Abstract
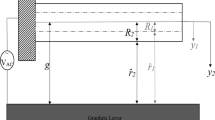
A new nonlinear electrostatic load model for initially curved clamped–clamped carbon nanotube (CNT) resonators is developed in this study. In particular, first a 3D finite element analysis is performed in order to obtain the electrostatic force distribution on a clamped–clamped CNT resonator (with and without initial curvature). A nonlinear model for the electrostatic load is then developed based on the 3D finite element analysis results. Based on the newly developed electrostatic load model, the nonlinear equations of motion of the initially curved CNT resonator are derived employing Hamilton’s principle together with the modified couple stress theory. Moreover, the Kelvin–Voigt viscoelastic model is employed to model the energy dissipation. The new nonlinear model of the system, consisting of two strongly nonlinear coupled partial differential equations, is discretized into a set of nonlinear ordinary differential equations via Galerkin’s technique, and solved employing the pseudo-arclength continuation method. The numerical results are obtained for both static and dynamic cases, with special focus on the static pull-in behaviour and on the effects of the newly developed electrostatic load model, viscoelasticity, initial curvature, and length-scale parameter on the nonlinear resonant response.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chowdhury, R., Adhikari, S., Mitchell, J.: Vibrating carbon nanotube based bio-sensors. Phys. E 42(2), 104–109 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.physe.2009.09.007
Eichler, A., Moser, J., Chaste, J., Zdrojek, M., Wilson-Rae, I., Bachtold, A.: Nonlinear damping in mechanical resonators made from carbon nanotubes and graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(6), 339–342 (2011)
Farokhi, H., Paidoussis, M.P., Misra, A.K.: A new nonlinear model for analyzing the behaviour of carbon nanotube-based resonators. J. Sound Vib. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2016.05.008
Hajnayeb, A., Khadem, S.E.: Nonlinear vibration and stability analysis of a double-walled carbon nanotube under electrostatic actuation. J. Sound Vib. 331(10), 2443–2456 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2012.01.008
Harik, V.: Ranges of applicability for the continuum beam model in the mechanics of carbon nanotubes and nanorods. Solid State Commun. 120(7–8), 331–335 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0038-1098(01)00383-0
Hayt, W., Buck, J.: Engineering Electromagnetics. McGraw-Hill, New York (2012)
Hüttel, A.K., Steele, G.A., Witkamp, B., Poot, M., Kouwenhoven, L.P., van der Zant, H.S.J.: Carbon nanotubes as ultrahigh quality factor mechanical resonators. Nano Lett. 9(7), 2547–2552 (2009). doi:10.1021/nl900612h
Kang, J.W., Kwon, O.K.: A molecular dynamics simulation study on resonance frequencies comparison of tunable carbon-nanotube resonators. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(6), 2014–2016 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.05.026
Ke, C., Espinosa, H.D.: Numerical analysis of nanotube-based nems devicespart. I: Electrostatic charge distribution on multiwalled nanotubes. J. Appl. Mech. 72(5), 721–725 (2005)
Kim, S.B., Kim, J.H.: Quality factors for the nano-mechanical tubes with thermoelastic damping and initial stress. J. Sound Vib. 330(7), 1393–1402 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2010.10.015
Lee, J.H., Kang, J.W.: Vibrational analysis of cantilevered carbon-nanotube resonator with different linear density of attached mass: molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10(8), 1863–1867 (2013). doi:10.1166/jctn.2013.3140
Li, C., Chou, T.W.: Mass detection using carbon nanotube-based nanomechanical resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(25), 5246–5248 (2004). doi:10.1063/1.1764933
Natsuki, T., Matsuyama, N., Ni, Q.Q.: Vibration analysis of carbon nanotube-based resonator using nonlocal elasticity theory. Appl. Phys. A 120(4), 1309–1313 (2015). doi:10.1007/s00339-015-9398-3
Natsuki, T., Matsuyama, N., Shi, J.X., Ni, Q.Q.: Vibration analysis of nanomechanical mass sensor using carbon nanotubes under axial tensile loads. Appl. Phys. A 116(3), 1001–1007 (2014). doi:10.1007/s00339-014-8289-3
Ouakad, H.M., Younis, M.I.: Natural frequencies and mode shapes of initially curved carbon nanotube resonators under electric excitation. J. Sound Vib. 330(13), 3182–3195 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2010.12.029
Ouakad, H.M., Younis, M.I.: Dynamic response of slacked single-walled carbon nanotube resonators. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 1419–1436 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11071-011-0078-3
Poot, M., Witkamp, B., Otte, M.A., van der Zant, H.S.J.: Modelling suspended carbon nanotube resonators. Phys. Status Solidi B 244(11), 4252–4256 (2007). doi:10.1002/pssb.200776130
Prabhakar, S., Païdoussis, M.P., Vengallatore, S.: Analysis of frequency shifts due to thermoelastic coupling in flexural-mode micromechanical and nanomechanical resonators. J. Sound Vib. 323(1–2), 385–396 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2008.12.010
Roman, C., Helbling, T., Hierold, C.: Single-walled carbon nanotube sensor concepts. In: Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology, pp. 403–425. Springer, Berlin (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02525-9_14
Ruzziconi, L., Younis, M.I., Lenci, S.: Multistability in an electrically actuated carbon nanotube: a dynamical integrity perspective. Nonlinear Dyn. 74(3), 533–549 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11071-013-0986-5
Souayeh, S., Kacem, N.: Computational models for large amplitude nonlinear vibrations of electrostatically actuated carbon nanotube-based mass sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 208, 10–20 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.sna.2013.12.015
Wu, D.H., Chien, W.T., Chen, C.S., Chen, H.H.: Resonant frequency analysis of fixed-free single-walled carbon nanotube-based mass sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 126(1), 117–121 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.sna.2005.10.005
Xu, T., Younis, M.I.: Nonlinear dynamics of carbon nanotubes under large electrostatic force. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11(2), 021009 (2016)
Yang, F., Chong, A., Lam, D., Tong, P.: Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39(10), 2731–2743 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0020-7683(02)00152-X
Zang, X., Zhou, Q., Chang, J., Liu, Y., Lin, L.: Graphene and carbon nanotube (CNT) in mems/nems applications. Microelectron. Eng. 132, 192–206 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.mee.2014.10.023
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Fonds de recherche du Québec—Nature et technologies (FRQNT) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farokhi, H., Misra, A.K. & Païdoussis, M.P. A new electrostatic load model for initially curved carbon nanotube resonators: pull-in characteristics and nonlinear resonant behaviour. Nonlinear Dyn 88, 1187–1211 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3304-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3304-1