Abstract
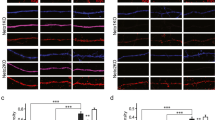
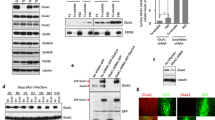
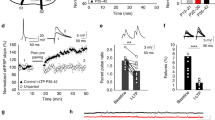
During the course of development, molecular mechanisms underlying activity-dependent synaptic plasticity change considerably. At immature CA3–CA1 synapses in the hippocampus, PKA-driven synaptic insertion of GluA4 AMPA receptors is the predominant mechanism for synaptic strengthening. However, the physiological significance of the developmentally restricted GluA4-dependent plasticity mechanisms is poorly understood. Here we have used microelectrode array (MEA) recordings in GluA4 deficient slice cultures to study the role of GluA4 in early development of the hippocampal circuit function. We find that during the first week in culture (DIV2–6) when GluA4 expression is restricted to pyramidal neurons, loss of GluA4 has no effect on the overall excitability of the immature network, but significantly impairs synchronization of the CA3 and CA1 neuronal populations. In the absence of GluA4, the temporal correlation of the population spiking activity between CA3–CA1 neurons was significantly lower as compared to wild-types at DIV6. Our data show that synapse-level defects in transmission and plasticity mechanisms are efficiently compensated for to normalize population firing rate at the immature hippocampal network. However, lack of the plasticity mechanisms typical for the immature synapses may perturb functional coupling between neuronal sub-populations, a defect frequently implicated in the context of developmentally originating neuropsychiatric disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akgül G, McBain CJ (2016) Diverse roles for ionotropic glutamate receptors on inhibitory interneurons in developing and adult brain. J Physiol 594(19):5471–5490
Beneyto M, Meador-Woodruff JH (2006) Lamina-specific abnormalities of AMPA receptor trafficking and signaling molecule transcripts in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Synapse 60:585–598
Boehm J, Kang M-G, Johnson RC, Esteban J, Huganir RL, Malinow R (2006) Synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors during LTP is controlled by a PKC phosphorylation site on GluR1. Neuron 51:213–225
Caputi A, Fuchs EC, Allen K, Le Magueresse C, Monyer H (2012) Selective reduction of AMPA currents onto hippocampal interneurons impairs network oscillatory activity. PLoS ONE 7(6):e37318
Cutts CS, Eglen SJ (2014) Detecting pairwise correlations in spike trains: an objective comparison of methods and application to the study of retinal waves. J Neurosci 34(43):14288–14303
Esteban JA, Shi SH, Wilson C, Nuriya M, Huganir RL, Malinow R (2003) PKA phosphorylation of AMPA receptor subunits controls synaptic trafficking underlying plasticity. Nat Neurosci 6:136–143
Fatemi SH, Folsom TD (2009) The neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia revisited. Schizophr Bull 35:528–548
Fuchs EC, Zivkovic AR, Cunningham MO, Middleton S, Lebeau FEN, Bannerman DM, Rozov A, Whittington MA, Traub RD, Rawlins JNP, Monyer H (2007) Recruitment of parvalbumin-positive interneurons determines hippocampal function and associated behavior. Neuron 53:591–604
Gascon E, Lynch K, Ruan H, Almeida S, Verheyden JM, Seeley WW, et al (2014) Alterations in microRNA-124 and AMPA receptors contribute to social behavioral deficits in frontotemporal dementia. Nat Med 20:1444–1451
Granger AJ, Shi Y, Lu W, Cerpas M, Nicoll RA (2013) LTP requires a reserve pool of glutamate receptors independent of subunit type. Nature 493:495–500
Groc L, Gustafsson B, Hanse E (2006) AMPA signalling in nascent glutamatergic synapses: there and not there! Trends Neurosci 29:132–139
Hanse E, Taira T, Lauri S, Groc L (2009) Glutamate synapse in developing brain: an integrative perspective beyond the silent state. Trends Neurosci 32:532–537
Huupponen J, Molchanova SM, Taira T, Lauri SE (2007) Susceptibility for homeostatic plasticity is down-regulated in parallel with maturation of the rat hippocampal synaptic circuitry. J Physiol 581(Pt 2):505–514
Huupponen J, Atanasova T, Taira T, Lauri SE (2016) GluA4 subunit of AMPA receptors mediates the early synaptic response to altered network activity in the developing hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 115(6):2989–2996
Huupponen J, Molchanova SM, Lauri SE, Taira T (2013) Ongoing intrinsic synchronous activity is required for the functional maturation of CA3–CA1 glutamatergic synapses. Cereb Cortex 23(11):2754–2764
Kasyanov AM, Safiulina VF, Voronin LL, Cherubini E (2004) GABA-mediated giant depolarizing potentials as coincidence detectors for enhancing synaptic efficacy in the developing hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3967–3972
Katz LC, Shatz CJ (1996) Synaptic activity and the construction of cortical circuits. Science 274(5290):1133–1138
Lauri SE, Vesikansa A, Segerstrale M, Collingridge GL, Isaac JTR, Taira T (2006) Functional maturation of CA1 synapses involves activity-dependent loss of tonic kainate receptor mediated inhibition of glutamate release. Neuron 50:415–429
Lee HK, Takamiya K, He K, Song L, Huganir RL (2010) Specific roles of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) phosphorylation sites in regulating synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region of hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 103:479–489
Lee HK, Takamiya K, Kameyama K, He K, Yu S, Rossetti L, Wilen D, Huganir RL (2007) Identification and characterization of a novel phosphorylation site on the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci 36:86–94
Levelt CN, Hübener M (2012) Critical-period plasticity in the visual cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 35:309–330
Lohmann C, Kessels HW (2014) The developmental stages of synaptic plasticity. J Physiol 592:13–31
Luchkina NV, Sallert M, Clarke VR, Taira T, Lauri SE (2013) Mechanisms underlying induction of LTP-associated changes in short-term dynamics of transmission at immature synapses. Neuropharmacology 67:494–502
Luchkina NV, Huupponen J, Clarke VR, Coleman SK, Keinänen K, Taira T, Lauri SE (2014) Developmental switch in the kinase dependency of long-term potentiation depends on expression of GluA4 subunit-containing AMPA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(11):4321–4326
Luchkina NV, Coleman SK, Huupponen J, Cai C, Kivistö A, Taira T, Keinänen K, Lauri SE (2017) Molecular mechanisms controlling synaptic recruitment of GluA4 subunit-containing AMPA-receptors critical for functional maturation of CA1 glutamatergic synapses. Neuropharmacology 112(Pt A):46–56
Makino C, Fujii Y, Kikuta R, Hirata N, Tani A, Shibata A, Ninomiya H, Tashiro N, Shibata H, Fukumaki Y (2003) Positive association of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR4 gene (GRIA4) haplotype with schizophrenia: linkage disequilibrium mapping using SNPs evenly distributed across the gene region. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 116B:17–22
Mohajerani MH, Sivakumaran S, Zacchi P, Aguilera P, Cherubini E (2007) Correlated network activity enhances synaptic efficacy via BDNF and the ERK pathway at immature CA3 CA1 connections in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13176–13181
Paz JT, Bryant AS, Peng K, Fenno L, Yizhar O, Frankel WN, Deisseroth K, Huguenard JR (2011) A new mode of corticothalamic transmission revealed in the Gria4(-/-) model of absence epilepsy. Nat Neurosci 14(9):1167–1173
Pelkey KA, Barksdale E, Craig MT, Yuan X, Sukumaran M, Vargish GA, Mitchell RM, Wyeth MS, Petralia RS, Chittajallu R, Karlsson RM, Cameron HA, Murata Y, Colonnese MT, Worley PF, McBain CJ (2015) Pentraxins coordinate excitatory synapse maturation and circuit integration of parvalbumin interneurons. Neuron 85:1257–1272
Quiroga RQ, Nadasdy Z, Ben-Shaul Y (2004) Unsupervised spike detection and sorting with wavelets and superparamagnetic clustering. Neural Comput 16:1661–1687
Sagata N, Iwaki A, Aramaki T, Takao K, Kura S, Tsuzuki T, Kawakami R, Ito I, Kitamura T, Sugiyama H, Miyakawa T, Fukumaki Y (2010) Comprehensive behavioural study of GluR4 knockout mice: implication in cognitive function. Genes Brain Behav 9:899–909
Slomowitz E, Styr B, Vertkin I, Milshtein-Parush H, Nelken I, Slutsky M, Slutsky I (2015) Interplay between population firing stability and single neuron dynamics in hippocampal networks. Elife 4:e04378
Spellman TJ, Gordon JA (2015) Synchrony in schizophrenia: a window into circuit-level pathophysiology. Curr Opin Neurobiol 30:17–23
Vesikansa A, Sallert M, Taira T, Lauri SE (2007) Activation of kainate receptors controls the number of functional glutamatergic synapses in the area CA1 of rat hippocampus. J Physiol 583(Pt 1):145-157
Yashiro K, Philpot BD (2008) Regulation of NMDA receptor subunit expression and its implications for LTD, LTP, and metaplasticity. Neuropharmacology 55:1081–1094
Yasuda H, Barth AL, Stellwagen D, Malenka RC (2003) A developmental switch in the signaling cascades for LTP induction. Nat Neurosci 6:15–16
Zhu JJ, Esteban JA, Hayashi Y, Malinow R (2000) Postnatal synaptic potentiation: delivery of GluR4-containing AMPA receptors by spontaneous activity. Nat Neurosci 3:1098–1106
Funding
The funding was provided by Suomen Akatemia, Sigrid Juséliuksen Säätiö, Jane ja Aatos Erkon Säätiö and CIMO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atanasova, T., Kharybina, Z., Kaarela, T. et al. GluA4 Dependent Plasticity Mechanisms Contribute to Developmental Synchronization of the CA3–CA1 Circuitry in the Hippocampus. Neurochem Res 44, 562–571 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2392-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2392-8