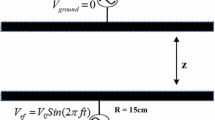
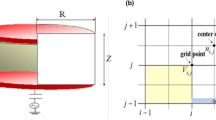
Abstract
In this work, a fluid model has been applied to study HBr/Ar capacitively coupled plasma discharges that are being used for anisotropic etching process. Based on time average reaction rates, the model identify the most dominant species in HBr/Ar plasma. Our simulation results show that the neutral species like H and Br, which are the key precursors in chemical etching, have bell shape distribution while ions like HBr+, Br+ and Ar+ which plays a dominant role in the physical etching, have double humped distribution and shows peaks near electrodes. The effect of HBr/Ar mixing ratios on densities of dominant species are analyzed. The addition of Ar to HBr plasma decreases H, Br and HBr+ densities slightly while increases Br+ and Ar+ densities. It was found that the dilution of HBr by Ar results in an increase in electron density and electron temperature, which results in more ionization and dissociation. The densities and hence the fluxes of the neutrals and positive ions for etching and subsequently chemical etching versus physical etching in HBr/Ar plasmas discharge can be controlled by tuning Ar concentration in the discharge and the desire etching can be achieved.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liberman MA, Lichtenberg AJ (2005) Principles of plasma discharges and materials processing, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Vahedi V, Birdsall CK, Lieberman MA, DiPeso G, Rognlien TD (1993) Phys Fluids B Plasma Phys 5:2719
Georgieva V, Bogaerts A, Gijbels R (2003) J Appl Phys 94:3748
Kim HC, Iza F, Yang SS, Radmilović-Radjenović M, Lee JK (2005) J Phys D Appl Phys 38:R283
Ji-Myon L, Ki-Myung C, Kyoung-Kook K, Won-Kook C, Seong-Ju P (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:G1
Shin MH, Park MS, Jung SH, Boo JH, Lee NE (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:4950
Na SW, Shin MH, Chung YM, Han JG, Jeung SH, Boo JH, Lee N-E (2006) Microelectron Eng 83:328
Kim H-K, Bae JW, Kim T-K, Kim K-K, Seong T-Y, Adesida I (2003) J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanom Struct 21:1273
Bae J-W, Jeong C-H, Kim H-K, Kim K-K, Cho N-G, Seong T-Y, Park S-J, Adesida I, Yeom G-Y (2003) Jpn J Appl Phys 42:L535
Pearton SJ, Chakrabarti UK, Lane E, Perley AP, Abernathy CR, Hobson WS, Jones KS (1992) J Electrochem Soc 139:856
Kuo Y, Tai TL (1998) J Electrochem Soc 145:4313
Shul RJ, McClellan GB, Briggs RD, Rueger DJ, Pearton SJ, Abernathy CR, Lee JW, Constantine C, Barrat C (1997) J Vac Sci Technol A Vac Surf Film 15:633
Flamm D (1990) Pure Appl Chem 62:1709
Aldao CM, Weaver JH (2001) Prog Surf Sci 68:189
Roth JR (1995) Industrial plasma engineering. The Institute of Physics, London
Sugano T (1985) Applications of plasma processes to VLSI technology, 1st edn. Wiley, New York
Flamm DL, Donnelly VM, Mucha JA (1981) J Appl Phys 52:3633
Winters H, Coburn J (1992) Surf Sci Rep 14:161
Layadi N, Colonell J, Lee J (1999) Bell Labs Tech J 4:155
Mahorowala AP, Sawin HH, Jones R, Labun AH (2002) J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanom Struct 20:1055
Desvoivres L, Vallier L, Joubert O (2000) J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanom Struct 18:156
Smirnov AA, Efremov AM, Svettsov VI (2010) Russ Microelectron 39:418
Ham Y-H, Efremov A, Yun SJ, Kim JK, Min N-K, Kwon K-H (2009) Thin Solid Films 517:4242
Lee HW, Kim M, Min N-K, Efremov A, Lee C-W, Kwon K-H (2008) Jpn J Appl Phys 47:6917
Efremov A, Kim Y, Lee H, Kwon K (2011) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 31:259
Ham Y-H, Efremov A, Lee HW, Yun SJ, Min NK, Baek K-H, Do L-M, Kwon K-H (2011) Vacuum 85:1021
Gul B, Tinck S, De Schepper P, Rehman A, Bogaerts A (2015) J Phys D Appl Phys 48:025202
Kim D-p, Kim G-H, Woo J-C, Kim H-J, Kim C-I, Lee C-I, Lee S-K, Jung T-W, Moon S-C, Park S-W (2009) J Korean Phys Soc 54:934
Chung CW, Byun YH, Kim HI (2002) Korean J Chem Eng 19:524
Lishan D, Lee J, Kim G (2001) InP processing using an HBr high density ICP plasma. GaAs MANTECH, Inc.
Ping AT, Adesida I, Asif M, Kuznia JN (1994) Electron Lett 30:1895
Min SR, Cho HN, Li YL, Chung CW (2008) Thin Solid Films 516:3521
Panda S, Wise R, Mosden A, Sugiyama K, Camilleri J (2004) Microelectron Eng 75:275
Šašić O, Dujko S, Makabe T, Petrović ZL (2012) Chem Phys 398:154
Hagelaar GJM, Pitchford LC (2005) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 14:722
Tachibana K (1986) Phys Rev A 34:1007
Rapp D, Englander-Golden P (1965) J Chem Phys 43:1464
Tinck S, Boullart W, Bogaerts A (2009) J Phys D Appl Phys 42:095204
Kushner MJ (2009) J Phys D Appl Phys 42:194013
Ali MA, Kim Y-K (2008) J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys 41:145202
Corrigan SJB (1965) J Chem Phys 43:4381
Banks P (1966) Planet Space Sci 14:1085
Kushner MJ (1988) J Appl Phys 63:2532
Rehman A, Kwon HC, Park WT, Lee JK (2011) Phys Plasmas 18:093502
Gul B, Rehman A (2016) Phys Plasmas 23:043506
Perrin J, Leroy O, Bordage M (1996) Contrib Plasma Phys 36:3
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (HEC) for financial support under the Indigenous PhD Program. Authors are grateful to O. Šašić (Institute of physics, Belgrade, Serbia) for provision of electrons cross section and transport coefficient data of HBr for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gul, B., Rehman, Au. Fluid Simulation of Capacitively Coupled HBr/Ar Plasma for Etching Applications. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36, 1363–1375 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9726-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9726-1