Abstract
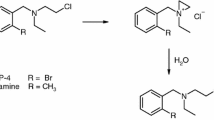
The goal of our study was to assess the monoaminergic changes in locus coeruleus (LC) and dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) following noradrenaline (NA) depletion. Seven days after a single N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine (DSP-4) intraperitoneal administration in mice, we observed a decrease of NA in both the LC and DRN, as well as in prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus (HIPP). Moreover, an increase of serotonin (5-HT) and 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5-HIAA) was detected at LC level, while no change was found in DRN. DSP-4 also caused a significant decrease of dopamine (DA) tissue content in HIPP and DRN, without affecting the LC and the PFC. A decrease of DA metabolite, homovanillic acid (HVA), was found in the DRN of NA-depleted mice. These results highlight that the neurotoxic action of DSP-4 is not restricted to LC terminal projections but also involves NA depletion at the cell body level, where it is paralleled by adaptive changes in both serotonergic and dopaminergic systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim MA, Lee HS, Lee BY et al (2004) Reciprocal connections between subdivisions of the dorsal raphe and the nuclear core of the locus coeruleus in the rat. Brain Res 1026:56–67. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.08.022
Calamandrei G, Wilkinson LS, Keverne EB (1992) Olfactory recognition of infants in laboratory mice: role of noradrenergic mechanisms. Physiol Behav 52:901–907. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(92)90369-D
Carli M, Robbins TW, Evenden JL et al (1983) Effects of lesions to ascending noradrenergic neurones on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction task in rats; implications for theories of dorsal noradrenergic bundle function based on selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 9:361–380. doi:10.1016/0166-4328(83)90138-9
Ferry B, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL (1999) Role of norepinephrine in mediating stress hormone regulation of long-term memory storage: a critical involvement of the amygdala. Biol Psychiatry 46:1140–1152. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00157-2
Sakai K, Salvert D, Touret M et al (1977) Afferent connections of the nucleus raphe dorsalis in the cat as visualized by the horseradish peroxidase technique. Brain Res 137:11–35. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(77)91010-1
Haddjeri N, de Montigny C, Blier P (1997) Modulation of the firing activity of noradrenergic neurones in the rat locus coeruleus by the 5-hydroxtryptamine system. Br J Pharmacol 120:865–875. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0700968
Singewald N, Philippu A (1998) Release of neurotransmitters in the locus coeruleus. Prog Neurobiol 56:237–267. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(98)00039-2
Luppi PH, Aston-Jones G, Akaoka H et al (1995) Afferent projections to the rat locus coeruleus demonstrated by retrograde and anterograde tracing with cholera-toxin B subunit and Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. Neuroscience 65:119–160. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(94)00481-J
Clement HW, Gemsa D, Wesemann W (1992) Serotonin–norepinephrine interactions: a voltammetric study on the effect of serotonin receptor stimulation followed in the N. raphe dorsalis and the Locus coeruleus of the rat. J Neural Transm 88:11–23. doi:10.1007/BF01245033
Svensson TH, Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1975) Inhibition of both noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in brain by the alpha-adrenergic agonist clonidine. Brain Res 92:291–306. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(75)90276-0
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H et al (1992) Alpha 2-adrenoceptor modulation of 5-HT biosynthesis in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 139:53–56. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(92)90856-3
Aston-Jones G, Akaoka H, Charlety P et al (1991) Serotonin selectively attenuates glutamate-evoked activation of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. J Neurosci 11:760–769
Bobker DH, Williams JT (1989) Serotonin agonists inhibit synaptic potentials in the rat locus ceruleus in vitro via 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:37–43
Chiang C, Aston-Jones G (1993) A 5-hydroxytryptamine2 agonist augments gamma-aminobutyric acid and excitatory amino acid inputs to noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience 54:409–420. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(93)90262-E
Hallman H, Jonsson G (1984) Pharmacological modifications of the neurotoxic action of the noradrenaline neurotoxin DSP4 on central noradrenaline neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 103:269–278. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(84)90487-4
Jonsson G, Hallman H, Ponzio F et al (1981) DSP4 (N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine)—a useful denervation tool for central and peripheral noradrenaline neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 72:173–188. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(81)90272-7
Landa ME, Rubio MC, Jaim-Etcheverry G (1984) The neurotoxic compound N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine hydrochloride (DSP4) depletes endogenous norepinephrine and enhances release of [3H]norepinephrine from rat cortical slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231:131–136
Dooley DJ, Bittiger H, Hauser KL et al (1983) Alteration of central alpha 2- and beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat after DSP-4, a selective noradrenergic neurotoxin. Neuroscience 9:889–898. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(83)90277-4
Jaim-Etcheverry G, Zieher LM (1980) DSP-4: a novel compound with neurotoxic effects on noradrenergic neurons of adult and developing rats. Brain Res 188:513–523. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(80)90049-9
Logue MP, Growdon JH, Coviella IL et al (1985) Differential effects of DSP-4 administration on regional brain norepinephrine turnover in rats. Life Sci 37:403–409. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(85)90401-1
Dailly E, Chenu F, Petit-Demouliere B et al (2006) Specificity and efficacy of noradrenaline, serotonin depletion in discrete brain areas of Swiss mice by neurotoxins. J Neurosci Methods 150:111–115. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.06.008
Wolfman C, Abo V, Calvo D et al (1994) Recovery of central noradrenergic neurons one year after the administration of the neurotoxin DSP4. Neurochem Int 25:395–400. doi:10.1016/0197-0186(94)90147-3
Zaczek R, Fritschy JM, Culp S et al (1990) Differential effects of DSP-4 on noradrenaline axons in cerebral cortex and hypothalamus may reflect heterogeneity of noradrenaline uptake sites. Brain Res 522:308–314. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)91474-U
Sanders JD, Happe HK, Bylund DB et al (2005) Development of the norepinephrine transporter in the rat CNS. Neuroscience 130:107–117. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.014
Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK (1981) Noradrenergic innervation of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe: demonstration by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res 204:1–11. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(81)90646-6
Fuxe K (1965) Evidence for the existence of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system. 3. The monoamine nerve terminal. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 65:573–596. doi:10.1007/BF00337069
Grzanna R, Molliver ME (1980) The locus coeruleus in the rat: an immunohistochemical delineation. Neuroscience 5:21–40. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(80)90068-8
Saavedra JM, Grobecker H, Zivin J (1976) Catecholamines in the raphe nuclei of the rat. Brain Res 114:337–345. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(76)90677-6
Smith HR, Beveridge TJ, Porrino LJ (2006) Distribution of norepinephrine transporters in the non-human primate brain. Neuroscience 138:703–714. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.11.033
O’Leary OF, Bechtholt AJ, Crowley JJ et al (2007) The role of noradrenergic tone in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the mouse in the acute behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:215–226. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2006.06.012
Cryan JF, O’Leary OF, Jin SH et al (2004) Norepinephrine-deficient mice lack responses to antidepressant drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:8186–8191. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401080101
Barone P, Scarzella L, Marconi R et al (2006) Pramipexole versus sertraline in the treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease: a national multicenter parallel-group randomized study. J Neurol 253:601–607. doi:10.1007/s00415-006-0067-5
Goldberg JF, Burdick KE, Endick CJ (2004) Preliminary randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pramipexole added to mood stabilizers for treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Am J Psychiatry 161:564–566. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.161.3.564
Branchi I, D’Andrea I, Armida M et al (2008) Nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: investigating early-phase onset of behavioral dysfunction in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model. J Neurosci Res 86:2050–2061. doi:10.1002/jnr.21642
Weinshenker D, Schroeder JP (2007) There and back again: a tale of norepinephrine and drug addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1433–1451. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301263
Fornai F, Torracca MT, Bassi L et al (1996) Norepinephrine loss selectively enhances chronic nigrostriatal dopamine depletion in mice and rats. Brain Res 735:349–353. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(96)00891-8
Fornai F, Giorgi FS, Alessandri MG et al (1999) Effects of pretreatment with N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine (DSP-4) on methamphetamine pharmacokinetics and striatal dopamine losses. J Neurochem 72:777–784. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0720777.x
Kalen P, Skagerberg G, Lindvall O (1988) Projections from the ventral tegmental area and mesencephalic raphe to the dorsal raphe nucleus in the rat. Evidence for a minor dopaminergic component. Exp Brain Res 73:69–77. doi:10.1007/BF00279662
Beckstead RM, Domesick VB, Nauta WJ (1979) Efferent connections of the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in the rat. Brain Res 175:191–217. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(79)91001-1
Herve D, Pickel VM, Joh TH et al (1987) Serotonin axon terminals in the ventral tegmental area of the rat: fine structure and synaptic input to dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 435:71–83. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)91588-5
Heffner TG, Hartman JA, Seiden LS (1980) A rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:453–456. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(80)90254-3
Lechin F, van der DB, Hernandez-Adrian G (2006) Dorsal raphe vs. median raphe serotonergic antagonism. Anatomical, physiological, behavioral, neuroendocrinological, neuropharmacological and clinical evidences: relevance for neuropharmacological therapy. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:565–585. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2005.11.025
Fritschy JM, Grzanna R (1991) Experimentally induced neuron loss in the locus coeruleus of adult rats. Exp Neurol 111:123–127. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(91)90058-K
Waterman SA, Harding CF (2008) Neurotoxic effects of DSP-4 on the central noradrenergic system in male zebra finches. Behav Brain Res 188:271–280. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.11.004
Peyron C, Luppi PH, Fort P et al (1996) Lower brainstem catecholamine afferents to the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. J Comp Neurol 364:402–413. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960115)364:3<402::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-8
Szabo ST, Blier P (2001) Functional and pharmacological characterization of the modulatory role of serotonin on the firing activity of locus coeruleus norepinephrine neurons. Brain Res 922:9–20. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(01)03121-3
Kaehler ST, Singewald N, Philippu A (1999) Dependence of serotonin release in the locus coeruleus on dorsal raphe neuronal activity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 359:386–393. doi:10.1007/PL00005365
Szabo ST, Blier P (2001) Serotonin (1A) receptor ligands act on norepinephrine neuron firing through excitatory amino acid and GABA(A) receptors: a microiontophoretic study in the rat locus coeruleus. Synapse 42:203–212. doi:10.1002/syn.10009
Devoto P, Flore G, Pani L et al (2001) Evidence for co-release of noradrenaline and dopamine from noradrenergic neurons in the cerebral cortex. Mol Psychiatry 6:657–664. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4000904
Devoto P, Flore G, Vacca G et al (2003) Co-release of noradrenaline and dopamine from noradrenergic neurons in the cerebral cortex induced by clozapine, the prototype atypical antipsychotic. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 167:79–84
Devoto P, Flore G, Pira L et al (2004) Alpha2-adrenoceptor mediated co-release of dopamine and noradrenaline from noradrenergic neurons in the cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 88:1003–1009
Devoto P, Flore G, Saba P et al (2005) Stimulation of the locus coeruleus elicits noradrenaline and dopamine release in the medial prefrontal and parietal cortex. J Neurochem 92:368–374. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02866.x
Kawahara H, Kawahara Y, Westerink BH (2001) The noradrenaline–dopamine interaction in the rat medial prefrontal cortex studied by multi-probe microdialysis. Eur J Pharmacol 418:177–186. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(01)00863-9
Guiard BP, El Mansari M, Merali Z et al (2008) Functional interactions between dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine neurons: an in vivo electrophysiological study in rats with monoaminergic lesions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:625–639
Weinshenker D, Ferrucci M, Busceti CL et al (2008) Genetic or pharmacological blockade of noradrenaline synthesis enhances the neurochemical, behavioral, and neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 105:471–483. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05145.x
Gesi M, Soldani P, Giorgi FS et al (2000) The role of the locus coeruleus in the development of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:655–668. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(00)00028-2
Rommelfanger KS, Weinshenker D (2007) Norepinephrine: the redheaded stepchild of Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 74:177–190. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.036
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Antonio Petrella at the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale della Puglia e della Basilicata for his invaluable veterinary assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Cassano and S. Gaetani have contributed equally to the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassano, T., Gaetani, S., Morgese, M.G. et al. Monoaminergic Changes in Locus Coeruleus and Dorsal Raphe Nucleus Following Noradrenaline Depletion. Neurochem Res 34, 1417–1426 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9928-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9928-5