Abstract
Purpose
In vitro transfection of secreting cells is regarded as one strategy for improved cell engineering/transplantation. Insulin-secreting insulinoma cell lines or pancreatic β-cells could be genetically engineered using designed polymeric vectors which are safer than viral vectors. This study investigates the effects of the constituents in transfection media on polymeric transfection.
Methods
Polyplexes conjugated with sulfonylurea (SU) were evaluated under different transfection conditions for gene transfection and their effects on cytotoxicity and insulin secretion. Several components in transfection media specifically associated with the insulin secretion pathway were amino acids, vitamins, Ca2+ and K+. The interactions of the polyplexes with insulin were monitored by surface charge and particle size to monitor how insulin as a protein influences transfection.
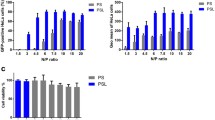
Results
For an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F), polyplexes in Ca2+-containing KRH medium (Ca2+(+)KRH) enhanced transfection and did not cause damage to biological functions. When adding amino acids, vitamins, or K+ or depleting Ca2+ from Ca2+(+)KRH, poly(l-lysine)/DNA complexes showed a greater reduction in transfection than SU receptor (SUR)-targeting polyplexes (SU-polyplex). Positively charged polyplexes interacted with insulin, developing a negative surface charge, and these interactions may cause a decrease in transfection.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that in vitro and ex vivo polymeric transfection of insulin-secreting cells can be modulated and enhanced by adjusting the transfection conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Ricordi and T. B. Strom. Clinical islet transplantation: advances and immunological challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:259–268 (2004).
M. K. Lee and Y. H. Bae. Cell transplantation for endocrine disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 42:103–120 (2000).
R. Bottino, P. Lemarchand, M. Trucco, and N. Giannoukakis. Gene- and cell-based therapeutics for type I diabetes mellitus. Gene Ther. 10:875–889 (2003).
A. S. Narang, K. Cheng, J. Henry, C. Zhang, O. Sabek, D. Fraga, M. Kotb, A. O. Gaber, and R. I. Mahato. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene delivery for revascularization in transplanted human islets. Pharm. Res. 21:15–25 (2004).
D. Casper, S. J. Engstrom, G. R. Mirchandani, A. Pidel, D. Palencia, P. H. Cho, M. Brownlee, D. Edelstein, H. J. Federoff, and W. J. Sonstein. Enhanced vascularization and survival of neural transplants with ex vivo angiogenic gene transfer. Cell Transplant 11:331–349 (2002).
G. Leibowitz, G. M. Beattie, T. Kafri, V. Cirulli, A. D. Lopez, A. Hayek, and F. Levine. Gene transfer to human pancreatic endocrine cells using viral vectors. Diabetes 48:745–753 (1999).
H. C. Kang, S. Kim, M. Lee, and Y. H. Bae. Polymeric gene carrier for insulin secreting cells: Poly(l-lysine)-g-sulfonylurea for receptor mediated transfection. J. Control. Release 105:164–176 (2005).
D. Martinez-Fong, I. Navarro-Quiroga, I. Ochoa, I. Alvarez-Maya, M. A. Meraz, J. Luna, and J. A. Arias-Montano. Neurotensin-SPDP-poly-l-lysine conjugate: a nonviral vector for targeted gene delivery to neural cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 69:249–262 (1999).
J. Zeng and S. Wang. Enhanced gene delivery to PC12 cells by a cationic polypeptide. Biomaterials. 26:679–686 (2005).
H. C. Kang, M. Lee, and Y. H. Bae. Polymeric gene carriers. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 15:317–342 (2005).
B. I. Florea, C. Meaney, H. E. Junginger, and G. Borchard. Transfection efficiency and toxicity of polyethylenimine in differentiated Calu-3 and nondifferentiated COS-1 cell cultures. AAPS PharmSci 4:E12 (2002).
R. Acosta, C. Montanez, P. Gomez, and B. Cisneros. Delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to PC12 cells. Neurosci. Res. 43:81–86 (2002).
S. Charles, T. Tamagawa, and J. C. Henquin. A single mechanism for the stimulation of insulin release and 86Rb+ efflux from rat islets by cationic amino acids. Biochem. J. 208:301–308 (1982).
A. Sener, F. Blachier, J. Rasschaert, A. Mourtada, F. Malaisse-Lagae, and W. J. Malaisse. Stimulus-secretion coupling of arginine-induced insulin release: comparison with lysine-induced insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 124:2558–2567 (1989).
N. H. McClenaghan, C. R. Barnett, F. P. O'Harte, and P. R. Flatt. Mechanisms of amino acid-induced insulin secretion from the glucose-responsive BRIN-BD11 pancreatic B-cell line. J. Endocrinol. 151:349–357 (1996).
C. Li, C. Buettger, J. Kwagh, A. Matter, Y. Daikhin, I. B. Nissim, H. W. Collins, M. Yudkoff, C. A. Stanley, and F. M. Matschinsky. A signaling role of glutamine in insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 279:13393–13401 (2004).
H. Sone, M. Ito, K. Sugiyama, M. Ohneda, M. Maebashi, and Y. Furukawa. Biotin enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas of the rat. J. Nutr. Biochem. 10:237–243 (1999).
P. Rathanaswami, A. Pourany, and R. Sundaresan. Effects of thiamine deficiency on the secretion of insulin and the metabolism of glucose in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Biochem. Int. 25:577–583 (1991).
C. J. Barker, I. B. Leibiger, B. Leibiger, and P. O. Berggren. Phosphorylated inositol compounds in β-cell stimulus-response coupling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 283:E1113–E1122 (2002).
P. Rorsman and E. Renstrom. Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 46:1029–1045 (2003).
A. T. L. Young, R. B. Moore, A. G. Murray, J. C. Mullen, and J. R. T. Lakey. Assessment of different transfection parameters in efficiency optimization. Cell Transplant 13:179–185 (2004).
M. Ogris, S. Brunner, S. Schuller, R. Kircheis, and E. Wagner. PEGylated DNA/transferrin-PEI complexes: reduced interaction with blood components, extended circulation in blood and potential for systemic gene delivery. Gene Ther. 6:595–605 (1999).
D. Mears. Regulation of insulin secretion in islets of Langerhans by Ca(2+)channels. J. Membr. Biol. 200:57–66 (2004).
M. Komatsu, T. Schermerhorn, T. Aizawa, and G. Sharp. Glucose stimulation of insulin release in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ and in the absence of any increase in intracellular Ca2+ in rat pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:10728–10732 (1995).
I. Quesada, J. Rovira, F. Martin, E. Roche, A. Nadal, and B. Soria. Nuclear KATP channels trigger nuclear Ca2+ transients that modulate nuclear function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:9544–9549 (2002).
B. J. Zunkler, M. Wos-Maganga, and U. Panten. Fluorescence microscopy studies with a fluorescent glibenclamide derivative, a high-affinity blocker of pancreatic beta-cell ATP-sensitive K+ currents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 67:1437–1444 (2004).
M. Molinete, J. C. Irminger, S. A. Tooze, and P. A. Halban. Trafficking/sorting and granule biogenesis in the beta-cell. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 11:243–251 (2000).
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by NIH DK 56884. The authors acknowledge Deepa Mishra for her proof-reading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H.C., Bae, Y.H. Polymeric Gene Transfection on Insulin-Secreting Cells: Sulfonylurea Receptor-Mediation and Transfection Medium Effect. Pharm Res 23, 1797–1808 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9027-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9027-0