Abstract
Aims
Soil hydrolysable P can be a main P source for biota in P-limited tropical rain forests. Soil hydrolysable P occurs in various chemical fractions, including, monoester P, diester P, pyrophosphate and phytate, which need enzymatic hydrolysis into orthophosphate before their assimilation into biota. We examined whether P-limited plants and microbes preferentially hydrolyzed specific fraction of soil hydrolysable P and whether those in different successional stages had different abilities to hydrolyze various soil hydrolysable P.
Methods
We measured four classes of phosphatase (phosphomonoesterase, PME; phosphodiesterase, PDE; pyrophosphatase, PyP; and phytase, PhT) activities for fine-roots and soils in nitrogen (N) and P fertilized primary and secondary tropical rain forests in Sabah, Malaysia.
Results
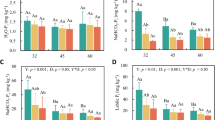
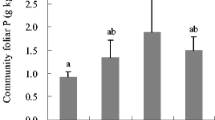
P fertilization reduced PME, PyP and PhT activities for fine-roots and PME and PyP activities for soils. Fine-roots in primary forests had higher PME and PyP activities whereas those in secondary forests had higher PhT activities.
Conclusions
We suggest that P-limited trees and microbes depend more on hydrolysable P degraded by one step of enzymatic reaction (monoester P, pyrophosphate, and phytate) as a P source. We also suggest that trees have different soil-organic-P acquisition strategies in association with their life history strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PME:
-
Phosphomonoesterase
- PDE:
-
Phosphodiesterase
- PyP:
-
Pyrophosphatase
- PhT:
-
Phytase
References
Allison VJ, Condron LM, Peltzer DA, Richardson SJ, Turner BL (2007) Changes in enzyme activities and soil microbial community composition along carbon and nutrient gradients at the Franz Josef chronosequence, New Zealand. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1770–1781. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.02.006
Aoki M, Fujii K, Kitayama K (2012) Environmental control of root exudation of low-molecular weight organic acids in tropical rainforests. Ecosystems 15:1194–1203. doi:10.1007/s10021-012-9575-6
Aoyagi R, Imai N, Kitayama K (2013) Ecological significance of the patches dominated by pioneer trees for the regeneration of dipterocarps in a Bornean logged-over secondary forest. Forest Ecol Manag 289:378–384. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.037
Brundrett MC (2009) Mycorrhizal associations and other means of nutrition of vascular plants: understanding the global diversity of host plants by resolving conflicting information and developing reliable means of diagnosis. Plant Soil 320(1–2):37–77. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9877-9
Celi L, Barberis E (2007) Abiotic reactions of inositol phosphates in soil. In: Turner BL, Richardson AE, Mullaney EJ (eds) Inositol phosphates: linking agriculture and the environment. Biddles Ltd., UK, pp 207–220
Clarholm M (1993) Microbial biomass P, labile P, and acid phosphatase activity in the humus layer of a spruce forest, after repeated additions of fertilizers. Biol Fertil Soils 16:287–292. doi:10.1007/BF00369306
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Schmidt SK (2002) Phosphorus limitation of microbial processes in moist tropical forests: evidence from short-term laboratory incubations and field studies. Ecosystems 5:680–691. doi:10.1007/s10021-002-0202-9
Dick WA, Tabatabai MA (1978) Inorganic pyrophosphatase activity of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 10:58–65. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(78)90011-1
Fanin N, Hättenschwiler S, Schimann H, Fromin N (2015) Interactive effects of C, N and P fertilization on soil microbial community structure and function in an Amazonian rain forest. Funct Ecol 29(1):140–150. doi:10.1111/1365-2435.12329
Finegan B (1996) Pattern and process in Neotropical secondary rain forests, the first 100 years of succession. Trends Ecol Evol 11:119–124. doi:10.1016/0169-5347(96)81090-1
Fujii K, Aoki M, Kitayama K (2012) Biodegradation of low molecular weight organic acids in rhizosphere soils from a tropical montane rain forest. Soil Biol Biochem 47:142–148. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.018
George TS, Gregory PJ, Hocking P, Richardson AE (2008) Variation in root-associated phosphatase activities in wheat contributes to the utilization of organic P substrates in vitro, but does not explain differences in the P-nutrition of plants when grown in soils. Environ Exp Bot 64:239–249. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.05.002
Gerke J (2015) The acquisition of phosphate by higher plants: effect of carboxylate release by the roots. A Critical Review J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:351–364. doi:10.1002/jpln.201400590
Giles CD, Cade-menun BJ, Hill JE (2011) The inositol phosphates in soils and manures : abundance, cycling, and measurement. Can J Soil Sci 3:397–416. doi:10.4141/CJSS09090
Hall SJ, Asner GP, Kitayama K (2004) Substrate, climate, and land use controls over soil N dynamics and N-oxide emissions in Borneo. Biogeochemistry 70:27–58. doi:10.1023/B:BIOG.0000049335.68897.87
Hayes JE, Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (2000) Components of organic phosphorus in soil extracts that are hydrolised by phytase and acid phosphatase. Biol Fertil Soils 32:279–286. doi:10.1007/s003740000249
Heuck C, Weig A, Spohn M (2015) Soil microbial biomass C: N: P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 85:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.02.029
Hietz P, Turner BL, Wanek W, Richter A, Nock CA, Wright SJ (2011) Long-term change in the nitrogen cycle of tropical forests. Science 334(6056):664–666. doi:10.1126/science.1211979
Imai N, Kitayama K, Titin J (2010) Distribution of phosphorus in an above-to-below-ground profile in a Bornean tropical rain forest. J Trop Ecol 26:627–636. doi:10.1017/S0266467410000350
Imai N, Samejima H, Langner A, Ong RC, Kita S, Titin J, Chung AYC, Lagan P, Lee YF, Kitayama K (2009) Co-benefits of sustainable forest management in biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration. PLoS One 4. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008267
Imai N, Seino T, Aiba S, Takyu M, Titin J, Kitayama K (2012) Effects of selective logging on tree species diversity and composition of Bornean tropical rain forests at different spatial scales. Plant Ecol 213:1413–1424. doi:10.1007/s11258-012-0100-y
Ishidzuka N (1999) Soil enzyme activities in: the Japanese Society of Forest Environment (ed) the methods of forest environment studies (in Japanese). Hakuyusha, Tokyo, pp 219–222
Jackson RB, Mooney HA, Schulze ED (1997) A global budget for fine root biomass, surface area, and nutrient contents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7362–7366. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7362
Janos DP (1980) Mycorrhizae influence tropical succession. Biotropica 12(2):56–64. doi:10.2307/2388157
Jenkinson DS, Brookes PC, Powlson DS (2004) Measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 36:5–7. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2003.10.002
Keiluweit M, Bougoure JJ, Nico PS, Pett-Ridge J, Weber PK, Kleber M (2015) Mineral protection of soil carbon counteracted by root exudates. Nat Clim Chang 5:588–595. doi:10.1038/nclimate2580
Kitayama K (2013) The activities of soil and root acid phosphatase in the nine tropical rain forests that differ in phosphorus availability on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Plant Soil 367:215–224. doi:10.1007/s11104-013-1624-1
Kitayama K, Aiba S (2002) Ecosystem structure and productivity of tropical rain forests along altitudinal gradients with contrasting soil phosphorus pools on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. J Ecol 90:37–51. doi:10.1046/j.0022-0477.2001.00634.x
Kitayama K, Majalap-Lee N, Aiba S (2000) Soil phosphorus fractionation and phosphorus-use efficiencies of tropical rainforests along altitudinal gradients of Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Oecologia 123:342–349. doi:10.1007/s004420051020
Kuzyakov Y, Cheng W (2001) Photosynthesis controls of rizosphere respiration and organic mater decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1915–1925. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00117-1
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193:696–704. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03967.x
Marschner P, Crowley D, Rengel Z (2011) Rhizosphere interactions between microorganisms and plants govern iron and phosphorus acquisition along the root axis - model and research methods. Soil Biol Biochem 43:883–894. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.01.005
McDowell RW, Cade-Menun B, Stewart I (2007) Organic phosphorus speciation and pedogenesis: analysis by solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur J Soil Sci 58:1348–1357. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.00933.x
Menezes-Blackburn D, Jorquera M, Greiner R, Gianfreda L, De La Luz MM (2013) Phytases and phytase-labile organic phosphorus in manures and soils. Crit Rev Environ Sci Tech 43:916–954. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.627019
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Renella G, Puglisi E, Ceccanti B, Masciandaro G, Fornasier F, Moscatelli MC, Marinari S (2012) Soil enzymology: classical and molecular approaches. Biol Fertil Soils 48:743–762. doi:10.1007/s00374-012-0723-0
Nash DM, Haygarth PM, Turner BL, Condron LM, McDowell RW, Richardson AE, Watkins M, Heaven MW (2014) Using organic phosphorus to sustain pasture productivity: a perspective. Geoderma 221-222:11–19. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.12.004
Olander LP, Vitousek PM (2000) Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability. Biogeochemistry 49:175–190. doi:10.1023/A:1006316117817
Ong RC, Langner A, Imai N, Kitayama K (2013) Management history of the study sites: the Deramakot and Tangkulap Forest reserves. In: Kitayama K (ed) Co-benefits of sustainable Forestry. Springer, Japan pp, pp 1–21
Ostertag R (2001) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus availability on fine-root dynamics in Hawaiian montane forests. Ecology 82(2):485–499. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[0485:EONAPA]2.0.CO;2
Phillips RP, Fahey TJ (2006) Tree species and mycorrhizal associations influence the magnitude of rhizosphere effects. Ecology 87(5):1302–1313. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1302:TSAMAI]2.0.CO;2
Reitzel K, Turner BL (2014) Quantification of pyrophosphate in soil solution by pyrophosphatase hydrolysis. Soil Biol Biochem 74:95–97. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.001
Richardson AE, Hadobas PA, Hayes JE (2000) Acid phosphomonoesterase and phytase activities of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) roots and utilization of organic phosphorus substrates by seedlings grown in sterile culture. Plant Cell Environ 23:397–405. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2000.00557.x
Sabah Forestry Department (2005) Forest management plan 2. Deramakot Forest Reserve, Forest Management Unit No. 19, Sandakan
Sanguin H, Wilson NL, Kertesz MA (2015) Assessment of functional diversity and structure of phytate-hydrolysing bacterial community in Lolium perenne rhizosphere. Plant Soil 401:151–167. doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2512-7
Smith AP, Marin-Spiotta E, Balser T (2015) Successional and seasonal variations in soil and litter microbial community structure and function during tropical postagricultural forest regeneration: a multiyear study. Glob Chang Biol 21:3532–3547. doi:10.1111/gcb.12947
Strickland MS, Rousk J (2010) Considering fungal: bacterial dominance in soils - methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1385–1395. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.05.007
Stutter MI, Shand CA, George TS, Blackwell MSA, Dixon L, Bol R, MacKay RL, Richardson AE, Condron LM, Haygarth PM (2015) Land use and soil factors affecting accumulation of phosphorus species in temperate soils. Geoderma 257-258:29–39. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.03.020
Sullivan BW, Alvarez-Clare S, Castle SC, Porder S, Reed SC, Schreeg L, Townsend AR, Cleveland CC (2014) Assessing nutrient limitation in complex forested ecosystems: alternatives to large-scale fertilization experiments. Ecology 95:668–681. doi:10.1890/13-0825.1
Treseder KK, Vitousek PM (2001) Effects of soil nutrient availability on investment in acquisition of N and P in Hawaiian rain forests. Ecology 82:946–954. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[0946:EOSNAO]2.0.CO;2
Turner BL (2008) Resource partitioning for soil phosphorus: a hypothesis. J Ecol 96:698–702. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01384.x
Turner BL (2010) Variation in pH optima of hydrolytic enzyme activities in tropical rain Forest soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6485–6493. doi:10.1128/AEM.00560-10
Turner BL, Condron LM, Richardson SJ, Peltzer DA, Allison VJ (2007) Soil organic phosphorus transformations during pedogenesis. Ecosystems 10:1166–1181. doi:10.1007/s10021-007-9086-z
Turner BL, Engelbrecht BMJ (2011) Soil organic phosphorus in lowland tropical rain forests. Biogeochemistry 103:297–315. doi:10.1007/s10533-010-9466-x
Turner BL, Haygarth PM (2005) Phosphatase activity in temperate pasture soils: potential regulation of labile organic phosphorus turnover by phosphodiesterase activity. Sci Total Environ 344:27–36. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.003
Turner BL, McKelvie ID, Haygarth PM (2002) Characterisation of water-extractable soil organic phosphorus by phosphatase hydrolysis. Soil Biol Biochem 34(1):27–35. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00144-4
Turner BL, Wright SJ (2014) The response of microbial biomass and hydrolytic enzymes to a decade of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium addition in a lowland tropical rain forest. Biogeochemistry 117:115–130. doi:10.1007/s10533-013-9848-y
Ushio M, Fujiki Y, Hidaka A, Kitayama K (2015) Linkage of root physiology and morphology as an adaptation to soil phosphorus impoverishment in tropical montane forests. Funct Ecol 29:1235–1245. doi:10.1111/1365-2435.12424
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Vincent AG, Turner BL, Tanner EVJ (2010) Soil organic phosphorus dynamics following perturbation of litter cycling in a tropical moist forest. Eur J Soil Sci 61:48–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01200.x
Vincent AG, Vestergren J, Gröbner G, Persson P, Schleucher J, Giesler R (2013) Soil organic phosphorus transformations in a boreal forest chronosequence. Plant Soil 367:149–162. doi:10.1007/s11104-013-1731-z
Vitousek PM (1984) Litterfall, nutrient cycling, and nutrient limitation in tropical rainforests. Ecology 65:285–298. doi:10.2307/1939481
Vitousek PM, Sanford JR (1986) Nutrient cycling in moist tropical forest. Annu Rev Ecol Systemat 17:137–167. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.17.110186.001033
Waldrop MP, Balser TC, Firestone MK (2000) Linking microbial community composition to function in a tropical soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32(13):1837–1846
Walker TW, Syers JK (1976) The fate of phosphorus during pedogenesis. Geoderma 15:1–19. doi:10.1016/0016-7061(76)90066-5
Waring BG, Averill C, Hawkes CV (2013) Differences in fungal and bacterial physiology alter soil carbon and nitrogen cycling: insights from meta-analysis and theoretical models. Ecol Lett 16:887–894. doi:10.1111/ele.12125
Wolfenden R, Spence G (1967) Derepression of phophomonoesterase and phosphodiesterase activities in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta 146(1):296–298. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(67)90099-X
Wu J, He ZL, Wei WX, O’Donnell AG, Syers JK (2000) Quantifying microbial biomass phosphorus in acid soils. Biol Fertil Soils 32:500–507. doi:10.1007/s003740000284
Wurzburger N, Wright SJ (2015) Fine-root responses to fertilization reveal multiple nutrient limitation in a lowland tropical forest. Ecology 96(8):2137–2146. doi:10.1890/14-1362.1
Zhang A, Chen Z, Zhang G, Chen L, Wu Z (2012) Soil phosphorus composition determined by 31 P NMR spectroscopy and relative phosphatase activities influenced by land use. Eur J Soil Biol 52:73–77. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2012.07.001
Acknowledgements
We thank staffs of Sabah Forestry Department and Forest Research Centre, Sabah, for their kind assistance in all aspects. We thank local coworkers for the assistance in fieldwork. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI JP22255002 to K. Kitayama and JP15K18711 to N. Imai, and partially supplemented by JSPS KAKENHI JP16J11390 to D. Yokoyama.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tim S. George.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoyama, D., Imai, N. & Kitayama, K. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on the activities of four different classes of fine-root and soil phosphatases in Bornean tropical rain forests. Plant Soil 416, 463–476 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3225-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3225-x