Abstract
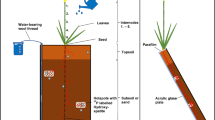
Water extraction from subsoil in upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) was examined as related to topsoil desiccation and subsoil compaction. The water extraction was observed by measurements of heavy water concentrations in transpiring plants. The plants were grown in pots that were filled with sandy soil and vertically compartmented into two columns. Heavy water was applied to the subsoil. Plants exposed to mild topsoil desiccation (−120 kPa in water potential) eventually increased water extraction from the subsoil and maintained photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance at the wet condition level. The rates of the plants subjected to severely droughted topsoil (−190 kPa) were significantly lowered due to less water uptake from the subsoil. Subsoil compaction at bulk densities of 1.45 and 1.50 Mg m−3 inhibited increase of root length densities. Limited water extraction from the subsoil was insufficient to maintain plant productivity under drought conditions. Daily water uptake per unit of root length in the lower tube did not apparently increase even if water demand on the unit root length increased. When water to topsoil was completely withheld, water extraction from the subsoil gradually increased as the topsoil dried out. Plants that were watered and rewatered took up very little water from the subsoil. The extraction from the subsoil occurred only when water potential of the topsoil was below about −190 kPa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
S G K Adiku C W Rose R D Braddock H Ozier-Lafontaine (2000) ArticleTitleOn the simulation of root water extraction: Examination of a minimum energy hypothesis Soil Sci. 165 226–236 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00010694-200003000-00005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXit1Klsbc%3D
H Araki M Iijima (1998) ArticleTitleRooting nodes of deep roots in rice and maize grown in a long tube Plant Prod. Sci. 1 242–247
T E Dawson (1993) Water sources of plants as determined from xylem-water isotopic composition: Perspectives on Plant competition, distribution, and water relations J R Ehleringer A S Hall G D Farquhar (Eds) Stable Isotopes and Plant Carbon-Water Relations Academic Press San Diego 465–496
T E Dawson R C Pausch H M Parker (1998) The role of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in understanding water movement along the soil-plant-atmospheric continuum H Griffiths (Eds) Stable Isotopes: Integration of Biological, Ecological and Geochemical Processes BIOS Scientific Publishers Oxford 169–183
M Dingkuhn A Y Audebert M P Jones K Etienne A Sow (1999) ArticleTitleControl of stomatal conductance and leaf rolling in O. sativa and O. glaberrima upland rice Field Crops Res. 61 223–236
C Doussan L Pagès G Vercambre (1998a) ArticleTitleModelling of the hydraulic architecture of root systems: An integrated approach to water absorption – Model description Ann. Bot. 81 213–223 Occurrence Handle10.1006/anbo.1997.0540
C Doussan G Vercambre L Pagès (1998b) ArticleTitleModelling of the hydraulic architecture of root systems: An integrated approach to water absorption – Distribution of axial and radial conductances in maize Ann. Bot. 81 225–232 Occurrence Handle10.1006/anbo.1997.0541
A H Fitter R K M Hay (2002) Environmental Physiology of Plants Academic Press London 131–190
L B Flanagan (1993) Environmental and biological influences on the stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of leaf water J R Ehleringer A S Hall G D Farquhar (Eds) Stable Isotopes and Plant Carbon-Water Relations Academic Press San Diego 71–90
S Fukai M Cooper (1995) ArticleTitleDevelopment of drought-resistant cultivars using physio-morphological traits in rice Field Crops Res. 40 67–86 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-4290(94)00096-U
W R Gardner (1983) Soil properties and efficient water use: An overview H M Taylor W R Jordan T R Sinclair (Eds) Limitations to Efficient Waster Use in Crop Production ASA-CSSA-SSSA Madison 45–64
W R Gardner (1991) ArticleTitleModeling water uptake by roots Irrig. Sci. 12 109–114 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00192281
B Huang J Fu (2000) ArticleTitlePhotosynthesis, respiration, and carbon allocation of two cool-season perennial grasses in surface soil drying Plant Soil 227 17–26 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026512212113 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXovVeqsw%3D%3D
M Iijima J Tatsumi Y Kono (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a device for estimating penetration resistance of the soil in the root box Environ. Control Biol. 28 53–60
A Kamoshita L Wade A Yamauchi (2000) ArticleTitleGenotypic variation in response of rainfed lowland rice to drought and rewatering. III.Water extraction during the drought period Plant Prod. Sci. 3 189–196
T Kobata T Okuno T Yamamoto (1996) ArticleTitleContributions of capacity for soil water extraction and water use efficiency to maintenance of dry matter production in rice subjected to drought Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 65 652–662 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjtlGjtQ%3D%3D
T Kobata M Hoque ParticleMd F Adachi (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of soil compaction on dry matter production and water use of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under water deficit stress during the reproductive stage Plant Prod. Sci. 3 306–315
M Kondo M V R Murty D V Aragones (2000) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of root growth and water uptake from soil in upland rice and maize under water stress Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 46 721–732
Y Li M Fuchs S Cohen Y Cohen R Wallach (2002a) ArticleTitleWater uptake profile of corn to soil moisture depletion Plant Cell Environ. 25 491–500 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.2002.00825.x
Y Li R Wallach Y Cohen (2002b) ArticleTitleThe role of soil hydraulic conductivity on the spatial and temporal variation of root water uptake in drip-irrigated corn Plant Soil 243 131–142 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1019911908635 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsFWmsbY%3D
J M Lilley S Fukai (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of timing and severity of water deficit on four diverse rice cultivars. I. Rooting pattern and soil water extraction Field Crops Res. 37 205–213 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-4290(94)90099-X
P A D Musters W Bouten (2000) ArticleTitleA method for identifying optimum strategies of measuring soil water contents for calibrating a root water uptake model J. Hydrol. 227 273–286 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00187-0
O’Toole J C 1982 Adaptation of rice to drought-prone environments. In Drought Resistance in Crops with Emphasis on Rice. Ed. International Rice Research Institute.pp. 195–213. IRRI, Los Baños.
Passioura J B 1982 The role of root system characteristics in the drought resistance of crop plants. In Drought Resistance in Crops with Emphasis on Rice. Ed. International Rice Research Institute. pp. 71–82. IRRI, Los Baños.
J B Passioura (1988) ArticleTitleWater transport in and to roots Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 39 245–265 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.pp.39.060188.001333
R E Sharp W J Davies (1985) ArticleTitleRoot growth and water uptake by maize plants in drying soil J. Exp. Bot. 36 1441–1456
E V Shein A Pachepsky Ya (1995) ArticleTitleInfluence of root density on the critical soil water potential Plant Soil 171 351–357 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmsVamtb4%3D
J S Sperry F R Adler G S Campbell J P Comstock (1998) ArticleTitleLimitation of plant water use by rhizosphere and xylem conductance: Results from a model Plant Cell Environ. 21 347–359 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.1998.00287.x
J S Sperry V Stiller U G Hacke (2002) Soil water uptake and water transport through root systems Y Waisel A Eshel U Kafkafi (Eds) Plant Root: The Hidden Half. Marcel Dekker Inc New York 663–681
P J Thorburn G R Walker (1993) The source of water transpired by Eucalyptus camaldulensis: Soil, groundwater or streams? J R Ehleringer A S Hall G D Farquhar (Eds) Stable Isotopes and Plant Carbon-Water Relations Academic Press San Diego 511–527
G Walker J P Brunel J Dighton K Holland F Leaney K McEwan L Mensforth P Thorburn C Walker (2001) use of stable isotopes of water for determining sources of water for plant transpiration M Unkovich J Pate A McNeill D J Gibbs (Eds) Stable Isotope Techniques in the Study of Biological Processes and Functioning of Ecosystems Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht 57–89
Yoshida S and Hasegawa S 1982 Rice root systems: their development and function. In Drought Resistance in Crops with Emphasis on Rice. Ed. International Rice Research Institute. pp. 97–114. IRRI, Los Baños.
J Zhuang K Nakayama G Yu T Urushisaki (2001) ArticleTitleEstimation of root water uptake of maize: An ecophysiological perspective Field Crops Res. 69 201–213 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-4290(00)00142-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, H., Iijima, M. Stable isotope analysis of water extraction from subsoil in upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) as affected by drought and soil compaction. Plant Soil 270, 147–157 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-1304-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-1304-2