Abstract
Vegetation patterns can reflect the spatial distribution of vegetation in both space and time. In semi-arid regions, the absorption of water by vegetation is a nonlocal process meaning that its roots can absorb water from themselves throughout the region. However, the effects of the nonlocal interaction on the distribution of vegetation pattern are not clear. In this paper, a dynamical model of vegetation pattern with nonlocal delay is investigated. Through the analysis of Turing instability, we obtain the conditions for the generation of stationary patterns. By numerical simulations, various spatial distribution of vegetation in semi-arid areas are qualitatively depicted. It is found that the stripe intervals in pattern decrease with the increase in the intensity of nonlocal delay effect, and then a dot-line mixed pattern appears, which eventually evolves into a high-density dot pattern. This indicates that vegetation has evolved from low-density stripe distribution to high-density point distribution. The results show that the nonlocal delay effect enhances vegetation biomass. Therefore, we can take measures to increase the intensity of nonlocal delay effect to increase vegetation density, which theoretically provides new guidance for vegetation protection and desertification control.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, C.G., Lawton, J.H., Shachak, M.: Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69, 373–386 (1994)
Lemordant, L., Gentine, P., et al.: Critical impact of vegetation physiology on the continental hydrologic cycle in response to increasing CO\(_{2}\). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115, 4093–4098 (2018)
Gallagher, R.V., Allen, S., Wright, I.J.: Safety margins and adaptive capacity of vegetation to climate change. Sci. Rep. 9, 8241 (2019)
Danielsen, F.: The Asian Tsunami: a protective role for coastal vegetation. Science 310, 643 (2005)
Hillerislambers, R., Rietkerk, M., Frank, V.D.B., et al.: Vegetation pattern formation in semi-arid grazing systems. Ecology 82, 50–61 (2001)
Couteron, P., Lejeune, O.: Periodic spotted patterns in semi “rid vegetation explained by a propagation” inhibition model. J. Ecol. 89, 616–628 (2001)
Sun, G.-Q.: Mathematical modeling of population dynamics with Allee effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1–12 (2016)
Von, J.H., Meron, E., Shachak, M., et al.: Diversity of vegetation patterns and desertification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 198101 (2001)
Shnerb, N.M., Sara, P., Lavee, H., et al.: Reactive glass and vegetation patterns. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 038101 (2002)
Barbier, N., Couteron, P., Lejoly, J., et al.: Self-organized vegetation patterning as a fingerprint of climate and human impact on semi-arid ecosystems. J. Ecol. 94, 537–547 (2006)
Ursino, N., Rulli, M.C.: Combined effect of fire and water scarcity on vegetation patterns in arid lands. Ecol. Model. 221, 2353–2362 (2010)
Rietkerk, M., Boerlijst, M.C., et al.: Self-organization of vegetation in arid ecosystems. Am. Nat. 160, 524–530 (2002)
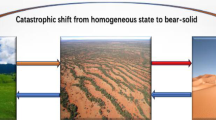
Rietkerk, M.: Self-organized patchiness and catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Science 305, 1926–1929 (2004)
Herrmann, H.-J.: Pattern formation of dunes. Nonlinear Dyn. 44, 315–317 (2006)
Marinov, K., Wang, T., Yang, Y.: On a vegetation pattern formation model governed by a nonlinear parabolic system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14, 507–525 (2013)
Evaristo, J., Jasechko, S., Mcdonnell, J.J.: Global separation of plant transpiration from groundwater and streamflow. Nature 525, 91–94 (2015)
Zemp, D.C., Schleussner, C.F., et al.: Self-amplified Amazon forest loss due to vegetation-atmosphere feedbacks. Nat. Commun. 8, 14681 (2017)
Brandt, M., Hiernaux, P., Rasmussen, K., et al.: Changes in rainfall distribution promote woody foliage production in the Sahel. Commu. Biol. 2, 133 (2019)
Meron, E., Gilad, E., et al.: Vegetation patterns along a rainfall gradient. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 19, 367–376 (2004)
Maestre, F.T., et al.: Plant species richness and ecosystem multifunctionality in global drylands. Science 335, 214–218 (2012)
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Wu, S., et al.: Water memory effects and their impacts on global vegetation productivity and resilience. Sci. Rep. 8, 2962 (2018)
Rees, M., et al.: Long-term studies of vegetation dynamics. Science 293, 650–655 (2001)
Klausmeier, C.A.: Regular and irregular patterns in semiarid vegetation. Science 284, 1826–1828 (1999)
Borgogno, F., D’Odorico, P., Laio, F., Ridolfi, L.: Mathematical models of vegetation pattern formation in ecohydrology. Rev. Geophys. 47, RG1005 (2009)
Sun, G.-Q., et al.: Effects of feedback regulation on vegetation patterns in semi-arid environments. Appl. Math. Model. 61, 200–215 (2018)
Sherratt, J.A., Synodinos, A.D.: Vegetation patterns and desertification waves in semi-arid environments: mathematical models based on local facilitation in plants. Discrete Cont. Dyn. B 17, 2815–2827 (2012)
Hillerislambers, R., Rietkerk, M., et al.: Vegetation pattern formation in semi-arid grazing systems. Ecology 82, 50–61 (2001)
Handa, I., Harmsen, R., Jefferies, R.: Patterns of vegetation change and the recovery potential of degraded areas in a coastal marsh system of the Hudson Bay lowlands. J. Ecol. 90, 86–99 (2002)
Rietkerk, M., Bosch, Fvd, Koppel, Jvd: Site-specific properties and irreversible vegetation changes in semi-arid grazing systems. Oikos 80, 241–252 (1997)
Rietkerk, M., Ketner, P., Burger, J., Hoorens, B., Olff, H.: Multiscale soil and vegetation patchiness along a gradient of herbivore impact in a semi-arid grazing system in West Africa. Plant Ecol. 148, 207–224 (2000)
Van de Koppel, J., Rietkerk, M., van Langevelde, F., et al.: Spatial heterogeneity and irreversible vegetation change in semiarid grazing systems. Am. Nat. 159, 209–218 (2002)
Wilson, A., et al.: Positive-feedback switches in plant communities. Adv. Ecol. Res. 23, 263–336 (1992)
Deblauwe, V., Couteron, P., Bogaert, J., et al.: Determinants and dynamics of banded vegetation pattern migration in arid climates. Ecol. Monogr. 82, 3–21 (2012)
Van de Koppel, J., Rietkerk, M.: Spatial interactions and resilience in arid ecosystems. Am. Nat. 163, 113–121 (2004)
Kefi, S., Rietkerk, M., Alados, C.L., Pueyo, Y., Papanastasis, V.P., ElAich, A., De Ruiter, P.C.: Spatial vegetation patterns and imminent desertification in Mediterranean arid ecosystems. Nature 449, 213–217 (2007)
Bastiaansen, R., Jaibi, O., Deblauwe, V., et al.: Multistability of model and real dryland ecosystems through spatial self-organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115, 11256–11261 (2018)
Seddon, A.W.R., Macias-Fauria, M., et al.: Sensitivity of global terrestrial ecosystems to climate variability. Nature 531, 229–232 (2016)
Braswell, B.H., et al.: The response of global terrestrial ecosystems to interannual temperature variability. Science 278, 870–873 (1997)
Forzieri, G., Alkama, R., et al.: Satellites reveal contrasting responses of regional climate to the widespread greening of Earth. Science 356, 1180–1184 (2017)
Kutzbach, J.E., Bonan, G.B., Foley, J.A., et al.: Vegetation and soils feedbacks on the response of the African monsoon response to orbital forcing in early to middle holocene. Nature 384, 19–26 (1996)
Forzieri, G., Alkama, R., et al.: Satellites reveal contrasting responses of regional climate to the widespread greening of Earth. Science 360, 022701 (2018)
Gowda, K., Riecke, H., Silber, M.: Transitions between patterned states in vegetation models for semiarid ecosystems. Phys. Rev. E 89, 022701 (2014)
Gowda, K., et al.: Assessing the robustness of spatial pattern sequences in a dryland vegetation model. Proc. R. Soc. A 472, 20150893 (2016)
Lejeune, O., Tlidi, M., et al.: Vegetation spots and stripes: Dissipative structures in arid landscapes. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 98, 261–271 (2004)
Zelnik, Y.R., Kinast, S., et al.: Regime shifts in models of dryland vegetation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 371, 20120358 (2013)
Bel, G., Hagberg, A., Meron, E.: Gradual regime shifts in spatially extended ecosystems. Theor. Ecol. 5, 591–604 (2012)
Martone, M., et al.: High-resolution forest mapping from Tandem-X interferometric data exploiting nonlocal filtering. Remote Sens. 10, 1477 (2018)
Biswas, A., et al.: Identifying effects of local and nonlocal factors of soil water storage using cyclical correlation analysis. Hydrol. Process 26, 3669–3677 (2012)
Thompson, S., Katul, G., Terborgh, J., et al.: Spatial organization of vegetation arising from non-local excitation with local inhibition in tropical rainforests. Physica D 238, 1061–1067 (2009)
Chen, S.-S., et al.: Threshold dynamics of a diffusive nonlocal phytoplankton model with age structure. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 50, 55–56 (2019)
Guo, S.-J.: Stability and bifurcation in a reaction–diffusion model with nonlocal delay effect. J. Differ. Equ. 259, 1409–1448 (2015)
Winckler, J., Lejeune, Q., et al.: Nonlocal effects dominate the global mean surface temperature response to the biogeophysical effects of deforestation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46, 745–755 (2019)
Boushaba, K., Ruan, S.-G.: Instability in diffusive ecological models with nonlocal delay effects. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 258, 269–286 (2001)
Sun, G.-Q., Wang, S.-L., Ren, Q., Jin, Z., Wu, Y.-P.: Effects of time delay and space on herbivore dynamics: linking inducible defenses of plants to herbivore outbreak. Sci. Rep. 5, 11246 (2015)
Bao, X.-M., Tian, C.: Delay driven vegetation patterns of a plankton system on a network. Physica A 521, 74–88 (2019)
Wang, K.-K., Ye, H., Wang, Y.-J., et al.: Time-delay-induced dynamical behaviors for an ecological vegetation growth system driven by cross-correlated multiplicative and additive noises. Eur. Phys. J. E 41, 60 (2018)
Zeng, C., Han, Q., Yang, T., et al.: Noise- and delay-induced regime shifts in an ecological system of vegetation. J. Stat. Mech. Theory E 10, P10017 (2013)
Li, L., Jin, Z., Li, J.: Periodic solutions in a herbivore-plant system with time delay and spatial diffusion. Appl. Math. Model. 40, 4765–4777 (2016)
Wu, T., Fu, H., Feng, F., et al.: A new approach to predict normalized difference vegetation index using time-delay neural network in the arid and semi-arid grassland. Int. J. Remote Sens. 40, 1–14 (2019)
Tian, C.-R., Ling, Z., Zhang, L.: Delay-driven spatial patterns in a network-organized semiarid vegetation model. Appl. Math. Comput. (in Press) (2020)
Han, Q., Yang, T., Zeng, C., et al.: Impact of time delays on stochastic resonance in an ecological system describing vegetation. Physica A 408, 96–105 (2014)
Britton, N.F.: Aggregation and the competitive exclusion principle. J. Theor. Biol. 136, 57–66 (1989)
Guo, Z.-G., Song, L.-P., Sun, G.-Q., Li, C., Jin, Z.: Pattern dynamics of an SIS epidemic model with nonlocal delay. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29, 1950027 (2019)
Sun, G.-Q., Wang, C.-H., Wu, Z.Y.: Pattern dynamics of a Gierer–Meinhardt model with spatial effects. Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 1385–1396 (2017)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569–1578 (2017)
Wang, C., Ma, J.: A review and guidance for pattern selection in spatiotemporal system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1830003 (2018)
Ma, J., Qin, H., Song, X., et al.: Pattern selection in neuronal network driven by electric autapses with diversity in time delays. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29, 1450239 (2015)
Gourley, S.A., So, W.H.: Dynamics of a food-limited population model incorporating nonlocal delays on a finite domain. J. Math. Biol. 44, 49–78 (2002)
Koster, R.D., et al.: Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 305, 1138–1140 (2004)
Sun, G.-Q., Jusup, M., Jin, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Z.: Pattern transitions in spatial epidemics: mechanisms and emergent properties. Phys. Life Rev. 19, 43–73 (2016)
Wang, T.: Pattern dynamics of an epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Dyn. 77, 31–40 (2014)
Wang, Y., Cao, J., Li, X., Alsaedi, A.: Edge-based epidemic dynamics with multiple routes of transmission on random networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 403–420 (2018)
Wang, W., Liu, S., Liu, Z.: Spatiotemporal dynamics near the Turing–Hopf bifurcation in a toxic-phytoplankton–zooplankton model with cross-diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 98, 27–37 (2019)
Sun, G.-Q., Zhang, J., Song, L.-P., Jin, Z., Li, B.-L.: Pattern formation of a spatial predator–prey system. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 11151–11162 (2012)
Ghorai, S., Poria, S.: Pattern formation in a system involving prey–predation, competition and commensalism. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1309–1326 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The project is funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFE0109600), National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11671241 and 41875097, Outstanding Young Talents Support Plan of Shanxi province, Selective Support for Scientific and Technological Activities of Overseas Scholars of Shanxi province, and High-Level Talent Project of Jiangsu Province (Six Talent Peaks and Grant No. JNHB-071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Q., Sun, GQ., Liu, C. et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of a vegetation model with nonlocal delay in semi-arid environment. Nonlinear Dyn 99, 3407–3420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05486-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05486-w