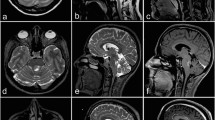
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to assess the benefit-risk ratio by determining diagnostic yield and safety of brainstem biopsies in adult patients. The secondary objectives were (i) to compare brainstem biopsy safety and postbiopsy patients’ outcomes and survival with those of patients biopsied for a brain or cerebellar lesion, and (ii) to assess the impact of brainstem biopsy on final diagnosis and further therapeutic management.
Methods
Among 1784 stereotactic biopsies performed in adult patients at a tertiary center between April 2009 and October 2020, we retrospectively examined 50 consecutive brainstem biopsies. We compared variables regarding diagnostic yield, safety and post-biopsy outcomes between brainstem biopsy patients and brain/cerebellum biopsy patients.
Results
Brainstem biopsy led to a diagnosis in 86% of patients (94.6% in patients with suspected tumor). Lesion contrast enhancement on imaging was the sole predictor of obtaining a diagnosis. Rates of symptomatic complications and mortality were significantly higher in brainstem biopsy patients compared to brain/cerebellum biopsy patients (20% vs 0%; p < 0.001 and 6% vs 0%; p = 0.01, respectively). Transfrontal trajectory and prebiopsy swallowing disorders were predictors of brainstem biopsy-related symptomatic complications. Brainstem biopsy findings led to diagnostic change in 22% of patients.
Conclusions
Stereotactic biopsy in adult patients with brainstem lesion has a high diagnostic yield. Although stereotactic brainstem biopsy is associated with more functional and fatal complications than biopsies targeting the brain/cerebellum, its safety profile appears acceptable. Thus, the benefit-risk ratio of stereotactic biopsy in patients with brainstem lesion is favorable but should nevertheless be carefully weighted on a case-by-case basis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ranjan A, Rajshekhar V, Joseph T et al (1993) Nondiagnostic CT-guided stereotactic biopsies in a series of 407 cases: influence of CT morphology and operator experience. J Neurosurg 79:839–844. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.6.0839
Hall WA (1998) The safety and efficacy of stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions. Cancer 82:1749–1755
Ferreira MP, Ferreira NP, Pereira Filho AA et al (2006) Stereotactic computed tomography–guided brain biopsy: diagnostic yield based on a series of 170 patients. Surg Neurol 65:S27–S32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.11.036
Mathon B, Amelot A, Mokhtari K, Bielle F (2019) Increasing the diagnostic yield of stereotactic brain biopsy using intraoperative histological smear. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 186:105544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105544
Noronha C, Figueiredo G, Pinheiro C et al (2019) Brain biopsy in suspected non-neoplastic neurological disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 161:1139–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-03910-8
Mathon B, Le Joncour A, Bielle F et al (2020) Neurological diseases of unknown etiology: Brain-biopsy diagnostic yields and safety. Eur J Intern Med 80:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.029
Riche M, Amelot A, Peyre M et al (2021) Complications after frame-based stereotactic brain biopsy: a systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 44:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01234-w
Grimm SA, Chamberlain MC (2013) Brainstem glioma: a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 13:346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-013-0346-3
Pérez-Gómez JL, Rodríguez-Alvarez CA, Marhx-Bracho A, Rueda-Franco F (2010) Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem tumors in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 26:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1000-x
Puget S, Beccaria K, Blauwblomme T et al (2015) Biopsy in a series of 130 pediatric diffuse intrinsic Pontine gliomas. Childs Nerv Syst 31:1773–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2832-1
Pfaff E, El Damaty A, Balasubramanian GP et al (2019) Brainstem biopsy in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma in the era of precision medicine: the INFORM study experience. Eur J Cancer 114:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.03.019
Morais BA, Solla DJF, Matushita H et al (2020) Pediatric intrinsic brainstem lesions: clinical, imaging, histological characterization, and predictors of survival. Childs Nerv Syst 36:933–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04453-0
Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Gittleman H et al (2019) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the united states in 2012–2016. Neuro Oncol 21:v1–v100. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz150
Gleason CA, Wise BL, Feinstein B (1978) Stereotactic localization (with computerized tomographic scanning), biopsy, and radiofrequency treatment of deep brain lesions. Neurosurgery 2:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-197805000-00006
Cheng G, Yu X, Zhao H et al (2020) Complications of stereotactic biopsy of lesions in the sellar region, pineal gland, and brainstem: A retrospective, single-center study. Medicine (Baltimore) 99:e18572. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018572
Riche M, Marijon P, Amelot A et al (2022) Severity, timeline, and management of complications after stereotactic brain biopsy. J Neurosurg 136:867–876. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.3.JNS21134
Mathon B, Favreau M, Degos V et al (2022) Brain biopsy for neurological diseases of unknown etiology in critically Ill patients: feasibility, safety, and diagnostic yield. Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000005439
Quick-Weller J, Lescher S, Bruder M et al (2016) Stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions: 21 years experiences of a single center. J Neurooncol 129:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2166-1
Chen S-Y, Chen C-H, Sun M-H et al (2011) Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem lesion: comparison of approaches and reports of 10 cases. J Chin Med Assoc 74:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.024
Dellaretti M, Touzet G, Reyns N et al (2012) Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging findings and histological diagnosis of intrinsic brainstem lesions in adults. Neuro Oncol 14:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor215
Manoj N, Arivazhagan A, Bhat DI et al (2014) Stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions: techniques, efficacy, safety, and disease variation between adults and children: a single institutional series and review. J Neurosci Rural Pract 5:32–39. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-3147.127869
Furtak J, Śledzińska P, Bebyn MG et al (2021) Infratentorial stereotactic biopsy of brainstem and cerebellar lesions. Brain Sci 11:1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111432
Jaradat A, Nowacki A, Fichtner J et al (2021) Stereotactic biopsies of brainstem lesions: which approach? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 163:1957–1964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04733-2
Guillamo JS, Monjour A, Taillandier L et al (2001) Brainstem gliomas in adults: prognostic factors and classification. Brain 124:2528–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.12.2528
Gonçalves-Ferreira AJ, Herculano-Carvalho M, Pimentel J (2003) Stereotactic biopsies of focal brainstem lesions. Surg Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(03)00379-3
Boviatsis EJ, Kouyialis AT, Stranjalis G et al (2003) CT-guided stereotactic biopsies of brain stem lesions: personal experience and literature review. Neurol Sci 24:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-003-0093-3
Shad A, Green A, Bojanic S, Aziz T (2005) Awake stereotactic biopsy of brain stem lesions: technique and results. Acta Neurochir. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0420-3
Samadani U, Stein S, Moonis G et al (2006) Stereotactic biopsy of brain stem masses: decision analysis and literature review. Surg Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2006.05.056
Kesari S, Kim RS, Markos V et al (2008) Prognostic factors in adult brainstem gliomas: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of 101 cases. J Neurooncol 88:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9545-1
Sanai N, Wachhorst SP, Gupta NM, McDermott MW (2008) Transcerebellar stereotactic biopsy for lesions of the brainstem and peduncles under local anesthesia. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000324731.68843.74
Rachinger W, Grau S, Holtmannspötter M et al (2009) Serial stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions in adults improves diagnostic accuracy compared with MRI only. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2009.174250
Haegelen C, Touzet G, Reyns N et al (2010) Stereotactic robot-guided biopsies of brain stem lesions: Experience with 15 cases. Neurochirurgie 56:363–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2010.05.006
Kickingereder P, Willeit P, Simon T, Ruge MI (2013) Diagnostic value and safety of stereotactic biopsy for brainstem tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1480 cases. Neurosurgery 72(6):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31828bf445
He L, He D, Qi Y et al (2021) Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem lesions: a meta-analysis with noncomparative binary data. Cancer Control 28:10732748211059858. https://doi.org/10.1177/10732748211059858
Duran-Peña A, Ducray F, Ramirez C et al (2022) Adult brainstem glioma differential diagnoses: an MRI-based approach in a series of 68 patients. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11070-6
Pafundi DH, Laack NN, Youland RS et al (2013) Biopsy validation of 18F-DOPA PET and biodistribution in gliomas for neurosurgical planning and radiotherapy target delineation: results of a prospective pilot study. Neuro Oncol 15:1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not002
Verger A, Kas A, Darcourt J, Guedj E (2022) PET Imaging in neuro-oncology: an update and overview of a rapidly growing area. Cancers (Basel) 14:1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051103
Hirano Y, Shinya Y, Aono T et al (2022) The role of stereotactic frame-based biopsy for brainstem tumors in the era of molecular-based diagnosis and treatment decisions. Curr Oncol 29:4558–4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070360
Mathon B, Marijon P, Riche M et al (2022) Outpatient stereotactic brain biopsies. Neurosurg Rev 45:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01593-3
Mathon B, Malaizé H, Amelot A, PSL BRAIN-BIOPSY STUDY GROUP (2022) Stereotactic biopsies of brainstem lesions: dilemma on the best trajectory. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 164:745–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04924-x
Catapano G, Sgulò FG, Seneca V et al (2019) Fluorescein-assisted stereotactic needle biopsy of brain tumors: a single-center experience and systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 42:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-0947-z
Chabaane M, Amelot A, Riche M et al (2020) Efficacy of a second brain biopsy for intracranial lesions after initial negativity. J Clin Neurol 16:659–667. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2020.16.4.659
Quick-Weller J, Konczalla J, Duetzmann S et al (2017) General anesthesia versus local anesthesia in stereotactic biopsies of brain lesions: a prospective randomized study. World Neurosurg 97:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.09.064
Quick-Weller J, Tritt S, Behmanesh B et al (2017) Biopsies of pediatric brainstem lesions display low morbidity but strong impact on further treatment decisions. J Clin Neurosci 44:254–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.06.028
Feng J, Hao S, Pan C et al (2015) The H3.3 K27M mutation results in a poorer prognosis in brainstem gliomas than thalamic gliomas in adults. Hum Pathol 46:1626–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2015.07.002
Liu C-J, Lin S-Y, Yang C-F et al (2020) A new prognostic score for disease progression and mortality in patients with newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Med 9:2134–2145. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2872
Laigle-Donadey F, Loiseau H, au nom du groupe GLITRAD du réseau TUCERA de l’ANOCEF (2017) [The GLITRAD (Adult Brainstem Gliomas) network: A national multidisciplinary group dedicated to brainstem gliomas in adults]. Bull Cancer 104:593–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulcan.2017.03.007
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
The database is registered within a protected and anonymized File (N°2214386 – CNIL). The need for patient informed consent was waived by the IRB of Sorbonne University. The article was prepared according to the STROBE guidelines
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malaizé, H., Laigle-Donadey, F., Riche, M. et al. Roles and outcomes of stereotactic biopsy for adult patients with brainstem lesion. J Neurooncol 160, 159–170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04129-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04129-x