Abstract
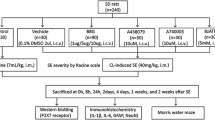
Drug-resistance epilepsy (DRE) is attributed to the brain P-glycoprotein (P-gp) overexpression. We previously reported that nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) played a critical role in regulating P-gp expression at the brain of the acute seizure rats. This study was extended further to investigate the interaction effect of NF-κB and pregnane X receptor (PXR) on P-gp expression at the brain of chronic epileptic rats treated with carbamazepine (CBZ). The chronic epileptic models were induced by the micro-injection of kainic acid (KA) into rats’ hippocampus. Subsequently, the successful models were treated with different intervention agents of CBZ; PMA(a non-specific PXR activity inhibitor) or PDTC(a specific NF-κB activity inhibitor) respectively. The expression levels of P-gp and its encoded gene mdr1a/b were significantly up-regulated on the brain of KA-induced chronic epilepsy rats or the epilepsy rats treated with CBZ for 1 week, meanwhile with a high expression of PXR. The treatment of PMA dramatically reduced both PXR and P-gp expressions at the protein and mRNA levels in the chronic epilepsy brain. By compared to the epilepsy model group, the P-gp expression was not markedly attenuated by the inhibition of NF-κB activity with PDTC treatment, nevertheless with a decrease of NF-κB expression in this intervention group. Higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines(IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) were found both in the brain tissue and the serum in the epilepsy rats of each group. There was a declined trend of the pro-inflammatory cytokines expression of the PDTC treatment group but with no statistical significance. This study demonstrates for the first time that P-gp up-regulation is due to increase PXR expression in the chronic phase of epilepsy, differently from that NF-κB signaling may induce the P-gp expression in the acute seizure phase. Our results offer insights into the mechanism underlying the development of DRE using or not using CBZ treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marras CE, Canevini MP, Colicchio G et al (2013) Health technology assessment report on the presurgical evaluation and surgical treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy[J]. Epilepsia 54(s7):49–58
Kwan P, Schachter SC, Brodie MJ (2011) Drug-resistant epilepsy[J]. N Engl J Med 365(10):919–926
Xiong J, Mao D, Liu L (2015) Research progress on the role of ABC transporters in the drug resistance mechanism of intractable epilepsy[J]. BioMed Res Int 2015:1.
Sisodiya SM, Lin WR, Harding BN et al (2002) Drug resistance in epilepsy: expression of drug resistance proteins in common causes of refractory epilepsy[J]. Brain 125(1):22–31
Zhang C, Kwan P, Zuo Z et al (2012) The transport of antiepileptic drugs by P-glycoprotein[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(10):930–942
Margineanu DG, Klitgaard H (2009) Mechanisms of drug resistance in epilepsy: relevance for antiepileptic drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov 4(1):23–32
Engel J, McDermott MP, Wiebe S et al (2012) Early surgical therapy for drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy: a randomized trial[J]. JAMA 307(9):922–930
Nunes VD, Sawyer L, Neilson J et al. Diagnosis and management of the epilepsies in adults and children: summary of updated NICE guidance[J]. BMJ, 2012, 344
Glauser T, Ben-Menachem E, Bourgeois B et al (2013) Updated ILAE evidence review of antiepileptic drug efficacy and effectiveness as initial monotherapy for epileptic seizures and syndromes[J]. Epilepsia 54(3):551–563
Luo G, Cunningham M, Kim S et al (2002) CYP3A4 induction by drugs: correlation between a pregnane X receptor reporter gene assay and CYP3A4 expression in human hepatocytes[J]. Drug Metab Dispos 30(7):795–804
Mencarelli A, Renga B, Palladino G et al (2011) Inhibition of NF-κB by a PXR-dependent pathway mediates counter-regulatory activities of rifaximin on innate immunity in intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Eur J Pharmacol 668(1):317–324
Lombardo L, Pellitteri R, Balazy M et al (2008) Induction of nuclear receptors and drug resistance in the brain microvascular edothelial cells treated with antiepileptic drugs. Curr Neurovasc Res 5(2):82–92
Gu, Xinsheng, Ke, Sui, Liu, Duan et al (2006) Role of NF-κB in regulation of PXR-mediated gene expression. A mechanism for the suppression of cytochrome P-450 3A4 by proinflammatory agents. J Biol Chem 281(26):882–889
The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30
Paxino, G., Watson, C. (2005) The rat Brain in Sterotaxic Coordinates. 5th ed, Elsevier, London
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32(3):281–294
Yu N, Di Q, Liu H, Hu Y, Jiang Y, Yan YK, Zhang YF, Zhang YD (2011) Nuclear factor-kappa B activity regulates brain expression of P-glycoprotein in the kainic acid-induced seizure rats. Mediators Inflamm 2011:670613
Yu N, Liu H, Zhang YF et al (2014) Effects of brain IKKβ gene silencing by small interfering RNA on P-glycoprotein expression and brain damage in the rat Kainic Acid-induced seizure model[J]. Curr Drug Targets-CNS Neurol Disord 13(4):661–672
Dou W, Zhang J, Zhang E et al (2013) Chrysin ameliorates chemically induced colitis in the mouse through modulation of a PXR/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 345(3):473–482
Qosa H, Miller DS, Pasinelli P et al (2015) Regulation of ABC efflux transporters at blood-brain barrier in health and neurological disorders[J]. Brain Res 1628:298–316
French JA (2013) P-glycoprotein expression and antiepileptic drug resistance[J]. Lancet Neurol 12(8):732–733
Feldmann M, Asselin MC, Liu J, Koepp MJ (2013) P-glycoprotein expression and function in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 12(8):777–785
Puranik YG, Birnbaum AK, Marino SE et al (2013) Association of carbamazepine major metabolism and transport pathway gene polymorphisms and pharmacokinetics in patients with epilepsy[J]. Pharmacogenomics 14(1):35–45
Fung KL, Hunt RC, Kimchi-Sarfaty C et al (2016) Genetic polymorphisms of P-glycoprotein: echoes of silence[M]//ABC transporters-40 Years on. Springer, Berlin, p 105–134
Potschka H (2010) Transporter hypothesis of drug-resistant epilepsy: challenges for pharmacogenetic approaches[J]. Pharmacogenomics 11(10):1427–1438
Schmidt D, Löscher W (2005) Drug resistance in epilepsy: putative neurobiologic and clinical mechanisms[J]. Epilepsia 46(6):858–877
Zhang B, Xie W, Krasowski MD (2008) PXR: a xenobiotic receptor of diverse function implicated in pharmacogenetics. Pharmacogenomics 9(11):1695–1709
Chan G N Y, Hoque M, Cummins CL et al (2011) Regulation of P-glycoprotein by orphan nuclear receptors in human brain microvessel endothelial cells[J]. J Neurochem 118(2):163–175
Bauer B, Hartz A M S, Lucking JR et al (2008) Coordinated nuclear receptor regulation of the efflux transporter, Mrp2, and the phase-Ii metabolizing enzyme, GSTπ, at the blood—brain barrier[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(6):1222–1234
Bauer B, Hartz A M S, Fricker G et al (2004) Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier[J]. Mol Pharmacol 66(3):413–419
Owen A, Goldring C, Morgan P et al (2006) Induction of P-glycoprotein in lymphocytes by carbamazepine and rifampicin: the role of nuclear hormone response elements[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol 62(2):237–242
Volk H, Potschka H, L ö scher W (2005) Immunohistochemical localization of P-glycoprotein in rat brain and detection of its increased expression by seizures are sensitive to fixation and staining variables. J Histochem Cytochem 53(4):517–531
Roberts DJ, Goralski KB (2008) A critical overview of the influence of inflammation and infection on P-glycoprotein expression and activity in the brain. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4(10):1–20
Yu N, Liu H, Di Q (2013) Modulation of immunity and the inflammatory response: a new target for treating drug-resistant epilepsy[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol 11(1):114–127
Oscarson M, Zanger UM, Rifki OF et al (2006) Transcriptional profiling of genes induced in the livers of patients treated with carbamazepine[J]. Clin Pharmacol Therapeutics 80(5):440–456
Malekshah OM, Lage H, Bahrami AR, Afshari JT, Behravan J (2012) PXR and NF- κ B correlate with the inducing effects of IL-1 β and TNF- α on ABCG2 expression in breast cancer cell lines. Eur J Pharm Sci 47(2):474–480
Xu F, Wang F, Yang T et al (2014) Differential drug resistance acquisition to doxorubicin and paclitaxel in breast cancer cells[J]. Cancer cell Int 14(1):1
Taub ME, Podila L, Ely D et al (2005) Functional assessment of multiple P-glycoprotein (P-gp) probe substrates: influence of cell line and modulator concentration on P-gp activity[J]. Drug Metab Dispos 33(11):1679–1687
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the two grants, one from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81400981, 81171222), and the other one from Nanjing Medical University Science and Technology Development Foundation of China (2013NJMU090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, N., Zhang, Yf., Zhang, K. et al. Pregnane X Receptor Not Nuclear Factor-kappa B Up-regulates P-glycoprotein Expression in the Brain of Chronic Epileptic Rats Induced by Kainic Acid. Neurochem Res 42, 2167–2177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2224-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2224-x