Abstract
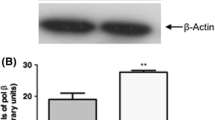
Fidelity of DNA polymerases is vital for maintaining genomic integrity. Deficient DNA repair leads to age related disorders or cancer. If the age at which the decline in activity of predominant DNA repair enzymes starts is identified, and the deficient proteins supplemented, then the manifestation of these diseases can be delayed promoting healthy aging. DNA polymerase β (pol β) is a predominant repair enzyme in brain. DNA pol β activity declines with age in rat brain/neurons but the exact age during the life time of rat when this decline begins is not known, and comparison of this activity was not made between post mitotic and proliferating tissues therefore the pattern of pol β with age was studied in rat brain and tissues. The decline in pol β activity started between 30 and 45 days postnatal in all the tissues. Post mitotic tissues showed pronounced decline than the proliferating tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- pols:
-
DNA polymerases
- pol β:
-
DNA polymerase β
- BER:
-
Base excision repair
- NHEJ:
-
Non-homologous end joining
- PPO:
-
2,5-di(phenyl)–1,3–oxazole
- POPOP:
-
2,2′-p-phenylene-bis [5-phenyloxazole]
References
Loeb LA, Monnat RJ Jr (2008) DNA polymerases and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 9:594–604
Hubscher U, Kuenzle CC, Spadari S (1977) Variation of DNA polymerases-alpha, -beta. and -gamma during perinatal tissue growth and differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 4:2917–2929
Hanaoka F, Sayato J, Arai H, Hasegawa N, Inui N, Mitsui Y, Yamada M (1983) Changes in DNA polymerases alpha, beta and gamma in mouse liver as a function of age. Mech Ageing Dev 23:315–327
Kaneko T, Tahara S, Tanno M, Taguchi T (2002) Age-related changes in the induction of DNA polymerases in rat liver by gamma-ray irradiation. Mech Ageing Dev 123:1521–1528
Waser J, Hubscher U, Spadari S, Kuenzle CC (1979) DNA polymerase-beta from brain neurons is a repair enzyme. Eur J Biochem 97:361–368
Subba Rao KV, Subba Rao K (1984) Increased DNA polymerase beta-activity in different regions of aging rat brain. Biochem Int 9:391–397
Starcevic D, Dalal S, Sweasy JB (2004) Is there a link between DNA polymerase beta and cancer? Cell Cycle 3:998–1001
Cabelof DC, Ikeno Y, Nyska A, Busuttil RA, Anyangwe N, Vijg J, Matherly LH, Tucker JD, Wilson SH, Richardson A, Heydari AR (2006) Haploinsufficiency in DNA polymerase beta increases cancer risk with age and alters mortality rate. Cancer Res 66:7460–7465
Prapurna DR, Rao KS (1997) DNA polymerases delta and epsilon in developing and aging rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:67–73
Rao KS (1993) Genomic damage and its repair in young and aging brain. Mol Neurobiol 7:23–48
Rao KS (1997) DNA-damage & DNA-repair in ageing brain. Indian J Med Res 106:423–437
Subrahmanyam K, Rao KS (1988) On the type of DNA polymerase activity in neuronal, astroglial, and oligodendroglial cell fractions from young, adult, and old rat brains. Biochem Int 16:1111–1117
Raji NS, Krishna TH, Rao KS (2002) DNA-polymerase alpha, beta, delta and epsilon activities in isolated neuronal and astroglial cell fractions from developing and aging rat cerebral cortex. Int J Dev Neurosci 20:491–496
Subba Rao K, Martin GM, Loeb LA (1985) Fidelity of DNA polymerase-beta in neurons from young and very aged mice. J Neurochem 45:1273–1278
Rao KS, Vinay Kumar D, Bhaskar MS, Sripad G (1994) On the ‘active’ molecules of DNA-polymerase beta in aging rat brain. Biochem Mol Biol Int 34:287–294
Krishna TH, Mahipal S, Sudhakar A, Sugimoto H, Kalluri R, Rao KS (2005) Reduced DNA gap repair in aging rat neuronal extracts and its restoration by DNA polymerase beta and DNA-ligase. J Neurochem 92:818–823
Rao KS, Annapurna VV, Raji NS (2001) DNA polymerase-beta may be the main player for defective DNA repair in aging rat neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 928:113–120
Rao KS, Annapurna VV, Raji NS, Harikrishna T (2000) Loss of base excision repair in aging rat neurons and its restoration by DNA polymerase beta. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 85:251–259
Rao KS (2007) DNA repair in aging rat neurons. Neuroscience 145:1330–1340
Subba Rao K (2007) Mechanisms of disease: DNA repair defects and neurological disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:162–172
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Serra I, Vanella A, Avola R, Giuffrida AM (1982) DNA polymerase and thymidine kinase activities in different regions of rat brain during postnatal development: effect of undernutrition. Neurochem Res 7:943–951
Xu G, Herzig M, Rotrekl V, Walter CA (2008) Base excision repair, aging and health span. Mech Ageing Dev 129:366–382
Cabelof DC, Raffoul JJ, Ge Y, Van Remmen H, Matherly LH, Heydari AR (2006) Age-related loss of the DNA repair response following exposure to oxidative stress. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61:427–434
Intano GW, Cho EJ, McMahan CA, Walter CA (2003) Age-related base excision repair activity in mouse brain and liver nuclear extracts. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 58:205–211
Cabelof DC, Raffoul JJ, Yanamadala S, Guo Z, Heydari AR (2002) Induction of DNA polymerase beta-dependent base excision repair in response to oxidative stress in vivo. Carcinogenesis 23:1419–1425
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) New Delhi. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is thanked for the Senior Research Fellowship and contingency grant to V. N. Vyjayanti and U.Swain. We thank Mr. Govardhan chary for maintaining the animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyjayanti, V.N., Swain, U. & Rao, K.S. Age-Related Decline in DNA Polymerase β Activity in Rat Brain and Tissues. Neurochem Res 37, 991–995 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0694-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0694-9