Abstract
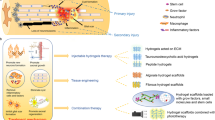
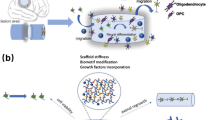
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a serious trauma, which often results in a permanent loss of motor and sensory functions, pain and spasticity. Despite extensive research, there is currently no available therapy that would restore the lost functions after SCI in human patients. Advanced treatments use regenerative medicine or its combination with various interdisciplinary approaches such as tissue engineering or biophysical methods. This review summarizes and critically discusses the research from specific interdisciplinary fields in SCI treatment such as the development of biomaterials as scaffolds for tissue repair, and using a magnetic field for targeted cell delivery. We compare the treatment effects of synthetic non-degradable methacrylate-based hydrogels and biodegradable biological scaffolds based on extracellular matrix. The systems using magnetic fields for magnetically guided delivery of stem cells loaded with magnetic nanoparticles into the lesion site are then suggested and discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varma AK, Das A, Gt Wallace, Barry J, Vertegel AA, Ray SK, Banik NL (2013) Spinal cord injury: a review of current therapy, future treatments, and basic science frontiers. Neurochem Res 38:895–905
Fitch MT, Silver J (2008) CNS injury, glial scars, and inflammation: Inhibitory extracellular matrices and regeneration failure. Exp Neurol 209:294–301
Kubinova S, Sykova E (2012) Biomaterials combined with cell therapy for treatment of spinal cord injury. Regen Med 7:207–224
Pego AP, Kubinova S, Cizkova D, Vanicky I, Mar FM, Sousa MM, Sykova E (2012) Regenerative medicine for the treatment of spinal cord injury: more than just promises? J Cell Mol Med 16:2564–2582
Straley KS, Foo CW, Heilshorn SC (2010) Biomaterial design strategies for the treatment of spinal cord injuries. J Neurotrauma 27:1–19
Liu S, Schackel T, Weidner N, Puttagunta R (2017) Biomaterial-supported cell transplantation treatments for spinal cord injury: challenges and perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci 11:430
Kubinova S (2015) New trends in spinal cord tissue engineering. Future Neurol 10:129–145
Fuhrmann T, Anandakumaran PN, Shoichet MS (2017) Combinatorial therapies after spinal cord injury: how can biomaterials help? Adv Healthc Mater 6:1601130
Theodore N, Hlubek R, Danielson J, Neff K, Vaickus L, Ulich TR, Ropper AE (2016) First human implantation of a bioresorbable polymer scaffold for acute traumatic spinal cord injury: a clinical pilot study for safety and feasibility. Neurosurgery 79:E305 E312
Assuncao-Silva RC, Gomes ED, Sousa N, Silva NA, Salgado AJ (2015) Hydrogels and cell based therapies in spinal cord injury regeneration. Stem Cells Int 2015:948040
Spang MT, Christman KL (2018) Extracellular matrix hydrogel therapies: in vivo applications and development. Acta Biomater 68:1–14
Sun Y, Li W, Wu X, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Ouyang S, Song X, Fang X, Seeram R, Xue W, He L, Wu W (2016) Functional self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels designed for nerve degeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:2348–2359
Hejcl A, Lesny P, Pradny M, Michalek J, Jendelova P, Stulik J, Sykova E (2008) Biocompatible hydrogels in spinal cord injury repair. Physiol Res 57(Suppl 3):S121–132
Kubinova S, Horak D, Hejcl A, Plichta Z, Kotek J, Proks V, Forostyak S, Sykova E (2015) SIKVAV-modified highly superporous PHEMA scaffolds with oriented pores for spinal cord injury repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 9:1298–1309
Kubinova S, Horak D, Kozubenko N, Vanecek V, Proks V, Price J, Cocks G, Sykova E (2010) The use of superporous Ac-CGGASIKVAVS-OH-modified PHEMA scaffolds to promote cell adhesion and the differentiation of human fetal neural precursors. Biomaterials 31:5966–5975
Kubinova S, Horak D, Vanecek V, Plichta Z, Proks V, Sykova E (2014) The use of new surface-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels in tissue engineering: treatment of the surface with fibronectin subunits versus Ac-CGGASIKVAVS-OH, cysteine, and 2-mercaptoethanol modification. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:2315–2323
Mackova H, Plichta Z, Proks V, Kotelnikov I, Kucka J, Hlidkova H, Horak D, Kubinova S, Jirakova K (2016) RGDS- and SIKVAVS-modified superporous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Macromol Biosci 16:1621–1631
Woerly S, Petrov P, Sykova E, Roitbak T, Simonova Z, Harvey AR (1999) Neural tissue formation within porous hydrogels implanted in brain and spinal cord lesions: ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and diffusion studies. Tissue Eng 5:467–488
Woerly S, Pinet E, de Robertis L, Van Diep D, Bousmina M (2001) Spinal cord repair with PHPMA hydrogel containing RGD peptides (NeuroGel). Biomaterials 22:1095–1111
Hejcl A, Sedy J, Kapcalova M, Toro DA, Amemori T, Lesny P, Likavcanova-Masinova K, Krumbholcova E, Pradny M, Michalek J, Burian M, Hajek M, Jendelova P, Sykova E (2010) HPMA-RGD hydrogels seeded with mesenchymal stem cells improve functional outcome in chronic spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Dev 19:1535–1546
Lesny P, Pradny M, Jendelova P, Michalek J, Vacik J, Sykova E (2006) Macroporous hydrogels based on 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate. Part 4: growth of rat bone marrow stromal cells in three-dimensional hydrogels with positive and negative surface charges and in polyelectrolyte complexes. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17:829–833
Hejcl A, Lesny P, Pradny M, Sedy J, Zamecnik J, Jendelova P, Michalek J, Sykova E (2009) Macroporous hydrogels based on 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate. Part 6: 3D hydrogels with positive and negative surface charges and polyelectrolyte complexes in spinal cord injury repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med 20:1571–1577
Kubinova S, Horak D, Sykova E (2009) Cholesterol-modified superporous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:4601–4609
Kubinova S, Horak D, Hejcl A, Plichta Z, Kotek J, Sykova E (2011) Highly superporous cholesterol-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) scaffolds for spinal cord injury repair. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 99:618–629
Ruzicka J, Romanyuk N, Hejcl A, Vetrik M, Hruby M, Cocks G, Cihlar J, Pradny M, Price J, Sykova E, Jendelova P (2013) Treating spinal cord injury in rats with a combination of human fetal neural stem cells and hydrogels modified with serotonin. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 73:102–115
Hejcl A, Ruzicka J, Proks V, Mackova H, Kubinova S, Tukmachev D, Cihlar J, Horak D, Jendelova P (2018) Dynamics of tissue ingrowth in SIKVAV-modified highly superporous PHEMA scaffolds with oriented pores after bridging a spinal cord transection. J Mater Sci-Mater Med 29:89
Hejcl A, Ruzicka J, Kekulova K, Svobodova B, Proks V, Mackova H, Jirankova K, Karova K, Machova Urdzikova L, Kubinova S, Cihlar J, Horak D, Jendelova P (2018) Modified methacrylate hydrogels improve tissue repair after spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci 19:2481
Hejcl A, Ruzicka J, Kapcalova M, Turnovcova K, Krumbholcova E, Pradny M, Michalek J, Cihlar J, Jendelova P, Sykova E (2013) Adjusting the chemical and physical properties of hydrogels leads to improved stem cell survival and tissue ingrowth in spinal cord injury reconstruction: a comparative study of four methacrylate hydrogels. Stem Cells Dev 22:2794–2805
Machova Urdzikova L, Ruzicka J, Karova K, Kloudova A, Svobodova B, Amin A, Dubisova J, Schmidt M, Kubinova S, Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Jendelova P (2017) A green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances neuroregeneration after spinal cord injury by altering levels of inflammatory cytokines. Neuropharmacology 126:213–223
Zhao RR, Fawcett JW (2013) Combination treatment with chondroitinase ABC in spinal cord injury–breaking the barrier. Neurosci Bull 29:477–483
Saldin LT, Cramer MC, Velankar SS, White LJ, Badylak SF (2017) Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: structure and function. Acta Biomater 49:1–15
Kubinova S (2017) Extracellular matrix based biomaterials for central nervous system tissue repair: the benefits and drawbacks. Neural Regen Res 12:1430–1432
Swinehart IT, Badylak SF (2016) Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds in tissue remodeling and morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 245:351–360
Medberry CJ, Crapo PM, Siu BF, Carruthers CA, Wolf MT, Nagarkar SP, Agrawal V, Jones KE, Kelly J, Johnson SA, Velankar SS, Watkins SC, Modo M, Badylak SF (2013) Hydrogels derived from central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 34:1033–1040
Cornelison RC, Gonzalez-Rothi EJ, Porvasnik SL, Wellman SM, Park JH, Fuller DD, Schmidt CE (2018) Injectable hydrogels of optimized acellular nerve for injection in the injured spinal cord. Biomed Mater 13:034110
Ghuman H, Massensini AR, Donnelly J, Kim SM, Medberry CJ, Badylak SF, Modo M (2016) ECM hydrogel for the treatment of stroke: characterization of the host cell infiltrate. Biomaterials 91:166–181
Ghuman H, Gerwig M, Nicholls FJ, Liu JR, Donnelly J, Badylak SF, Modo M (2017) Long-term retention of ECM hydrogel after implantation into a sub-acute stroke cavity reduces lesion volume. Acta Biomater 63:50–63
Raeder RH, Badylak SF, Sheehan C, Kallakury B, Metzger DW (2002) Natural anti-galactose alpha 1,3 galactose antibodies delay, but do not prevent the acceptance of extracellular matrix xenografts. Transpl Immunol 10:15–24
Badylak SF, Gilbert TW (2008) Immune response to biologic scaffold materials. Semin Immunol 20:109–116
Kurtz A, Oh SJ (2012) Age related changes of the extracellular matrix and stem cell maintenance. Prev Med 54(Suppl):S50–56
Koci Z, Vyborny K, Dubisova J, Vackova I, Jager A, Lunov O, Jirakova K, Kubinova S (2017) Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from human umbilical cord as a scaffold for neural tissue repair and its comparison with extracellular matrix from porcine tissues. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 23:333–345
Tukmachev D, Forostyak S, Koci Z, Zaviskova K, Vackova I, Vyborny K, Sandvig I, Sandvig A, Medberry CJ, Badylak SF, Sykova E, Kubinova S (2016) Injectable extracellular matrix hydrogels as scaffolds for spinal cord injury repair. Tissue Eng Part A 22:306–317
Sung HW, Chang WH, Ma CY, Lee MH (2003) Crosslinking of biological tissues using genipin and/or carbodiimide. J Biomed Mater Res A 64:427–438
Sung HW, Huang RN, Huang LL, Tsai CC, Chiu CT (1998) Feasibility study of a natural crosslinking reagent for biological tissue fixation. J Biomed Mater Res 42:560–567
Wassenaar JW, Braden RL, Osborn KG, Christman KL (2016) Modulating in vivo degradation rate of injectable extracellular matrix hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 4:2794–2802
Dalamagkas K, Tsintou M, Seifalian AM (2018) Stem cells for spinal cord injuries bearing translational potential. Neural Regen Res 13:35–42
Pal R, Gopinath C, Rao NM, Banerjee P, Krishnamoorthy V, Venkataramana NK, Totey S (2010) Functional recovery after transplantation of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy 12:792–806
Paul C, Samdani AF, Betz RR, Fischer I, Neuhuber B (2009) Grafting of human bone marrow stromal cells into spinal cord injury: a comparison of delivery methods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:328–334
Krupa P, Vackova I, Ruzicka J, Zaviskova K, Dubisova J, Koci Z, Turnovcova K, Urdzikova LM, Kubinova S, Rehak S, Jendelova P (2018) The effect of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's Jelly in spinal cord injury treatment is dose-dependent and can be facilitated by repeated application. Int J Mol Sci 19:1503
Cizkova D, Novotna I, Slovinska L, Vanicky I, Jergova S, Rosocha J, Radonak J (2011) Repetitive intrathecal catheter delivery of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells improves functional recovery in a rat model of contusive spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 28:1951–1961
Ruzicka J, Machova-Urdzikova L, Gillick J, Amemori T, Romanyuk N, Karova K, Zaviskova K, Dubisova J, Kubinova S, Murali R, Sykova E, Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Jendelova P (2017) A comparative study of three different types of stem cells for treatment of rat spinal cord injury. Cell Transpl 26:585–603
Cores J, Caranasos TG, Cheng K (2015) Magnetically targeted stem cell delivery for regenerative medicine. J Funct Biomater 6:526–546
Yanai A, Hafeli UO, Metcalfe AL, Soema P, Addo L, Gregory-Evans CY, Po K, Shan XH, Moritz OL, Gregory-Evans K (2012) Focused magnetic stem cell targeting to the retina using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Cell Transpl 21:1137–1148
Vandergriff AC, Hensley TM, Henry ET, Shen D, Anthony S, Zhang J, Cheng K (2014) Magnetic targeting of cardiosphere-derived stem cells with ferumoxytol nanoparticles for treating rats with myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 35:8528–8539
Kodama A, Kamei N, Kamei G, Kongcharoensombat W, Ohkawa S, Nakabayashi A, Ochi M (2012) In vivo bioluminescence imaging of transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells using a magnetic delivery system in a rat fracture model. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94:998–1006
Kamei G, Kobayashi T, Ohkawa S, Kongcharoensombat W, Adachi N, Takazawa K, Shibuya H, Deie M, Hattori K, Goldberg JL, Ochi M (2013) Articular cartilage repair with magnetic mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Sports Med 41:1255–1264
Kamei N, Ochi M, Adachi N, Ishikawa M, Yanada S, Levin LS, Kamei G, Kobayashi T (2018) The safety and efficacy of magnetic targeting using autologous mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:3626–3635
Sasaki H, Tanaka N, Nakanishi K, Nishida K, Hamasaki T, Yamada K, Ochi M (2011) Therapeutic effects with magnetic targeting of bone marrow stromal cells in a rat spinal cord injury model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36:933–938
Nucci LP, Silva HR, Giampaoli V, Mamani JB, Nucci MP, Gamarra LF (2015) Stem cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in a preclinical model of cerebral ischemia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:27
Vanecek V, Zablotskii V, Forostyak S, Ruzicka J, Herynek V, Babic M, Jendelova P, Kubinova S, Dejneka A, Sykova E (2012) Highly efficient magnetic targeting of mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury. Int J Nanomed 7:3719–3730
Tukmachev D, Lunov O, Zablotskii V, Dejneka A, Babic M, Sykova E, Kubinova S (2015) An effective strategy of magnetic stem cell delivery for spinal cord injury therapy. Nanoscale 7:3954–3958
Markides H, Rotherham M, El Haj AJ (2012) Biocompatibility and toxicity of magnetic nanoparticles in regenerative medicine. J Nanomater 2012:11
Jirakova K, Seneklova M, Jirak D, Turnovcova K, Vosmanska M, Babic M, Horak D, Veverka P, Jendelova P (2016) The effect of magnetic nanoparticles on neuronal differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural precursors. Int J Nanomed 11:6267–6281
Singh N, Jenkins GJ, Asadi R, Doak SH (2010) Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev 1:5358
Mahmoudi M, Hofmann H, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Petri-Fink A (2012) Assessing the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Rev 112:2323–2338
Novotna B, Jendelova P, Kapcalova M, Rossner P Jr, Turnovcova K, Bagryantseva Y, Babic M, Horak D, Sykova E (2012) Oxidative damage to biological macromolecules in human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells labeled with various types of iron oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 210:53–63
Smolkova B, Uzhytchak M, Lynnyk A, Kubinova S, Dejneka A, Lunov O (2018) A critical review on selected external physical cues and modulation of cell behavior: magnetic nanoparticles, non-thermal plasma and lasers. J Funct Biomater 10:2
Zablotskii V, Dejneka A, Kubinova S, Le-Roy D, Dumas-Bouchiat F, Givord D, Dempsey NM, Sykova E (2013) Life on magnets: stem cell networking on micro-magnet arrays. PLoS ONE 8:e70416
Zablotskii V, Lunov O, Kubinova S, Polyakova T, Sykova E, Dejneka A (2016) Effects of high-gradient magnetic fields on living cell machinery. J Phys D 49:493003
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Operational Programme Research, Development and Education in the framework of the Project “Center of Reconstructive Neuroscience”, Registration Number CZ.02.1.01/0.0./0.0/15_003/0000419 and by the Czech Science Foundation 17-03765S, 19-10365S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Special Issue : In honor of Prof Eva Sykova.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubinová, Š. Biomaterials and Magnetic Stem Cell Delivery in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Neurochem Res 45, 171–179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02808-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02808-2