Abstract
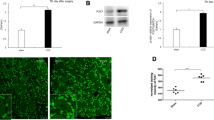
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and purinergic P2X receptors play critical roles in the nerve injury-induced pain hypersensitivity. Both HCN channels and P2XR are expressed in dorsal root ganglia sensory neurons. However, it is not clear whether the expression and function of P2X2 and P2X3 receptors can be modulated by HCN channel activity. For this reason, in rats with chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve, we evaluated the effect of intrathecal administration of HCN channel blocker ZD7288 on nociceptive behavior and the expression of P2X2 and P2X3 in rat DRG. The mechanical withdrawal threshold was measured to evaluate pain behavior in rats. The protein expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor in rat DRG was observed by using Western Blot. The level of cAMP in rat DRG was measured by ELISA. As a result, decreased MWT was observed in CCI rats on 1 d after surgery, and the allodynia was sustained throughout the experimental period. In addition, CCI rats presented increased expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor in the ipsilateral DRG at 7 d and 14 d after CCI operation. Intrathecal injection of ZD7288 significantly reversed CCI-induced mechanical hyperalgesia, and attenuated the increased expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor in rat DRG, which open up the possibility that the expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor in DRG is down-regulated by HCN channel blocker ZD7288 in CCI rats. Furthermore, the level of cAMP in rat DRG significantly increased after nerve injury. Intrathecal administration of ZD7288 attenuated the increase of cAMP in DRG caused by nerve injury. Subsequently, effects of HCN channel activity on ATP-induced current (IATP) in rat DRG neurons were explored by using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques. ATP (100 μM) elicited three types of currents (fast, slow and mixed IATP) in cultured DRG neurons. Pretreatment with ZD7288 concentration-dependently inhibited three types of ATP-activated currents. On the other hand, pretreatment with 8-Br-cAMP (a cell-permeable cAMP analog, also known as an activator of PKA) significantly increased the amplitude of fast, slow and mixed IATP in DRG neurons. The enhanced effect of 8-Br-cAMP on ATP-activated currents could be reversed by ZD7288. In a summary, our observations suggest that the opening of HCN channels could enhance the expression and function of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor via the cAMP-PKA signaling pathway. This may be important for pathophysiological events occurring within the DRG, for where it is implicated in nerve injury-induced pain hypersensitivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Jansen LR, Forster LA, Smith XL, Rubaharan M, Murphy AZ, Baro DJ (2021) Changes in peripheral HCN2 channels during persistent inflammation. Channels (Austin) 15(1):165–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336950.2020.1870086
Smith T, Al Otaibi M, Sathish J, Djouhri L (2015) Increased expression of HCN2 channel protein in L4 dorsal root ganglion neurons following axotomy of L5- and inflammation of L4-spinal nerves in rats. Neuroscience 295:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.041
Dini L, Del Lungo M, Resta F, Melchiorre M, Spinelli V, Di Cesare Mannelli L, Ghelardini C, Laurino A, Sartiani L, Coppini R, Mannaioni G, Cerbai E, Romanelli MN (2018) Selective blockade of HCN1/HCN2 channels as a potential pharmacological strategy against pain. Front Pharmacol 9:1252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01252
Weng X, Smith T, Sathish J, Djouhri L (2012) Chronic inflammatory pain is associated with increased excitability and hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) in C- but not Aδ-nociceptors. Pain 153(4):900–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2012.01.019
Djouhri L, Al Otaibi M, Kahlat K, Smith T, Sathish J, Weng X (2015) Persistent hindlimb inflammation induces changes in activation properties of hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) in rat C-fiber nociceptors in vivo. Neuroscience 301:121–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.05.074
Emery EC, Young GT, Berrocoso EM, Chen L, McNaughton PA (2011) HCN2 ion channels play a central role in inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Science. 333(6048):1462–1466. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206243
Yang YC, Meng QT, Pan X, Xia ZY, Chen XD (2014) Dexmedetomidine produced analgesic effect via inhibition of HCN currents. Eur J Pharmacol 740:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.06.031
Tsantoulas C, Laínez S, Wong S, Mehta I, Vilar B, McNaughton PA (2017) Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 2 (HCN2) ion channels drive pain in mouse models of diabetic neuropathy. Sci Transl Med 9(409):6072. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aam6072
Momin A, Cadiou H, Mason A, McNaughton PA (2008) Role of the hyperpolarization-activated current Ih in somatosensory neurons. J Physiol 586(24):5911–29. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.163154
Liu X, Zeng J, Zhao Y, Xiao Z, Fang C, Ruan H (2010) Inhibition of ATP-induced Ca2+ influx by corticosterone in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Res 35(5):804–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0138-y
Chen L, Liu YW, Yue K, Ru Q, Xiong Q, Ma BM, Tian X, Li CY (2016) Differential expression of ATP-gated P2X receptors in DRG between chronic neuropathic pain and visceralgia rat models. Purinergic Signal 12(1):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9481-4
Honore P, Kage K, Mikusa J, Watt AT, Johnston JF, Wyatt JR, Faltynek CR, Jarvis MF, Lynch K (2002) Analgesic profile of intrathecal P2X(3) antisense oligonucleotide treatment in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain states in rats. Pain 99(1–2):11–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3959(02)00032-5
Gao Y, Liu H, Deng L, Zhu G, Xu C, Li G, Liu S, Xie J, Liu J, Kong F, Wu R, Li G, Liang S (2011) Effect of emodin on neuropathic pain transmission mediated by P2X2/3 receptor of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res Bull 84(6):406–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.01.017
Ueno S, Tsuda M, Iwanaga T, Inoue K (1999) Cell type-specific ATP-activated responses in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Br J Pharmacol 126(2):429–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0702319
Chen Y, Li GW, Wang C, Gu Y, Huang LM (2005) Mechanisms underlying enhanced P2X receptor-mediated responses in the neuropathic pain state. Pain 119(1–3):38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.09.007
Wang S, Xu H, Zou L, Xie J, Wu H, Wu B, Yi Z, Lv Q, Zhang X, Ying M, Liu S, Li G, Gao Y, Xu C, Zhang C, Xue Y, Liang S (2016) LncRNA uc.48+ is involved in diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signal 12(1):139–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9488-x
Shinoda M, La JH, Bielefeldt K, Gebhart GF (2010) Altered purinergic signaling in colorectal dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to colorectal hypersensitivity. J Neurophysiol 104(6):3113–23. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00560.2010
Xu GY, Huang LY (2002) Peripheral inflammation sensitizes P2X receptor-mediated responses in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci 22(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00093.2002
Cockayne DA, Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Rong W, Hamilton SG, Knight GE, Ruan HZ, Ma B, Yip P, Nunn P, McMahon SB, Burnstock G, Ford AP (2005) P2X2 knockout mice and P2X2/P2X3 double knockout mice reveal a role for the P2X2 receptor subunit in mediating multiple sensory effects of ATP. J Physiol 567(Pt 2):621–39. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2005.088435
Wu X, Liao L, Liu X, Luo F, Yang T, Li C (2012) Is ZD7288 a selective blocker of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel currents? Channels (Austin) 6(6):438–42. https://doi.org/10.4161/chan.22209
Huang CC, Hsu KS (2003) Reexamination of the role of hyperpolarization-activated cation channels in short- and long-term plasticity at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Neuropharmacology 44(7):968–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00098-4
Chen C (2004) ZD7288 inhibits postsynaptic glutamate receptor-mediated responses at hippocampal perforant path-granule cell synapses. Eur J Neurosci 19(3):643–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0953-816x.2003.03174.x
Zhang XX, Min XC, Xu XL, Zheng M, Guo LJ (2016) ZD7288, a selective hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel blocker, inhibits hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neural Regen Res 11(5):779–86. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.182705
Huang W, Xiu Y, Yan JA, He WJ, Zhao YD, Hu ZA, Ruan HZ (2010) Facilitation of Ih channels by P2Y1 receptors activation in Mesencephalic trigeminal neurons. Neurosci Lett 482(2):156–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.07.023
Khakh BS, Henderson G (1998) Hyperpolarization-activated cationic currents (Ih) in neurones of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus of the rat. J Physiol 510(Pt 3):695–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.00695.x
Wang C, Li GW, Huang LY (2007) Prostaglandin E2 potentiation of P2X3 receptor mediated currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol Pain 3:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-3-22
Zhao J, Gao B, Zhang Y, Zheng B, Liu H, Cao JL (2014) Effects of intrathecal opioids combined with low-dose naloxone on motilin and its receptor in a rat model of postoperative pain. Life Sci 103(2):88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.03.032
Niu J, Huang D, Zhou R, Yue M, Xu T, Yang J, He L, Tian H, Liu X, Zeng J (2017) Activation of dorsal horn cannabinoid CB2 receptor suppresses the expression of P2Y12 and P2Y13 receptors in neuropathic pain rats. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):185. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0960-0
Størkson RV, Kjørsvik A, Tjølsen A, Hole K (1996) Lumbar catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 65(2):167–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(95)00164-6
Huang D, Yang J, Liu X, He L, Luo X, Tian H, Xu T, Zeng J (2018) P2Y6 receptor activation is involved in the development of neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. J Clin Neurosci 56:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.07.013
Fu M, Meng L, Ren H, Luo F (2019) Pulsed radiofrequency inhibits expression of P2X3 receptors and alleviates neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 132(14):1706–1712. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000302
Yang Y, Xia Z, Meng Q, Liu K, Xiao Y, Shi L (2018) Dexmedetomidine relieves neuropathic pain by inhibiting hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated currents in dorsal root ganglia neurons. Neuroreport 29(12):1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001068
Zhou R, Xu T, Liu X, Chen Y, Kong D, Tian H, Yue M, Huang D, Zeng J (2018) Activation of spinal dorsal horn P2Y13 receptors can promote the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 in rats with diabetic neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 11:615–628. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S154437
Gao SH, Shen LL, Wen HZ, Zhao YD, Ruan HZ (2017) Inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 alters the excitability of the commissural pyramidal neuron in the rat anterior cingulate cortex after chronic constriction injury to the sciatic nerve. Anesthesiology 127(3):515–533. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000001654
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9
Tao J, Liu L, Fan Y, Wang M, Li L, Zou L, Yuan H, Shi L, Yang R, Liang S, Liu S (2019) Role of hesperidin in P2X3 receptor-mediated neuropathic pain in the dorsal root ganglia. Int J Neurosci 129(8):784–793. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2019.1567512
Zheng XB, Zhang YL, Li Q, Liu YG, Wang XD, Yang BL, Zhu GC, Zhou CF, Gao Y, Liu ZX (2019) Effects of 1,8-cineole on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X2 receptor in the spinal cord dorsal horn. Sci Rep 9(1):7909. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44282-4
Zou L, Yu K, Fan Y, Cao S, Liu S, Shi L, Li L, Yuan H, Yang R, Yi Z, Gao Y, Li G, Greffrath W, Treede RD, Li M, Xu H, Zhang C, Liang S (2019) The Inhibition by Guanfu Base A of Neuropathic Pain Mediated by P2Y12 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(3):1318–1325. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00399
Yi Z, Rao S, Ouyang S, Bai Y, Yang J, Ma Y, Han X, Wu B, Zou L, Jia T, Zhao S, Hu X, Lei Q, Gao Y, Liu S, Xu H, Zhang C, Liang S, Li G (2017) A317491 relieved HIV gp120-associated neuropathic pain involved in P2X3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res Bull 130:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.01.002
Du L, Wang SJ, Cui J, He WJ, Ruan HZ (2013) The role of HCN channels within the periaqueductal gray in neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1500:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.01.035
Liu XH, Zeng JW, Zhao YD, Chen PH, Xiao Z, Ruan HZ (2008) Rapid inhibition of ATP-induced currents by corticosterone in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pharmacology 82(2):164–70. https://doi.org/10.1159/000149582
Gerevich Z, Müller C, Illes P (2005) Metabotropic P2Y1 receptors inhibit P2X3 receptor-channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 521(1–3):34–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.08.001
Ma Y, Chen J, Yu D, Wei B, Jin H, Zeng J, Liu X (2021) cAMP-PKA signaling is involved in regulation of spinal HCN channels function in diabetic neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 750:135763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135763
Li ZH, Cui D, Qiu CJ, Song XJ (2019) Cyclic nucleotide signaling in sensory neuron hyperexcitability and chronic pain after nerve injury. Neurobiol Pain 6:100028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100028
Tao T, Wei MY, Guo XW, Zhang J, Yang LY, Zheng H (2019) Modulating cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 attenuates functional and behavioural deficits in rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(6):2602–2611. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201903_17410.
Huang ZJ, Li HC, Cowan AA, Liu S, Zhang YK, Song XJ (2012) Chronic compression or acute dissociation of dorsal root ganglion induces cAMP-dependent neuronal hyperexcitability through activation of PAR2. Pain 153(7):1426–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2012.03.025
Zagotta WN, Olivier NB, Black KD, Young EC, Olson R, Gouaux E (2003) Structural basis for modulation and agonist specificity of HCN pacemaker channels. Nature 425(6954):200–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01922
Akimoto M, Zhang Z, Boulton S, Selvaratnam R, VanSchouwen B, Gloyd M, Accili EA, Lange OF, Melacini G (2014) A mechanism for the auto-inhibition of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel opening and its relief by cAMP. J Biol Chem 289(32):22205–20. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.572164
Shcherbatko A, Foletti D, Poulsen K, Strop P, Zhu G, Hasa-Moreno A, Melton Witt J, Loo C, Krimm S, Pios A, Yu J, Brown C, Lee JK, Stroud R, Rajpal A, Shelton D (2016) Modulation of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem 291(23):12254–70. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.722330
Chow YW, Wang HL (1998) Functional modulation of P2X2 receptors by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem 70(6):2606–12. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70062606.x
Wang S, Zhu HY, Jin Y, Zhou Y, Hu S, Liu T, Jiang X, Xu GY (2015) Adrenergic signaling mediates mechanical hyperalgesia through activation of P2X3 receptors in primary sensory neurons of rats with chronic pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308(8):G710-9. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00395.2014
Schnorr S, Eberhardt M, Kistner K, Rajab H, Käer J, Hess A, Reeh P, Ludwig A, Herrmann S (2014) HCN2 channels account for mechanical (but not heat) hyperalgesia during long-standing inflammation. Pain 155(6):1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.02.006
Sun W, Yang F, Wang Y, Fu H, Yang Y, Li CL, Wang XL, Lin Q, Chen J (2017) Contribution of large-sized primary sensory neuronal sensitization to mechanical allodynia by upregulation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated channels via cyclooxygenase 1 cascade. Neuropharmacology 113(Pt A):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.10.012
Acosta C, McMullan S, Djouhri L, Gao L, Watkins R, Berry C, Dempsey K, Lawson SN (2012) HCN1 and HCN2 in Rat DRG neurons: levels in nociceptors and non-nociceptors, NT3-dependence and influence of CFA-induced skin inflammation on HCN2 and NT3 expression. PLoS One 7(12):e50442. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050442
Forster LA, Jansen LR, Rubaharan M, Murphy AZ, Baro DJ (2020) Alterations in SUMOylation of the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 2 during persistent inflammation. Eur J Pain 24(8):1517–1536. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.1606
Jiang YQ, Xing GG, Wang SL, Tu HY, Chi YN, Li J, Liu FY, Han JS, Wan Y (2008) Axonal accumulation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels contributes to mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve injury in rat. Pain 137(3):495–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2007.10.011
Liu Y, Feng Y, Zhang T (2015) Pulsed radiofrequency treatment enhances dorsal root ganglion expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Mol Neurosci 57(1):97–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0582-x
Liu DL, Lu N, Han WJ, Chen RG, Cong R, Xie RG, Zhang YF, Kong WW, Hu SJ, Luo C (2015) Upregulation of Ih expressed in IB4-negative Aδ nociceptive DRG neurons contributes to mechanical hypersensitivity associated with cervical radiculopathic pain. Sci Rep 5:16713. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16713
Richards N, Dilley A (2015) Contribution of hyperpolarization-activated channels to heat hypersensitivity and ongoing activity in the neuritis model. Neuroscience 284:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.058
Burnstock G, Knight GE (2004) Cellular distribution and functions of P2 receptor subtypes in different systems. Int Rev Cytol 240:31–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7696(04)40002-3
Kobayashi K, Yamanaka H, Noguchi K (2013) Expression of ATP receptors in the rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord. Anat Sci Int 88(1):10–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-012-0163-9
Sharp CJ, Reeve AJ, Collins SD, Martindale JC, Summerfield SG, Sargent BS, Bate ST, Chessell IP (2006) Investigation into the role of P2X(3)/P2X(2/3) receptors in neuropathic pain following chronic constriction injury in the rat: an electrophysiological study. Br J Pharmacol 148(6):845–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706790
Kaan TK, Yip PK, Patel S, Davies M, Marchand F, Cockayne DA, Nunn PA, Dickenson AH, Ford AP, Zhong Y, Malcangio M, McMahon SB (2010) Systemic blockade of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors attenuates bone cancer pain behaviour in rats. Brain 133(9):2549–64. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq194
Jarvis MF, Burgard EC, McGaraughty S, Honore P, Lynch K, Brennan TJ, Subieta A, Van Biesen T, Cartmell J, Bianchi B, Niforatos W, Kage K, Yu H, Mikusa J, Wismer CT, Zhu CZ, Chu K, Lee CH, Stewart AO, Polakowski J, Cox BF, Kowaluk E, Williams M, Sullivan J, Faltynek C (2002) A-317491, a novel potent and selective non-nucleotide antagonist of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors, reduces chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(26):17179–84. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.252537299
McGaraughty S, Wismer CT, Zhu CZ, Mikusa J, Honore P, Chu KL, Lee CH, Faltynek CR, Jarvis MF (2003) Effects of A-317491, a novel and selective P2X3/P2X2/3 receptor antagonist, on neuropathic, inflammatory and chemogenic nociception following intrathecal and intraplantar administration. Br J Pharmacol 140(8):1381–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705574
Wu G, Whiteside GT, Lee G, Nolan S, Niosi M, Pearson MS, Ilyin VI (2004) A-317491, a selective P2X3/P2X2/3 receptor antagonist, reverses inflammatory mechanical hyperalgesia through action at peripheral receptors in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 504(1–2):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.09.056
Rahn EJ, Guzman-Karlsson MC, David Sweatt J (2013) Cellular, molecular, and epigenetic mechanisms in non-associative conditioning: implications for pain and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 105:133–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2013.06.008
Alvarez-Baron CP, Klenchin VA, Chanda B (2018) Minimal molecular determinants of isoform-specific differences in efficacy in the HCN channel family. J Gen Physiol 150(8):1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201812031
Cheng Q, Zhou Y (2013) Novel role of KT5720 on regulating hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel activity and dorsal root ganglion neuron excitability. DNA Cell Biol 32(6):320–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2013.2021
Brown DA (1803) Yule DI (2010) Protein kinase A regulation of P2X(4) receptors: requirement for a specific motif in the C-terminus. Biochim Biophys Acta 2:275–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.12.002
Siegelbaum SA (2000) Presynaptic facilitation by hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels. Nat Neurosci 3(2):101–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/72038
Felix R, Sandoval A, Sánchez D, Gómora JC, De la Vega-Beltrán JL, Treviño CL, Darszon A (2003) ZD7288 inhibits low-threshold Ca(2+) channel activity and regulates sperm function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311(1):187–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.09.197
Michels G, Brandt MC, Zagidullin N, Khan IF, Larbig R, van Aaken S, Wippermann J, Hoppe UC (2008) Direct evidence for calcium conductance of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and human native If at physiological calcium concentrations. Cardiovasc Res 78(3):466–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn032
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81960161) and the fund of Zunyi Medical University Master's research start (F-978) and the fund of Zunyi Science and Technology (2019) 29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: XL, YY. Data acquisition, data analysis, and interpretation: XL, XL. Drafting the article or critically revising it for important intellectual content: XL, JZ. Final approval of the version to be published: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
Ethical Approval
The protocol was prepared from SD rats in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide-lines in a manner that minimized animal suffering and animal numbers. All experiments were carried out in accordance with China animal welfare legislation and were approved by the Zunyi Medical University Committee on Ethics in the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, X., Zeng, J., Yan, Y. et al. Blockage of HCN Channels Inhibits the Function of P2X Receptors in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Neurochem Res 47, 1083–1096 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03509-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03509-5