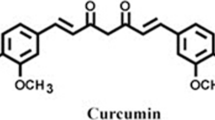
Abstract
Oxidative stress is believed to contribute to neurodegeneration following ischemic injury. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the possible antioxidant neuroprotective effect of curcumin (Cur) on neuronal death of hippocampal CA1 neurons following transient forebrain ischemia in rat. Treatment of Cur (200 mg/kg/day, i.p.) at three different times (immediately, 3 h and 24 h after ischemia) significantly (P<0.01) reduced neuronal damage 7 days after ischemia. Also, treatment of ischemic rats with Cur decreased the elevated levels of MDA and increased GSH contents, catalase and SOD activities to normal levels. In the in vitro, Cur was as potent as antioxidant (IC50 = 1 μM) as butylated hydroxytoluene. The present study demonstrates that curcumin treatment attenuates forebrain ischemia-induced neuronal injury and oxidative stress in hippocampal tissue. Thus treatment with curcumin immediately or even delayed until 24 h may have the potential to be used as a protective agent in forebrain ischemic insult in human.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin VL, Lawes CMM, Bennett DA, Anderson CS (2003) Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. The Lancet Neurol 2:43–53
Wolfe CD (2000) The impact of stroke. Br Med Bull 56:275–286
Colbourne F, Li H, Buchan AM, Clemens JA (1999) Continuing postischemic neuronal death in CA1: influence of ischemia duration and cytoprotective doses of NBQX and SNX-111 in rats. Stroke 30:662–668
Rami A, Agarwal R, Botez G, Winckler J (2000) mu-Calpain activation, DNA fragmentation, and synergistic effects of caspase and calpain inhibitors in protecting hippocampal neurons from ischemic damage. Brain Res 866:299–312
Barber PA, Auer RN, Buchan AM, Sutherland GR (2001) Understanding and managing ischemic stroke. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 79:283–296
Candelario-Jalil E, Ajamieh HH, Sam S, Martínez G, Leon OS (2000) Nimesulide limits kainate-induced oxidative damage in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 39:295–298
Liu PK, Grossman RG, Hsu CY, Robertson CS (2001) Ischemic injury and faulty gene transcripts in the brain. Trends Neurosci 24:581–588
Candelario-Jalil E, Mhadu NH, Ai-Dalain SM, Martínez G, Leon OS (2001) Time course of oxidative damage in different brain regions following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci Res 41:233–241
Chan PH (1996) Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke 27:1124–1129
Reddy AP, Lokesh BR (1994) Effect of dietary turmeric (Curcuma longa) on iron-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat liver. Food Chem Toxicol 32:279–283
Araujo CC, Leon LL (2001) Biological activities of Curcuma longa L. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:723–728
Zhao BL, Li XJ, He RG, Cheng SJ, Xin WJ (1989) Scavenging effect of extracts of green tea and natural antioxidants on active oxygen radicals. Cell Biophys 14:175–185
Li JK, Lin-shia SY (2001) Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by curcumin. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B 25:59–66
Ringman JM, Frautschy SA, Cole GM, Masterman DL, Cummings JLA (2005) Potential role of the curry spice curcumin in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:131–136
Cole GM, Lim GP, Yang F, Teter B, Begum A, Ma Q, Harris-White ME, Frautschy SA (2005) Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: omega-3 fatty acid and phenolic anti-oxidant interventions. Neurobiol Aging 2:133–136
Huang MT, Newmark HL, Frenkel K (1997) Inhibitory effects of curcumin on tumorigenesis in mice. J Cell Biochem 27:26–34
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks RJL, Kaptein A, Farrow S, Howells L (1999) Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in colon cells by the chemoprevention agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signaling complex. Oncogene 18:6013–6020
Skrzypczak-Jankun E, McCabe NP, Selman SH, Jankun J (2000) Curcumin inhibits lipoxygenase by binding to its central cavity: theoretical and X-ray evidence. Int J Mol Med 6:521–526
Smith ML, Bendek G, Dahlgren N, Rosen I, Wieloch T, Siesjo BK (1984) Models for studying long-term recovery following forebrain ischemia in the rat, II: a 2-vessel occlusion model. Acta Neurol Scand 69:385–401
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Henrich-Noack P, Prehn JHM, Krieglstein J (1996) TGF-β1 protects hippocampal neurons against degeneration caused by transient global ischemia: dose response relationship and potential neuroprotective mechanisms. Stroke 27:1609–1615
Ohkawa H, Ohish N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfahydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Higgins C, Bachner R, McCallster J, Boxer L (1978) Polymorphonucler leukocyte species differences in the disposal of hydrogen peroxide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 158:478–481
McCord J, Fridovich I (1969) An enzymatic function for erythrocuprein (Hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Houghton PJ, Zarka R, de las Heras B, Hoult JR (1995) Fixed oil of Nigella sativa and derived thymoquinone inhibit eicosanoid generation in leukocytes and membrane lipid peroxidation. Planta Med 61:33–36
Knuckey NW, Palm D, Primiano M, Epstein MH, Johanson CE (1995) N-acetylcysteine enhances hippocampal neuronal survival after transient forebrain ischemia in rats. Stroke 26:305–311
Al Nita D, Nita V, Spulber S, Moldovan M, Popa DP, Zagrean AM, Zagrean L (2001) Oxidative damage following cerebral ischemia depends on reperfusion-a biochemical study in rat. J Cell Mol Med 5:163–170
Nanri K, Montecot C, Springhetti V, Seylaz J, Pinard E (1998) The selective inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase, 7-nitroindazole, reduces the delayed neuronal damage due to forebrain ischemia in rats. Stroke 29:1248–1254
Chandrasekaran K, Mehrabian Z, Spinnewyn B, Drieuand K, Fiskum G (2001) Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide, a component of the Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761), in gerbil global brain ischemia. Brain Res 922:282–292
Shen H, Zhang L, Yuen D, Logan R, Jung BP, Zhang G, Eubanks JH (2002) Expression and function of A1 adenosine receptors in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Neuroscience 114:547–556
Fuh KC, Meneshian A, Patel CB, Takiar V, Bulkley GB (2002) Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species: alternative paradigms for signaling specificity. Surgery 131:601–612
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N, Sonia Leon O (2003) Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils. Neurosci Res 47:245–253
Al-Majed AA (2004) Aminoguanidine prevents oxidative stress insult following transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus. Saudi Pharmaceutic J 12:150–156
Kono Y, Fridovich I (1982) Superoxide radical inhibits catalase. J Biol Chem 25:5751–5754
Tokuda Y, Uozumi T, Kawassaki T (1993) The superoxide dismutase activities of cerebral tissues, assayed by the chemiluminescence method, in the gerbil focal ischemia/reperfusion and global ischemia models. Neurochem Int 23:107–114
Homi HM, Freitas JJ, Curi R, Velasco IT, Junior BA (2002) Changes in superoxide dismutase and catalase activities of rat brain regions during early global cerebral transient ischemia/reperfusion. Neurosci Lett 333:37–40
Ghoneim AI, Abdel-naim AB, Khalifa AE, El-denshary ES (2002) Protective effects of curcumin against ischemia/reperfusion insult in rat forebrain. Pharmacol Res 46:273–279
Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS (2004) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci 74:969–985
Wang Q, Sun AY, Simonyi A, Jensen MD, Shelat PB, Rottinghaus GE, MacDonald RS, Miller DK, Lubahn DE, Weisman GA, Sun GY (2005) Neuroprotective mechanisms of curcumin against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis and behavioral deficits. J Neurosci Res 82:138–148
Naik RS, Mujumdar AM, Ghaskadbi S (2004) Protection of liver cells from ethanol cytotoxicity by curcumin in liver slice culture in vitro. J Eethanopharmacol 95:31–37
Shoskes DA (1998) Effect of bioflavonoids quercetin and curcumin on ischemic renal injury: a new class of renoprotective agents. Transplantation 27:147–152
Manikandan P, Sumitra M, Aishwarya S, Manohar BM, Lokanadam B, Puvanakrishnan R (2004) Curcumin modulates free radical quenching in myocardial ischaemia in rats. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1967–1980
Sinet PM, Heikkila RE, Cohen G (1980) Hydrogen peroxide production by rat brain in vivo. J Neurochem 34:1421–1428
Paget GE, Barnes JM (eds) (1964) In evaluation of drug activities: pharmacometrics. Academic press, New York and London
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, Hsu MM, Ho YF, Shen TS, Ko JY, Lin JT, Lin BR, Ming-Shiang W, Yu HS, Jee SH, Chen GS, Chen TM, Chen CA, Lai MK, Pu YS, Pan MH, Wang YJ, Tsai CC, Hsieh CY (2001) Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res 21:2895–2900
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by operating grant from King Abdulaziz City for Science & Technology (KACST; LP-8-49).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Omar, F.A., Nagi, M.N., Abdulgadir, M.M. et al. Immediate and Delayed Treatments with Curcumin Prevents Forebrain Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Damage and Oxidative Insult in the Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem Res 31, 611–618 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9059-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9059-1