ABSTRACT
Purpose
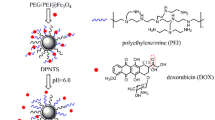
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were tested as a drug carrier system, as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agent, and for their ability to conjugate to an antibody.
Methods
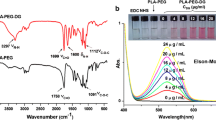
An iron oxide core coated with oleic acid (OA) and then with OA-PEG forms a water-dispersible MNP formulation. Hydrophobic doxorubicin partitions into the OA layer for sustained drug delivery. The T1 and T2 MRI contrast properties were determined in vitro and the circulation of the MNPs was measured in mouse carotid arteries. An N-hydroxysuccinimide group (NHS) on the OA-PEG-80 was used to conjugate the amine functional group on antibodies for active targeting in the human MCF-7 breast cancer cell line.
Results
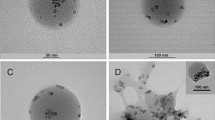
The optimized formulation had a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 184 nm with an ~8 nm iron-oxide core. The MNPs enhance the T2 MRI contrast and have a long circulation time in vivo with 30% relative concentration 50 min post-injection. Doxorubicin-loaded MNPs showed sustained drug release and dose-dependent antiproliferative effects in vitro; the drug effect was enhanced with transferrin antibody-conjugated MNPs.
Conclusion
PEG-functionalized MNPs could be developed as a targeted drug delivery system and MRI contrast agent.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bulte JW, Kraitchman DL. Monitoring cell therapy using iron oxide MR contrast agents. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2004;5:567–84.
Josephson L. Magnetic nanoparticles for MR imaging. US: Springer; 2007.
Bulte JW, Kraitchman DL. Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004;17:484–99.
Alexiou C, Arnold W, Klein RJ, Parak FG, Hulin P, Bergemann C, et al. Locoregional cancer treatment with magnetic drug targeting. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6641–8.
Beaven GH, Chen SH, d’Albis A, Gratzer WB. A spectroscopic study of the haemin–human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974;41:539–46.
Lehrer SS, Fasman GD. The fluorescence of lysozyme and lysozyme substrate complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966;23:133–8.
Chipman DM, Grisaro V, Sharon N. The binding of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to lysozyme. The specificity of binding subsites. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:4388–94.
Jeffery GH, Bassett J, Mendham J, Denny RC. Vogel’s text book of quantitative chemical analysis. New York: Wiley; 1989.
Moffat BA, Reddy GR, McConville P, Hall DE, Chenevert TL, Kopelman RR, et al. A novel polyacrylamide magnetic nanoparticle contrast agent for molecular imaging using MRI. Mol Imaging. 2003;2:324–32.
Yolles S, Aslund B, Morton JF, Olson OT, Rosenberg B. Timed-released depot for anticancer agents. II. Acta Pharm Suec. 1978;15:382–8.
Olivier JC, Huertas R, Lee HJ, Calon F, Pardridge WM. Synthesis of pegylated immunonanoparticles. Pharm Res. 2002;19:1137–43.
Gou ML, Qian ZY, Wang H, Tang YB, Huang MJ, Kan B, et al. Preparation and characterization of magnetic poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microspheres. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;19:1033–41.
Liu X, Kaminski MD, Chen H, Torno M, Taylor L, Rosengart AJ. Synthesis and characterization of highly-magnetic biodegradable poly(d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres. J Control Release. 2007;119:52–8.
Okassa LN, Marchais H, Douziech-Eyrolles L, Herve K, Cohen-Jonathan S, Munnier E, et al. Optimization of iron oxide nanoparticles encapsulation within poly(d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) sub-micron particles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:31–8.
Hamoudeh M, Al Faraj A, Canet-Soulas E, Bessueille F, Leonard D, Fessi H. Elaboration of PLLA-based superparamagnetic nanoparticles: characterization, magnetic behaviour study and in vitro relaxivity evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2007;338:248–57.
Bhattacharya S, Eckert F, Boyko V, Pich A. Temperature-, pH-, and magnetic-field-sensitive hybrid microgels. Small. 2007;3:650–7.
Shen F, Poncet-Legrand C, Somers S, Slade A, Yip C, Duft AM, et al. Properties of a novel magnetized alginate for magnetic resonance imaging. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003;83:282–92.
Bonacchi D, Caneschi A, Dorignac D, Falqui A, Gatteschi D, Rovai D, et al. Nanosized iron oxide particles entrapped in pseudo-single crystals gamma-cyclodextrin. Chem Mater. 2004;16:2016–20.
Bonacchi D, Caneschi A, Gatteschi D, Sangregorio C, Sessoli R, Falqui A. Synthesis and characterisation of metal oxides nanoparticles entrapped in cyclodextrin. J Phys Chem Solids. 2004;65:719–22.
Mikhaylova M, Kim DK, Bobrysheva N, Osmolowsky M, Semenov V, Tsakalakos T, et al. Superparamagnetism of magnetite nanoparticles: dependence on surface modification. Langmuir. 2004;20:2472–7.
Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Wang FH, Kehr J, Bjelke B, Zhang Y, et al. Starch-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as MR contrast agents. Chem Mater. 2003;15:4343–51.
Pardoe H, Chua-anusorn W, St. Pierre TG, Dobson J. Structural and magnetic properties of nanoscale iron oxide particles synthesized in the presence of dextran or polyvinyl alcohol. J Magn Magn Mater. 2001;225:41–6.
Lee H, Yu MK, Park S, Moon S, Min JJ, Jeong YY, et al. Thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and application as a dual imaging probe for cancer in vivo. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:12739–45.
Wan S, Huang J, Guo M, Zhang H, Cao Y, Yan H, et al. Biocompatible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle dispersions stabilized with poly(ethylene glycol)-oligo(aspartic acid) hybrids. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;80:946–54.
Lutz JF, Stiller S, Hoth A, Kaufner L, Pison U, Cartier R. One-pot synthesis of pegylated ultrasmall iron-oxide nanoparticles and their in vivo evaluation as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:3132–8.
Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, Hou Y, Sun S. Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater. 2007;19:3163–6.
Ditsch A, Laibinis PE, Wang DI, Hatton TA. Controlled clustering and enhanced stability of polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2005;21:6006–18.
Weissleder R, Elizondo G, Wittenberg J, Lee AS, Josephson L, Brady TJ. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide: an intravenous contrast agent for assessing lymph nodes with MR imaging. Radiology. 1990;175:494–8.
McCarthy JR, Weissleder R. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1241–51.
Okuhata Y. Delivery of diagnostic agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;37:121–37.
Yigit MV, Mazumdar D, Lu Y. MRI detection of thrombin with aptamer functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:412–7.
Jun YW, Huh YM, Choi JS, Lee JH, Song HT, Kim S, et al. Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:5732–3.
Jain TK, Richey J, Strand M, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Flask CA, Labhasetwar V. Magnetic nanoparticles with dual functional properties: drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials. 2008;29:4012–21.
Bulte JWM, Cuyper MD, Despres D, Frank JA. Preparation, relaxometry, and biokinetics of PEGylated magnetoliposomes as MR contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater. 1999;194:204–9.
Zhang Y, Kohler N, Zhang MQ. Surface modification of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake. Biomaterials. 2002;23:1553–61.
Arruebo M, Fernandez-Pacheco R, Ibarra MR, Santamaria J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today. 2007;2:22–32.
Lewin M, Carlesso N, Tung CH, Tang XW, Cory D, Scadden DT, et al. Tat peptide-derivatized magnetic nanoparticles allow in vivo tracking and recovery of progenitor cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:410–4.
Seo SB, Yang J, Hyung W, Cho EJ, Lee TI, Song YJ, et al. Novel multifunctional PHDCA/PEI nano-drug carriers for simultaneous magnetically targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. Nanotechnology. 2007;18:1–8.
Jain TK, Reddy MK, Morales MA, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V. Biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles in rats. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2008;5:316–27.
Jain TK, Foy SP, Erokwu B, Dimitrijevic S, Flask CA, Labhasetwar V. Magnetic resonance imaging of multifunctional pluronic stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6748–56.
Neuberger T, Schopf B, Hofmann H, Hofmann M, von Rechenberg B. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J Magn Magn Mater. 2005;293:483–96.
Jun YW, Lee JH, Cheon J. Chemical design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:5122–35.
Jain TK, Morales MA, Sahoo SK, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V. Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2005;2:194–205.
Kosaka N, Ogawa M, Longmire MR, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Multi-targeted multi-color in vivo optical imaging in a model of disseminated peritoneal ovarian cancer. J Biomed Opt. 2009;14:014023.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The study reported here is funded by grant R01 EB005822 (to VL) from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health. SPF is a predoctoral student in Cleveland Clinic’s Molecular Medicine Ph.D. Program, which is funded by the “Med into Grad” initiative of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (http://www.lerner.ccf.org/molecmed/phd/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary materials
(DOC 96 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yallapu, M.M., Foy, S.P., Jain, T.K. et al. PEG-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications. Pharm Res 27, 2283–2295 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0260-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0260-1