Abstract
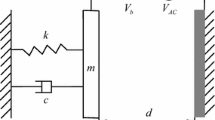
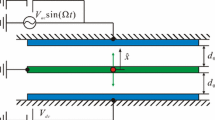
The dynamics of a close-loop electrostatic MEMS resonator, proposed as a platform for ultra sensitive mass sensors, is investigated. The parameter space of the resonator actuation voltage is investigated to determine the optimal operating regions. Bifurcation diagrams of the resonator response are obtained at five different actuation voltage levels. The resonator exhibits bi-stability with two coexisting stable equilibrium points located inside a lower and an upper potential wells. Steady-state chaotic attractors develop inside each of the potential wells and around both wells. The optimal region in the parameter space for mass sensing purposes is determined. In that region, steady-state chaotic attractors develop and spend most of the time in the safe lower well while occasionally visiting the upper well. The robustness of the chaotic attractors in that region is demonstrated by studying their basins of attraction. Further, regions of large dynamic amplification are also identified in the parameter space. In these regions, the resonator can be used as an efficient long-stroke actuator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lang, H.P., Berger, R., Battiston, F., Ramseyer, J.P., Meyer, E., Andreoli, C., Brugger, J., Vettiger, P., Despont, M., Mezzacasa, T., Scandella, L., Güntherodt, H.-J., Gerber, Ch., Gimzewski, J.K.: A chemical sensor based on a micromechanical cantilever array for the identification of gases and vapors. Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 66, 61–64 (1998)
Cherian, S., Gupta, R.K., Mullin, B.C., Thundat, T.: Detection of heavy metal ions using protein-functionalized microcantilever sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 19(5), 411–416 (2003)
Wachter, E.A., Thundat, T.: Micromechanical sensors for chemical and physical measurements. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66, 3662 (1995)
Zhang, W., Baskaran, R., Turner, K.L.: Effect of cubic nonlinearity on auto-parametrically amplified resonant MEMS mass sensor. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 102(1–2), 139–150 (2002)
Khater, M., Abdel-Rahman, E., Nayfeh, A.: A mass sensing technique for electrostatically-actuated mems. In: International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, ASME 2009, San Diego, California, USA (2009)
Spletzer, M., Raman, A., Sumali, H., Sullivan, J.P.: Highly sensitive mass detection and identification using vibration localization in coupled microcantilever arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 114102 (2008)
Yin, S.H., Epureanu, B.I.: Experimental enhanced nonlinear dynamics and identification of attractor morphing modes for damage detection. J. Vib. Acoust. 129, 763 (2007)
Strogatz, S.H.: Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering. Perseus Books, New York (2001)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics. Wiley, New York (1995)
Epureanu, B.I., Yin, S.H., Dowell, E.H.: Enhanced nonlinear dynamics for accurate identification of stiffness loss in a thermo-shielding panel. Nonlinear Dyn. 39(1), 197–211 (2005)
Ghafari, S.H., Golnaraghi, F., Ismail, F.: Effect of localized faults on chaotic vibration of rolling element bearings. Nonlinear Dyn. 53(4), 287–301 (2008)
Wu, Y.T., Shyu, K.K., Chen, T.R., Guo, W.Y.: Using three-dimensional fractal dimension to analyze the complexity of fetal cortical surface from magnetic resonance images. Nonlinear Dyn., 1–8 (2009)
Bienstman, J., Vandewalle, J., Puers, R.: The autonomous impact resonator: a new operating principle for a silicon resonant strain gauge. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 66(1–3), 40–49 (1998)
Wang, Y.C., Adams, S.G., Thorp, J.S., MacDonald, N.C., Hartwell, P., Bertsch, F.: Chaos in MEMS, parameter estimation and its potential application. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Fundam. Theory Appl. 45(10), 1013–1020 (1998)
DeMartini, B.E., Butterfield, H.E., Moehlis, J., Turner, K.L.: Chaos for a microelectromechanical oscillator governed by the nonlinear Mathieu equation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16(6), 1314–1323 (2007)
De, S.K., Aluru, N.R.: Complex oscillations and chaos in electrostatic microelectromechanical systems under superharmonic excitations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(20), 204101 (2005)
Najar, F., Nayfeh, A.H., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Choura, S., El-Borgi, S.: Dynamics and global stability of beam-based electrostatic microactuators. J. Vib. Control, 1–4 (2010)
Liu, S., Davidson, A., Lin, Q.: Simulation studies on nonlinear dynamics and chaos in a MEMS cantilever control system. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14(7), 1064–1073 (2004)
Lu, M.S.C., Fedder, G.K.: Position control of parallel-plate microactuators for probe-based data storage. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13(5), 759–769 (2004)
Towfighian, S., Heppler, G.R., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Analysis of a chaotic electrostatic micro-oscillator. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 6, 011001 (2011)
Towfighian, S., Seleim, A., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Heppler, G.R.: A large-stroke electrostatic micro-actuator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 21, 075023 (2011)
Senturia, S.D.: Microsystem Design. Kluwer Academic, Norwell (2001)
Najar, F., Nayfeh, A.H., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Choura, S., El-Borgi, S.: Nonlinear analysis of MEMS electrostatic microactuators: primary and secondary resonances of the first mode. J. Vib. Control 16(9), 1321–1349 (2010)
Simoyi, R.H., Wolf, A., Swinney, H.L.: One-dimensional dynamics in a multicomponent chemical reaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49(4), 245–248 (1982)
Metropolis, N., Stein, M.L., Stein, P.R.: Finite limit sets for transformations on the unit interval. J. Comb. Theory 15, 25–43 (1973)
Carnahan, B., Luther, H.A., Wilkes, J.O.: Applied Numerical Methods. Wiley, New York (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seleim, A., Towfighian, S., Delande, E. et al. Dynamics of a close-loop controlled MEMS resonator. Nonlinear Dyn 69, 615–633 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0292-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0292-z