt T, Frouz J, Hedlund K, Hemerik L, Hol WHG, Hotes S, Mortimer SR, Setälä H, Sgardelis SP, Uteseny K, van der Puttenk WH, Wolters V, Bardgett RD (2013) Soil food web properties explain ecosystem services across European land use systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:14296–14301
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Reich PB, Jeffries TC, Gaitan JJ, Encinar D, Berdugo M, Campbell CD, Singh BK (2016) Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat Commun 7:10541. doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10541
Ewers RM, Didham RK (2006) Confounding factors in the detection of species responses to habitat fragmentation. Biol Rev 81:117–142
Fahrig L (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu Rev Ecol Evol S 34:487–515
Fahrig L (2017) Ecological responses to habitat fragmentation per se. Annu Rev Ecol Evol S 48:1–23
Falcucci A, Maiorano L, Boitani L (2007) Changes in land-use/land-cover patterns in Italy and their implications for biodiversity conservation. Landsc Ecol 22:617–631
Feng Q, Li FR, Liu JL, Sun TS, Chen LJ (2015) Ground-dwelling arthropod community response to native grassland conversion in a temperate desert of northwestern China. J Insect Conserv 19:105–117
Filazzola A, Westphal M, Powers M, Liczner AR, Woollett DAS, Johnson B, Lortie CJ (2017) Non-trophic interactions in deserts: facilitation, interference, and an endangered lizard species. Basic Appl Ecol 20:51–61
Filser J (2002) The role of Collembola in carbon and nitrogen cycling in soil. Pedobiologia 46:234–245
Filser J, Fromm H, Nagel RF, Winter K (1995) Effects of previous intensive agricultural management on microorganisms and the biodiversity of soil fauna. Plant Soil 170:123–129
Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS III, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309:570–574
Fu SL, Zou XM, Coleman DC (2009) Highlights and perspectives of soil biology and ecology research in China. Soil Biol Biochem 41:868–876
Gao MX, Sun X, Wu DH, Zhang XP (2014) Spatial autocorrelation at multi-scales of soil collembolan community in farmland of the Sanjiang plain, Northeast China. Acta Ecol Sin 34(17):4980–4990 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Goudard A, Loreau M (2008) Nontrophic interactions, biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: an interaction web model. Am Nat 171:91–106
Griffin JN, Byrnes JEK, Cardinale BJ (2013) Effects of predator richness on prey suppression: a meta-analysis. Ecology 94:2180–2187
Griffiths RI, Thomson BC, Plassart P, Gweon HS, Stone D, Creamer RE, Lemanceau P, Bailey MJ (2016) Mapping and validating predictions of soil bacterial biodiversity using European and national scale datasets. Appl Soil Ecol 97:61–68
Guisan A, Rahbek C (2011) SESAM—A new framework integrating macroecological and species distribution models for predicting spatiotemporal patterns of species assemblages. J Biogeogr 38:1433–1444
Holt RD (1997) Community modules. In: Gange AC, Brown VK (eds) Multitrophic interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Blackwell scientific, Oxford, UK, pp 333–349
Huffaker CB, Simmonds FJ, Laing JE (1976) The theoretical and empirical basis of biological control. In: Huffaker CB, Messenger PS (eds) Theory and practice of biological control. Academic Press, New York, pp 42–78
Jangid K, Williams MA, Franzluebbers AJ, Sanderlin JS, Reeves JH, Jenkins MB, Endale DM, Coleman DC, Whitman WB (2008) Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2843–2853
Jantz SM, Barker B, Brooks TM, Chini LP, Huang QY, Moore RM, Noel J, Hurtt GC (2015) Future habitat loss and extinctions driven by land-use change in biodiversity hotspots under four scenarios of climate-change mitigation. Conserv Biol 29:122–1131
Jetz W, Wilcove DS, Dobson AP (2007) Projected impacts of climate and land-use change on the global diversity of birds. PLoS Biology 5:e157. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050157
Jia HR, Geng LL, Li YH, Wang Q, Diao QY, Zhou T, Dai PL (2016) The effects of Bt Cry1Ie toxin on bacterial diversity in the midgut of Apis mellifera ligustica (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Scientific Reports 6:24664 | https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24664
Jing X, Sanders NJ, Shi Y, Chu HY, Classen AT, Zhao K, Chen LT, Jiang YX, He JS (2015) The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and belowground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nat Commun 6:8159. doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9159
Jørgensen HB, Johansson T, Canback B, Hedlund K, Tunlid A (2005) Selective foraging of fungi by collembolans in soil. Biol Lett 1:243–246
Kaneko N, McLean MA, Parkinson D (1998) Do mites and Collembola affect pine litter fungal biomass and microbial respiration? Appl Soil Ecol 9:209–213
Koellner T, Geyer R (2013) Global land use impact assessment on biodiversity and ecosystem services in LCA. Int J Life Cycle Ass 18:1185–1187
Krashevska V, Klarner B, Widyastuti R, Maraun M, Scheu S (2016) Changes in structure and functioning of protist (Testate Amoebae) communities due to conversion of lowland rainforest into Rubber and Oil Palm plantations. PLoS ONE 11:e0160179. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160179
Krauss J, Bommarco R, Guardiola M, Heikkinen RK, Helm A, Kuussaari M, Lindborg R, Öckinger E, Pärtel M, Pino J, Pöyry J, Raatikainen KM, Sang A, Stefanescu C, Teder T, Zobel M, Steffan-Dewenter I (2012) Habitat fragmentation causes immediate and time delayed biodiversity loss at different trophic levels. Ecol Lett 13:597–605
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araújo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Klener AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environ Microbiol 6:1244–1251
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microb 75:5111–5120
Letourneau DK, Jedlicka JA, Bothwell SG, Moreno CR (2009) Effects of natural enemy biodiversity on the suppression of arthropod herbivores in terrestrial ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:573–592
Levy-Booth DJ, Prescott CE, Susan J, Grayston SJ (2014) Microbial functional genes involved in nitrogen fixation, nitrification and denitrification in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 75:11–25
Li FR, Zhang H, Zhao LY, Shirato Y, Wang XZ (2003) Pedoecological effects of a sand-fixing poplar (Populus simonii Carr.) forest in a desertified sandy land of Inner Mongolia, China. Plant Soil 256:431–442
Li FR, Feng Q, Liu JL, Sun TS, Ren W, Guan ZH (2013) Effects of the conversion of native vegetation to farmlands on soil microarthropod biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a desert oasis. Ecosystems 16:1364–1377
Li FR, Liu JL, Sun TS, Jin BW, Chen LJ (2014) Converting natural vegetation to farmland alters functional structure of ground-dwelling beetles and spiders in a desert oasis. J Insect Conserv 18:57–67
Li CH, Tang LS, Jia ZJ, Li Y (2015) Profile changes in the soil microbial community when desert becomes oasis. PLoS ONE 10:e0139626. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139626
Li FR, Liu JL, Sun TS, Ma LF, Liu LL, Yang K (2016) Impact of established shrub shelterbelts around oases on the diversity of ground beetles in arid ecosystems of northwestern China. Insect Conserv Divers 9:135–148
Liao JB, Bearup D, Wang YQ, Nijs I, Bonte D, Li YH, Brose U, Wang SP, Blasius B (2017) Robustness of metacommunities with omnivory to habitat destruction: disentangling patch fragmentation from patch loss. Ecology 98:1631–1639
Liu YH, Yu ZR, Gu WB, Axmacher JC (2006) Diversity of carabids (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the desalinized agricultural landscape of Quzhou county, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 113(1–4):45–50
Liu JL, Li FR, Liu LL, Yang K (2017) Responses of different Collembola and mite taxa to experimental rain pulses in an arid ecosystem. Catena 155:53–61
Mackay WP, Silva S, Lightfoot DC, Pagani MI, Whitford WG (1986) Effect of increased soil moisture and reduced soil temperature on a desert soil arthropod community. Am Midl Nat 116:45–56
Maestre FT, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Jeffries TC, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Quero JL, García-Gómez M, Gallardo A, Ulrich W, Bowker MA, Arredondo T, Barraza-Zepeda C, Bran D, Florentino A, Gaitán J, Gutiérrez JR, Huber-Sannwald E, Jankju M, Mau RL, Miriti M, Naseri K, Ospina A, Stavi I, Wang D, Woods NN, Yuan X, Zaady E, Singh BK (2015) Increasing aridity reduces soil microbial diversity and abundance in global drylands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15684–15689
Mantyka-pringle CS, Martin TG, Rhodes JR (2012) Interactions between climate and habitat loss effects on biodiversity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 18:1239–1252
Maraun M, Migge S, Schaefer M, Scheu S (1998) Selection of microfungal food by six oribatid mite species (Oribatida, Acari) from two different beech forests. Pedobiologia 42:232–240
May RM, Hassell MP (1988) Population dynamics and biological control. Phil Trans R Soc B 318:129–169
McCann KS, Rasmussen JR, Umbanhowar J (2005) The dynamics of spatially coupled food webs. Ecol Lett 8:513–523
McHugh TA, Compson Z, van Gestel N, Hayer M, Ballard L, Haverty M, Hines J, Irvine N, Krassner D, Lyons T, Musta EJ, Schiff M, Zint P, Schwartz E (2017) Climate controls prokaryotic community composition in desert soils of the southwestern United States. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fix116. doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fix116
Megías AG, Sánchez-Piñero F, Hódar JA (2011) Trophic interactions in an arid ecosystem: from decomposers to top-predators. J Arid Environ 75:1333–1341
Mestre L, Piñol J, Barrientos JA, Cama A, Espadaler X (2012) Effects of ant competition and bird predation on the spider assemblage of a citrus grove. Basic Appl Ecol 13:355–362
Mortelliti A, Amori G, Capizzi D, Cervone C, Fagiani S, Pollini B, Boitani L (2011) Independent effects of habitat loss, habitat fragmentation and structural connectivity on the distribution of two arboreal rodents. J Appl Ecol 48:153–162
Neher DA, Weicht TR, Barbercheck ME (2012) Linking invertebrate communities to decomposition rate and nitrogen availability in pine forest soils. Appl Soil Ecol 54:14–23
Neilson JW, Quade J, Ortiz M, Nelson WM, Legatzki A, Tian F, LaComb M, Betancourt JL, Wing RA, Soderlund CA, Maier RM (2012) Life at the hyperarid margin: novel bacterial diversity in arid soils of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Extremophiles16:553–566
Newbold T, Hudson LN, Hill SLL, Contu S, Lysenko I, Senior RA, Börger L, Bennett DJ, Choimes A, Collen B, Day J, Palma AD, Díaz S, Echeverria-Londoño S, Edgar MJ, Feldman A, Garon M, Harrison MLK, Alhusseini T, Ingram DJ, Itescu Y, Kattge J, Kemp V, Kirkpatrick L, Kleyer M, Correia DLP, Martin CD, Meiri S, Novosolov M, Pan Y, Phillips HRP, Purves DW, Robinson A, Simpson J, Tuck SL, Weiher E, White HJ, Ewers RM, Mace GM, Scharlemann JPW, Purvis A (2015) Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 520:45–50
Nielsen UN, Osler GHR, Campbell CD, Burslem DFRP, van der Wal R (2010) The influence of vegetation type, soil properties and precipitation on the composition of soil mite and microbial communities at the landscape scale. J Biogeogr 37:1317–1328
Pasari JR, Levi T, Zavaleta ES, Tilman D (2013) Several scales of biodiversity affect ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10219–10222
Paz-Kagan T, Caras T, Herrmann I, Shachak M, Karnieli A (2017) Multiscale mapping of species diversity under changed land use using imaging spectroscopy. Ecol Appl 27:1466–1484
Riechert S, Lawrence K (1997) Test for predation effects of single versus multiple species of generalist predators: spider sand their insect prey. Entomol Exp Appl 84:147–155
Robinson SI, McLaughlin ÓB, Marteinsdóttir B, O'Gorman EJ (2018) Soil temperature effects on the structure and diversity of plant and invertebrate communities in a natural warming experiment. J Anim Ecol 87:634–646. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12798
Rousk J, Bååth E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Gregory Caporaso J, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351
Rusek J (1998) Biodiversity of Collembola and their functional role in the ecosystem. Biodivers Conserv 7:1207–1219
Schneider K, Renker C, Maraun M (2005) Oribatid mite (Acari, Oribatida) feeding on ectomycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 16:67–72
Shen CC, Xiong JB, Zhang HY, Feng YZ, Lin XG, Liang WJ, Chu HY (2013) Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol Biochem 57:204–211
Siepel H, Maaskamp F (1994) Mites of different feeding guilds affect decomposition of organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1389–1394
Soliveres S, van der Plas F, Manning P, Prati D, Gossner MM, Renner SC, Alt F, Arndt H, Baumgartner V, Binkenstein J, Birkhofer K, Blaser S, Blüthgen N, Boch S, Böhm S, Börschig C, Buscot F, Diekötter T, Heinze J, Hölzel N, Jung K, Klaus VH, Kleinebecker T, Klemmer S, Krauss J, Lange M, Morris EK, Müller J, Oelmann Y, Overmann J, Pašalić E, Rillig MC, Schaefer HM, Schloter M, Schmitt B, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Sikorski J, Socher SA, Solly EF, Sonnemann I, Sorkau E, Steckel J, Steffan-Dewenter I, Stempfhuber B, Tschapka M, Türke M, Venter PC, Weiner CN, Weisser WW, Werner M, Westphal C, Wilcke W, Wolters V, Wubet T, Wurst S, Fischer M, Allan E (2016) Biodiversity at multiple trophic levels is needed for ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature 536:456–459
Song DX, Zhu MS, Chen J (1999) The spiders of China. Hebei Science & Technology Publishing House, Baoding, China (in Chinese)
Straub CS, Snyder WE (2006) Species identity dominates the relationship between predator biodiversity and herbivore suppression. Ecology 87:277–282
Straub CS, Finke DL, Snyder WE (2008) Are the conservation of natural enemy biodiversity and biological control compatible goals? Biol Control 45:225–237
Szoboszlay M, Dohrmann AB, Poeplau C, Don A, Tebbe CC (2017) Impact of land-use change and soil organic carbon quality on microbial diversity in soils across Europe. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fix146. doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fix146
Ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012) Canoco reference manual and user's guide: Software for ordination (version 5.0). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Terrat S, Horrigue W, Dequietd S, Saby NPA, Lelièvre M, Nowak V, Tripied J, Régnier T, Jolivet C, Arrouays D, Wincker P, Cruaud C, Karimi B, Bispo A, Maron PA, Prévost-Bouré NC, Ranjard L (2017) Mapping and predictive variations of soil bacterial richness across France. PLoS ONE 12: e0186766. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186766
Tian Y, Tashpolat T, Li Y, Tang LS, Fan LL (2014) The survival and above/below ground growth of Haloxylon ammodendron seedlings. Acta Ecol Sin 34:2012–2019 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tscharntke T, Bommarco R, Clough Y, Crist TO, Kleijn D, Rand TA, Tylianakis JM, van Nouhuys S, Vidal S (2007) Conservation biological control and enemy diversity on a landscape scale. Biol Control 43:294–309
Tylianakis JM, Romo CM (2010) Natural enemy diversity and biological control: making sense of the context-dependency. Basic Appl Ecol 11:657–668
Van Nouhuys S (2005) Effects of habitat fragmentation on different trophic levels in insect communities. Ann Zool Fenn 42:433–447
Wagg C, Bender SF, Widmer F, van der Heijden MGA (2014) Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:5266–5270
Wang Q, Li FR, Zhao L, Zhang EH, Shi SL, Zhao WZ, Song WX, Vance MM (2010) Effects of irrigation and nitrogen application rates on nitrate nitrogen distribution and fertilizer nitrogen loss, wheat yield and nitrogen uptake on a recently reclaimed sandy farmland. Plant Soil 337:325–339
Whitford WG, Parker LW (1989) Contributions of soil fauna to decomposition and mineralization processes in semiarid and arid ecosystems. Arid Land Res Manag 3:199–215
Xia WW, Zhang CX, Zeng XW, Feng YZ, Weng JH, Lin XG, Zhu JG, Xiong ZQ, Xu J, Cai ZC, Jia ZJ (2011) Autotrophic growth of nitrifying community in an agricultural soil. The ISME Journal 5:1226–1236
Yin WY (2000) Pictorial keys to soil animals of China. Science Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Zhang L, Zhang X, Cui W (2014) Relationship between land use pattern and the structure and diversity of soil meso-micro arthropod community. Ecotoxicology 23:707–717
Zhao WZ, Yang R, Liu B, Yang QY, Li F (2016) Oasification of northwestern China: a review. J Desert Res 36:1–5 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng LY, Gui H (2004) Classification of insects in China. Nanjing Normal University publishing house. Nanjing, China (in Chinese)
Zhou XY (2012) Cloning of genes with salt resistance from Haloxylon ammodendron and transformation research on HaPrxQ. Ningxia University, Master Thesis (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the farmers and land managers who allowed us to work in their arable fields and tree/shrub plantations. We acknowledge the two anonymous reviewers for providing valuable comments and suggestions that significantly improved the quality of the manuscript. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 41471210) and the West Light Program for Talent Cultivation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Simon Jeffery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, FR., Liu, JL., Ren, W. et al. Land-use change alters patterns of soil biodiversity in arid lands of northwestern China. Plant Soil 428, 371–388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3673-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3673-y