Abstract
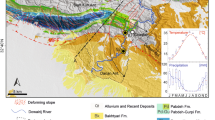
In this paper, we discuss historical and recent land subsidence in the Modern Yellow River Delta. Integrated analysis of leveling and relevant background data, including groundwater level, oil extraction, and geological structure, has revealed that land displacement is driven by natural and induced components acting at various depths. Since the 1950s, intense settlements occurred in the modern estuary delta lobes. Between 2002 and 2008, the subsidence center of Dongying and Guangrao exhibited a typical subsidence area with subsidence rates of 28.2 and 64.7 mm/years, respectively. Higher magnitudes are associated with groundwater withdrawals and oil–gas field exploitations, which induce the compaction of a deep clayey layer. There existed a significant linear positive correlation between groundwater level and elevation in the center of the deep groundwater depression cone. The major contributor of natural subsidence is tectonic movements, while moderate sinking due to the natural consolidation of the recent delta subsoil is still acting.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin HZ, Andreas H, Djaja R, Darmawan D, Gamal M (2008) Land subsidence characteristics of Jakarta between 1997 and 2005, as estimated using GPS surveys. GPS Solut 12(1):23–32. doi:10.1007/s10291-007-0061-0
Abidin HZ, Andreas H, Gumilar I, Fukuda Y, Pohan YE, Deguchi T (2011) Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat Hazards 59(3):1753–1771. doi:10.1007/s11069-011-9866-9
Aviles J, Perez-Rocha LE (2010) Regional subsidence of Mexico City and its effects on seismic response. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30(10):981–989. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.04.009
Bie J, Huang HJ, Bi SP (2006) Ground subsidence of the Modern Yellow River Delta and its causes. Quat Sci 26(04):29–35 (in Chinese)
Carbognin L, Teatini P, Tosi L (2004) Eustacy and land subsidence in the Venice Lagoon at the beginning of the new millennium. J Mar Syst 51(1–4):345–353. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.05.021
Carbognin L, Teatini P, Tomasin A, Tosi L (2010) Global change and relative sea level rise at Venice: what impact in term of flooding. Clim Dyn 35(6):1055–1063. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0617-5
Chen G, Yun SJ, Li TF (2001) Impact of deeplying cohesive soil on subsidence in Tianjin and the settlement calculation. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis 06:804–809 (in Chinese)
Chen QH, Liu CY, Lu HY, Lu HY, Wang GM, Li GX (2002) Character of sedimentary sequence and structural settlement of shallow layers in the Yellow River Delta. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 04:386–389 (in Chinese)
Chen CX, Pei SP, Jiao JJ (2003) Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou City, China. Hydrogeol J 11(2):275–287. doi:10.1007/s10040-002-0225-5
Chen B, Gong H, Li X, Lei K, Zhang Y, Li J, Gu Z, Dang Y (2011) Spatial-temporal characteristics of land subsidence corresponding to dynamic groundwater funnel in Beijing Municipality, China. Chin Geogr Sci 21(6):753–764. doi:10.1007/s11769-011-0509-6
Chu ZX, Sun XG, Zhai SK, Xu KH (2006) Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modem Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, China: based on remote sensing images. Mar Geol 227(1–2):13–30. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2005.11.013
Esaki T, Zhou GY, Jiang YJ, Sakai A, Hachiya Y (1996) A synthetical system for predicting and measuring groundwater flow and land subsidence in Saga Plain, Japan. A a Balkema, Rotterdam
Gallardo AH, Marui A, Takeda S, Okuda F (2009) Groundwater supply under land subsidence constrains in the Nobi Plain. Geosci J 13(2):151–159. doi:10.1007/s12303-009-0014-4
Gambolati G (1975) Numerical models in land subsidence control. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 5(2):227–237. doi:10.1016/0045-7825(75)90054-7
Geertsma J (1973) Land subsidence above compacting oil and gas reservoirs. J Petroleum Technol 25:734–744
Hu HM, Shen YJ (1991) The developing of ground subsidence in main cities of North China. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 2(4):1–9 (in Chinese)
Huang LR, Hu HM (1991) Sea level change along the western and southern coast of Bohai sea and recent crustal vertical movement in adjacent area. Crustal Deform Earthq 11(1):1–9 (in Chinese)
Hung WC, Hwang C, Chang CP, Yen JY, Liu CH, Yang WH (2010) Monitoring severe aquifer-system compaction and land subsidence in Taiwan using multiple sensors: Yunlin, the southern Choushui River Alluvial Fan. Environ Earth Sci 59(7):1535–1548. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0139-9
Ko JY, Day JW (2004) A review of ecological impacts of oil and gas development on coastal ecosystems in the Mississippi Delta. Ocean Coast Manag 47(11–12):597–623. doi:10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2004.12.004
Li QF, Wang HM (2006) A study on land subsidence in Shanghai. Geol J China Uiversities 02:169–178 (in Chinese)
Liu CH, Pan YW, Liao JJ, Huang CT, Ouyang S (2004) Characterization of land subsidence in the Choshui River alluvial fan, Taiwan. Environ Geol 45(8):1154–1166
Ma R, Wang YX, Ma T, Sun ZY, Yan SL (2006) The effect of stratigraphic heterogeneity on areal distribution of land subsidence at Taiyuan, northern China. Environ Geol 50(4):551–568. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0232-2
Ma FS, Wei AH, Han ZT, Zhao HJ, Guo J (2011) The characteristics and causes of land subsidence in Tanggu based on the GPS survey system and numerical simulation. Acta Geol Sinica-English Ed 85(6):1495–1507. doi:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00601.x
Mahara Y, Kitaoaka K (2009) Helium isotopic fingerprints of the heavy land subsidence left in groundwater of the Saga Plain, near Beppu-Shimabara graben, Kyushu, Japan. Appl Geochem 24(3):438–446. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.12.028
Mikita M, Yamanaka T, Lorphensri O (2011) Anthropogenic changes in a confined groundwater flow system in the Bangkok basin, Thailand, part I: was groundwater-recharge enhanced? Hydrol Process 25(17):2726–2733. doi:10.1002/hyp.8013
Niu XJ (1998) Characteristics of strata consolidation and land subsidence controlling by critical water level. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 9(02):68–74 (in Chinese)
Osmanoglu B, Dixon TH, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E, Jiang Y (2011) Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 13(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2010.05.009
Ovando-Shelley E, Ossa A, Romo MP (2007) The sinking of Mexico City: its effects on soil properties and seismic response. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 27(4):333–343. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2006.08.005
Phien-wej N, Giao PH, Nutalaya P (2006) Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng Geol 82(4):187–201. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.10.004
Pratt W, Johnson D (1926) Local subsidence in the Goose Creek oil field. J Geol 34:577–590
Ren ME (1993) Relativer sea level rise in Huanghe, Changjiang, Zhujiang (Yellow, Yangtze and Pearl River) delta over the last 30 years and predication for the next 40 years (2030). Acta Geographica Sinica 48(5):385–393 (in Chinese)
Sahu P, Sikdar PK (2011) Threat of land subsidence in and around Kolkata City and East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal, India. J Earth Syst Sci 120(3):435–446
Sato HP, Abe K, Ootaki O (2003) GPS-measured land subsidence in Ojiya City, Niigata Prefecture, Japan. Eng Geol 67(3–4):379–390. doi:10.1016/s0013-7952(02)00221-1
Sharp JM, Hill DW (1995) Land subsidence along the northeastern Texas gulf coast: effects of deep hydrocarbon production. Environ Geol 25(3):181–191
Shi CX, You LY, Li BY, Zhang ZL, Zhang OY (2003) Natural consolidation of deposits and its consequences at the Yellow River Delta. Scientia Geographica Sinica 02:175–181 (in Chinese)
Shi CX, Zhang D, You LY, Li BY, Zhang ZL, Zhang OY (2007) Land subsidence as a result of sediment consolidation in the Yellow River delta. J Coast Res 23(1):173–181. doi:10.2112/39951.1
Shi XQ, Xue YQ, Wu JC, Ye SJ, Zhang Y, Wei ZX, Yu J (2008) Characterization of regional land subsidence in Yangtze Delta, China: the example of Su-Xi-Chang area and the city of Shanghai. Hydrogeol J 16(3):593–607. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0237-2
Sun H, Grandstaff D, Shagam R (1999) Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal: potential damage of subsidence and sea level rise in southern New Jersey, USA. Environ Geol 37(4):290–296
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Bertoni W, Gonella M (2005) A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ Geol 47(6):831–846. doi:10.1007/s00254-004-1215-9
Teatini P, Castelletto N, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Janna C, Cairo E, Marzorati D, Colombo D, Ferretti A, Bagliani A, Bottazzi F (2011a) Geomechanical response to seasonal gas storage in depleted reservoirs: a case study in the Po River basin, Italy. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 116:1–21
Teatini P, Tosi L, Strozzi T (2011b) Quantitative evidence that compaction of Holocene sediments drives the present land subsidence of the Po Delta, Italy. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 116. doi:10.1029/2010jb008122
Teatini P, Tosi L, Strozzi T, Carbognin L, Cecconi G, Rosselli R, Libardo S (2012) Resolving land subsidence within the Venice Lagoon by persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. Phys Chem Earth 40–41:72–79. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2010.01.002
Tosi L, Teatini P, Carbognin L, Frankenfield J (2007) A new project to monitor land subsidence in the northern Venice coastland (Italy). Environ Geol 52(5):889–898. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0530-8
Tosi L, Teatini P, Carbognin L, Brancolini G (2009) Using high resolution data to reveal depth-dependent mechanisms that drive land subsidence: the Venice coast, Italy. Tectonophysics 474(1–2):271–284. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.026
Tosi L, Teatini P, Strozzi T, Carbognin L, Brancolini G, Rizzetto F (2010) Ground surface dynamics in the northern Adriatic coastland over the last two decades. Rendiconti Lincei-Scienze Fisiche E Naturali 21:115–129. doi:10.1007/s12210-010-0084-2
Tosi L, Teatini P, Bincoletto L, Simonini P, Strozzi T (2012) Integrating geotechnical and interferometric SAR measurements for secondary compressibility characterization of coastal soils. Surv Geophys 33(5):907–926. doi:10.1007/s10712-012-9186-y
Wang GY, You G, Shi B, Yu J, Tuck M (2009) Long-term land subsidence and strata compression in Changzhou, China. Eng Geol 104(1–2):109–118. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.09.001
Wei ZX (2002) The stress-strain analysis of the 4th confined aquifer in Shanghai City. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 01:1–4 (in Chinese)
Wu Q, Zheng XX, Xu H, Ying YF, Hou YS, Xie XC, Wang SX (2003) Relative sea-level rising and its control strategy in coastal regions of China in the 21st century. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci 46(1):74–83. doi:10.1360/03yd9007
Wu JC, Shi XQ, Ye SJ, Xue YQ, Zhang Y, Wei ZX, Fang Z (2010) Numerical simulation of viscoelastoplastic land subsidence due to groundwater overdrafting in Shanghai, China. J Hydrol Eng 15(3):223–236. doi:10.1061/(asce)he.1943-5584.0000172
Xiao DN, Han MK, Li XW, Liu YF (2003) Sea level rising around Bohai Sea and deltaic wetlands protection. Quat Sci 23(03):237–246 (in Chinese)
Xu YS, Shen SL, Cai ZY, Zhou GY (2008) The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat Hazards 45(1):123–135. doi:10.1007/s11069-007-9168-4
Xue YQ, Zhang Y, Ye SJ, Li QF (2003) Land subsidence in China and its problems. Quat Sci 23(6):585–593 (in Chinese)
Xue YQ, Zhang Y, Ye SJ, Wu JC, Li QF (2005) Land subsidence in China. Environ Geol 48(6):713–720. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0010-6
Yamanaka T, Mikita M, Lorphensri O, Shimada J, Kagabu M, Ikawa R, Nakamura T, Tsujimura M (2011) Anthropogenic changes in a confined groundwater flow system in the Bangkok Basin, Thailand, part II: how much water has been renewed? Hydrol Process 25(17):2734–2741. doi:10.1002/hyp.8014
Yi LX, Zhang F, Xu H, Chen SJ, Wang W, Yu Q (2011) Land subsidence in Tianjin, China. Environ Earth Sci 62(6):1151–1161. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0604-5
Yu ZT (2006) Investigation and study of salt water intrusion on the south coast plain of Laizhou Bay. Dissertation, Ocean University of China (in Chinese)
Zhang BM, Jin AS (1998) Effect of extracting geothermal resources on land subsidence in Binhai area of Tianjin City. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 02:114–119 (in Chinese)
Zhang AG, Wei ZX (2002) Past, present and future research on land subsidence in Shanghai City. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 2002(05):72–75 (in Chinese)
Zhang GH, Fei YH, Yang LZ, Liu ZP, Lian YL (2010) Variation characteristics and mechanisms of exploitation yield formation in the region with confined-groundwater depression cone. Adv Water Sci 03:370–376 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Ding Dong at the Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology and Chief Engineer Zou Zuguang at the Lubei Institute of Geological and Prospecting Engineering in Dezhou. This paper is financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40676037 and No. 41276082) and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KZCX2-EW-207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Huang, HJ. Characterization and mechanism of regional land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta, China. Nat Hazards 68, 687–709 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0648-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0648-4