Abstract
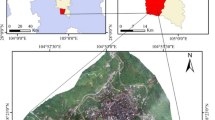
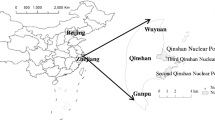
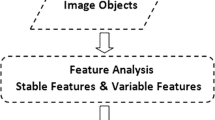
Sinkhole development is a typical geological disaster found in areas of carbonate bedrock. Compared with other geological disasters, sinkholes are considerably smaller and scattered according to scale and spatial distribution. Nevertheless, detecting and investigating sinkholes have become increasingly challenging. This study proposes a novel method by applying case-based reasoning (CBR) combined with object-based image analysis and genetic algorithms (GAs) to detect the sinkholes using high-resolution aerial images. This case study was performed in Paitan Town, Guangdong Province, China. The method comprises three major steps: (1) multi-image segmentation, (2) GA-based feature selection, and (3) application of CBR techniques. The detected sinkholes were categorized into three classes: buried, collapse type I, and collapse type II. The experiment demonstrated that the proposed method can obtain higher accuracy compared with the traditional supervised maximum likelihood classifier (MLC). The overall accuracy of CBR classification and MLC for the collapse area was 0.88 and 0.71, respectively. In addition, the kappa coefficient for CBR classification (0.81) was higher than that for MLC (0.5). A similar case library was also applied to another trial area for validation, the satisfactory results of which suggested that CBR is applicable for independently detecting sinkholes. The proposed method will be useful for preparing hazard maps that express the relative probability of a collapse in similar regions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamodt A, Plaza E (1994) Case-based reasoning: foundational issues, methodological variations, and system approaches. AI Commun 7:39–59
Ahn H, Kim K, Han I (2006) Hybrid genetic algorithms and case-based reasoning systems for customer classification. Expert Syst 23:127–144
Anders NS, Seijmonsbergen AC, Bouten W (2011) Segmentation optimization and stratified object-based analysis for semi-automated geomorphological mapping. Remote Sens Environ 115:2976–2985. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2011.05.007
Baatz M, Benz U, Dehghani S, Heynen M (2004) eCognition user guide 4. Definiens imagine GmbH, Munich, Germany
Benz UC, Hofmann P, Willhauck G et al (2004) Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 58:239–258. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2003.10.002
Blaschke T (2010) Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 65:2–16. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2009.06.004
Blaschke T, Strobl J (2001) What’s wrong with pixels ? Some recent developments interfacing remote sensing and GIS. Interfacing Remote Sens GIS 6:12–17
Chang T, Lin S (1999) Grey relation analysis of carbon dioxide emissions from industrial production and energy uses in Taiwan. J Environ Manag 247–257
Chang K-T, Liu J, Wang C (2012) An object-oriented analysis for characterizing the rainfall-induced shallow landslide. J Mar Sci Technol 20:647–656. doi:10.6119/JMST-012-0430-2
De Mantaras L, McSherry R, Bridge D et al (2005) Retrieval, reuse, revision and retention in case-based reasoning. Knowl Eng Rev 20:215–240. doi:10.1017/S000000000000000
Deng J-L (1982) Control problems of grey systems. Syst Control Lett 1:288–294. doi:10.1016/S0167-6911(82)80025-X
Denoeux T (1995) A k-nearest neighbor classification rule based on Dempster–Shafer theory. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25:804–813
Doloca A (2000) Feature selection for texture analysis using genetic algorithms. Int J Comput Math 74:279–292. doi:10.1080/00207160008804942
Dou J, Qian J, Zhang H et al (2009a) Landslides detection: a case study in Conghua city of Pearl River delta. In: Second International Conference on Earth Observation for Global Changes 74711K–11. doi:10.1117/12.836328
Dou J, Zheng X, Qian J et al (2009b) Intelligence based automatic detection and classification of ground collapses using object-based image analysis method: a case study in Paitan of Pearl River delta. In: Geoinformatics 2008 and Joint Conference on GIS and Built environment: Advanced Spatial Data Models and Analyses 7146:714623–12. doi:10.1117/12.813168
Dou J, Qian J, Chen S, Zhen X (2010) Object-based and case-based reasoning method for ground collapses detection. J Image Graph 15:900–910
Drăguţ L, Eisank C (2011) Object representations at multiple scales from digital elevation models. Geomorphology 129:183–189. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.03.003
Dronova I, Gong P, Wang L (2011) Object-based analysis and change detection of major wetland cover types and their classification uncertainty during the low water period at Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens Environ 115:3220–3236. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.006
Duro DC, Franklin SE, Dubé MG (2012) Multi-scale object-based image analysis and feature selection of multi-sensor earth observation imagery using random forests. Int J Remote Sens 33:4502–4526. doi:10.1080/01431161.2011.649864
Ehlers M, Gähler M, Janowsky R (2003) Automated analysis of ultra high resolution remote sensing data for biotope type mapping: new possibilities and challenges. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 57:315–326. doi:10.1016/S0924-2716(02)00161-2
Ford D, Williams PD (2007) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Wiley, Chichester, United Kingdom, p 562
García-Rodríguez MJ, Malpica JA, Benito B, Díaz M (2008) Susceptibility assessment of earthquake-triggered landslides in El Salvador using logistic regression. Geomorphology 95:172–191. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.06.001
Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S (2003) Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecol Modell 160:249–264
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc, Boston, MA, USA, p 343
Gómez H, Kavzoglu T (2005) Assessment of shallow landslide susceptibility using artificial neural networks in Jabonosa River Basin, Venezuela. Eng Geol 78:11–27. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.10.004
Guo Y, Hu J, Peng Y (2011) Research on CBR system based on data mining. Appl Soft Comput 11:5006–5014. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2011.05.057
Gutiérrez F, Guerrero J, Lucha P (2007) A genetic classification of sinkholes illustrated from evaporite paleokarst exposures in Spain. Environ Geol 53:993–1006. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0727-5
Gutiérrez F, Guerrero J, Lucha P (2008) Quantitative sinkhole hazard assessment. A case study from the Ebro Valley evaporite alluvial karst (NE Spain). Nat Hazards 45:211–233. doi:10.1007/s11069-007-9161-y
Gutiérrez F, Parise M, De Waele J, Jourde H (2014) A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci Rev 138:61–88. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.08.002
Hay GJ, Castilla G, Wulder MA, Ruiz JR (2005) An automated object-based approach for the multiscale image segmentation of forest scenes. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 7:339–359. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2005.06.005
Im J, Jensen JR, Tullis JA (2008) Object-based change detection using correlation image analysis and image segmentation. Int J Remote Sens 29:399–423. doi:10.1080/01431160601075582
Iovine G, D’Ambrosio D, Di Gregorio S (2005) Applying genetic algorithms for calibrating a hexagonal cellular automata model for the simulation of debris flows characterised by strong inertial effects. Geomorphology 66:287–303. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.09.017
Jyothi BN, Babu GR, Krishna IVM (2008) Object oriented and multi-scale image analysis: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats-A review. J Comput Sci 4:706–712. doi:10.3844/jcssp.2008.706.712
Kim S, Shim J (2013) Combining case-based reasoning with genetic algorithm optimization for preliminary cost estimation in construction industry. Can J Civ Eng 73:65–73
Kolodner JL (1992) An introduction to case-based reasoning. Artif Intell Rev 6:3–34. doi:10.1007/BF00155578
Kovačič G, Ravbar N (2013) Analysis of human induced changes in a karst landscape- the filling of dolines in the Kras plateau, Slovenia. Sci Total Environ 447:143–151. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.002
Kudo M, Sklansky J (2000) Comparison of algorithms that select features for pattern classifiers. Pattern Recognit 33:25–41
Li X, Yeh AG (2004) Multitemporal SAR images for monitoring cultivation systems using case-based reasoning. Remote Sens Environ 90:524–534. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2004.01.018
Lu IJ, Lin SJ, Lewis C (2008) Grey relation analysis of motor vehicular energy consumption in Taiwan. Energy Policy 36:2556–2561. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.03.015
Manzoor J, Asif S, Masud M, Khan MJ (2012) Automatic case generation for case-based reasoning systems using genetic algorithms. Third Glob Congr Intell Syst 2012:311–314. doi:10.1109/GCIS.2012.89
Martha TR, Kerle N, van Westen CJ et al (2012) Object-oriented analysis of multi-temporal panchromatic images for creation of historical landslide inventories. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 67:105–119. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2011.11.004
Micó M, Oncina J, Vidal E (1994) A new version of the nearest-neighbour approximating and eliminating search algorithm (AESA) with linear preprocessing time and memory requirements. Pattern Recognit Lett 15:9–17
Minor M, Bergmann R, Görg S, Walter K (2010) Towards case-based adaptation of workflows. Case-Based Reasoning, Research and Development, pp 421–435
Minor M, Bergmann R, Görg S (2014) Case-based adaptation of workflows. Inf Syst 40:142–152. doi:10.1016/j.is.2012.11.011
Parise M (2012) A present risk from past activities: Sinkhole occurrence above underground quarries. Carbonates Evaporites 27:109–118. doi:10.1007/s13146-012-0088-3
Qian J, Li X, Ai B et al (2007a) Land-use short-term change detection based on time series case based-reasoning. J Nat 22:735–746
Qian J, Liu R, Chen S, Dou J (2007b) Man-made ground collapse detection using high resolution aerial image and object-based classification: example of Pearl River delta. In: Proceedings of Second International ISCRAM Work. Inf. Syst. Cris. Response Manag. pp 1–6
Radoux J, Bogaert P, Fasbender D, Defourny P (2011) Thematic accuracy assessment of geographic object-based image classification. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 25:895–911. doi:10.1080/13658816.2010.498378
Raši R, Bodart C, Stibig HJ et al (2011) An automated approach for segmenting and classifying a large sample of multi-date Landsat imagery for pan-tropical forest monitoring. Remote Sens Environ 115:3659–3669. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2011.09.004
Shruthi RBV, Kerle N, Jetten V (2011) Object-based gully feature extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Geomorphology 134:260–268. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.07.003
Siart C, Bubenzer O, Eitel B (2009) Combining digital elevation data (SRTM/ASTER), high resolution satellite imagery (Quickbird) and GIS for geomorphological mapping: a multi-component case study on Mediterranean karst in Central Crete. Geomorphology 112:106–121. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.05.010
Slater J, Brown R (2000) Changing landscapes: monitoring environmentally sensitive areas using satellite imagery. Int J Remote Sens 21:2753–2767
Sumer E, Turker M (2013) An adaptive fuzzy-genetic algorithm approach for building detection using high-resolution satellite images. Comput Environ Urban Syst 39:48–62. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.01.004
Torres RDS, Falcão AX, Gonçalves MA et al (2009) A genetic programming framework for content-based image retrieval. Pattern Recognit 42:283–292. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2008.04.010
Tu JV (1996) Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 49:1225–1231
Vancoillie F, Verbeke L, Dewulf R (2007) Feature selection by genetic algorithms in object-based classification of IKONOS imagery for forest mapping in Flanders, Belgium. Remote Sens Environ 110:476–487. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2007.03.020
Waltham A, Fookes P (2003) Engineering classification of karst ground conditions. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol Eng 36:101–118
Yu Q, Gong P, Clinton N et al (2006) Object-based detailed vegetation classification with airborne high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 72:799–811. doi:10.14358/PERS.72.7.799
Zhai L-Y, Khoo L-P, Zhong Z-W (2009) Design concept evaluation in product development using rough sets and grey relation analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36:7072–7079. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.08.068
Zhang C, Xie Z (2012) Combining object-based texture measures with a neural network for vegetation mapping in the Everglades from hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens Environ 124:310–320. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2012.05.015
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the funding from the Geological Survey of Guangzhou City (Project No. 1212010511106-05). Jie Dou deeply thanks Dr. Jun-ping Qian for her kind instruction and help. The authors also appreciate two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions that significantly improved the quality of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, J., Li, X., Yunus, A.P. et al. Automatic detection of sinkhole collapses at finer resolutions using a multi-component remote sensing approach. Nat Hazards 78, 1021–1044 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1756-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1756-0