ABSTRACT
Purpose
Overexpression of the androgen receptor (AR) and anti-apoptotic genes including X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) provide tumors with a proliferative advantage. Therefore, our objective was to determine whether novel antiandrogen (CBDIV17) and XIAP inhibitor based combination therapy can treat advanced prostate cancer.
Methods
CBDIV17 and embelin-6g were synthesized and their effect on cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle and AR and XIAP gene silencing determined.
Results
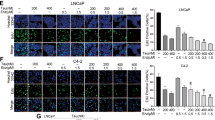
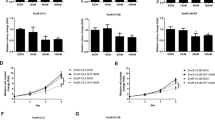
CBDIV17 was more potent than bicalutamide and inhibited proliferation of C4-2 and LNCaP cells, IC50 for CBDIV17 was ∼12 μM and ∼21 μM in LNCaP and C4-2 cells, respectively, whereas bicalutamide had IC50 of ∼46 μM in LNCaP cells and minimal effect in C4-2 cells. CBDIV17 induced apoptosis more effectively compared to bicalutamide and significantly inhibited DNA replication. Combination of CBDIV17 and embelin resulted in supra-additive antiproliferative and apoptotic effects. Embelin downregulated AR expression and decreased androgen-mediated AR phosphorylation at Ser81. These hydrophobic drugs were solubilized using micelles prepared with polyethylene glycol-b-poly (carbonate-co-lactide) (PEG-b-p(CB-co-LA)) copolymer. Combination therapy inhibited prostate tumor growth more effectively compared to control or monotherapy in vivo.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated that CBDIV17 in combination with embelin can potentially treat advanced prostate cancer.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Gittes RF. Carcinoma of the prostate. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:236–45.
Kozlowski JM, Ellis WJ, Grayhack JT. Advanced prostatic carcinoma. Early versus late endocrine therapy. Urol Clin North Am. 1991;18:15–24.
Bracarda S, de Cobelli O, Greco C, Prayer-Galetti T, Valdagni R, Gatta G, et al. Cancer of the prostate. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005;56:379–96.
Goktasand S, Crawford ED. Optimal hormonal therapy for advanced prostatic carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 1999;26:162–73.
Danquah M, Li F, Duke 3rd CB, Miller DD, Mahato RI. Micellar delivery of bicalutamide and embelin for treating prostate cancer. Pharm Res. 2009;26:2081–92.
Scherand HI, Sawyers CL. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8253–61.
Taplinand ME, Balk SP. Androgen receptor: a key molecule in the progression of prostate cancer to hormone independence. J Cell Biochem. 2004;91:483–90.
Danquah MK, Zhang XA, Mahato RI. Extravasation of polymeric nanomedicines across tumor vasculature. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:623–39.
Danquah M, Fujiwara T, Mahato RI. Self-assembling methoxypoly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(carbonate-co-L-lactide) block copolymers for drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2010;31:2358–70.
Li F, Danquah M, Mahato RI. Synthesis and characterization of amphiphilic lipopolymers for micellar drug delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2010;11:2610–20.
Li F, Danquah M, Singh S, Wu H, Mahato RI. Paclitaxel- and lapatinib-loaded lipopolymer micelles overcome multidrug resistance in prostate cancer. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2011;1:240–8.
Sun C, Shi Y, Xu LL, Nageswararao C, Davis LD, Segawa T, et al. Androgen receptor mutation (T877A) promotes prostate cancer cell growth and cell survival. Oncogene. 2006;25:3905–13.
Wu Y, Chhipa RR, Zhang H, Ip C. The antiandrogenic effect of finasteride against a mutant androgen receptor. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:902–9.
Chen J, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Wang G, Qiu S, Wang S. Design, synthesis, and characterization of new embelin derivatives as potent inhibitors of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:5805–8.
Chang C, Saltzman A, Yeh S, Young W, Keller E, Lee HJ, et al. Androgen receptor: an overview. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1995;5:97–125.
Takahashi R, Deveraux Q, Tamm I, Welsh K, Assa-Munt N, Salvesen GS, et al. A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:7787–90.
Fesik SW. Insights into programmed cell death through structural biology. Cell. 2000;103:273–82.
Riedl SJ, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R, Zhou Q, Sun C, Fesik SW, et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell. 2001;104:791–800.
Chai J, Shiozaki E, Srinivasula SM, Wu Q, Datta P, Alnemri ES, et al. Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell. 2001;104:769–80.
Liu S, Yuan Y, Okumura Y, Shinkai N, Yamauchi H. Camptothecin disrupts androgen receptor signaling and suppresses prostate cancer cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394:297–302.
Ren F, Zhang S, Mitchell SH, Butler R, Young CY. Tea polyphenols down-regulate the expression of the androgen receptor in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 2000;19:1924–32.
Chen L, Meng S, Wang H, Bali P, Bai W, Li B, et al. Chemical ablation of androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1311–9.
Purushottamachar P, Khandelwal A, Chopra P, Maheshwari N, Gediya LK, Vasaitis TS, et al. First pharmacophore-based identification of androgen receptor down-regulating agents: discovery of potent anti-prostate cancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:3413–21.
Lecis D, Drago C, Manzoni L, Seneci P, Scolastico C, Mastrangelo E, et al. Novel SMAC-mimetics synergistically stimulate melanoma cell death in combination with TRAIL and Bortezomib. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1707–16.
Huerta S, Gao X, Livingston EH, Kapur P, Sun H, Anthony T. In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization of colorectal cancer HT-29 cells by the smac mimetic JP-1201. Surgery. 2010;148:346–53.
Onetto N, Canetta R, Winograd B, Catane R, Dougan M, Grechko J, et al. Overview of Taxol safety. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1993;131–9.
Dai Y, Desano J, Qu Y, Tang W, Meng Y, Lawrence TS, et al. Natural IAP inhibitor Embelin enhances therapeutic efficacy of ionizing radiation in prostate cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2011;1:128–43.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
This work is supported by an Idea Award (W81XWH-10-1-0969) from the Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program. We would also like to thank Dr. Liguo Song for his help in obtaining HRMS data. Molecular weight measurement was performed at the Mass Spectrometry Center of the Department of Chemistry at the University of Tennessee at Knoxville using a JEOL (Peabody, MA) AccuTOF-D time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer with a DART (direct analysis in real time) ionization source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PPTX 471 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danquah, M., Duke, C.B., Patil, R. et al. Combination Therapy of Antiandrogen and XIAP Inhibitor for Treating Advanced Prostate Cancer. Pharm Res 29, 2079–2091 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0737-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0737-1